Abstract
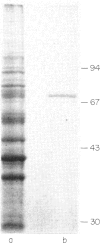
This study was done to examine the nature of the membrane constituents involved in the secretion of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) from human blood eosinophils. Three mouse monoclonal antibodies were used, which showed greater binding to membrane antigens on activated, and light density eosinophils from patients with an eosinophilia, than on nonactivated or normal density eosinophils. All three antibodies (EoN4, EoN5 & EoN6) stimulated normal density human eosinophils to secrete ECP, either alone or in association with sepharose-C3b. The antibodies bound to at least two separate sites on the membrane, which were distinct from the receptors for immunoglobulins, C3b, and eosinophil activating factor. One combination of antibodies increased the amount of ECP which was secreted. The membrane antigen recognized by antibody EoN4 was a glycoprotein, molecular weight 75 kD. These findings showed that ECP secretion may be induced by a wider range of stimuli than has been previously recognized, and that the antigens recognized by these monoclonal antibodies may play an important role in the induction of eosinophil degranulation.
Full text
PDF



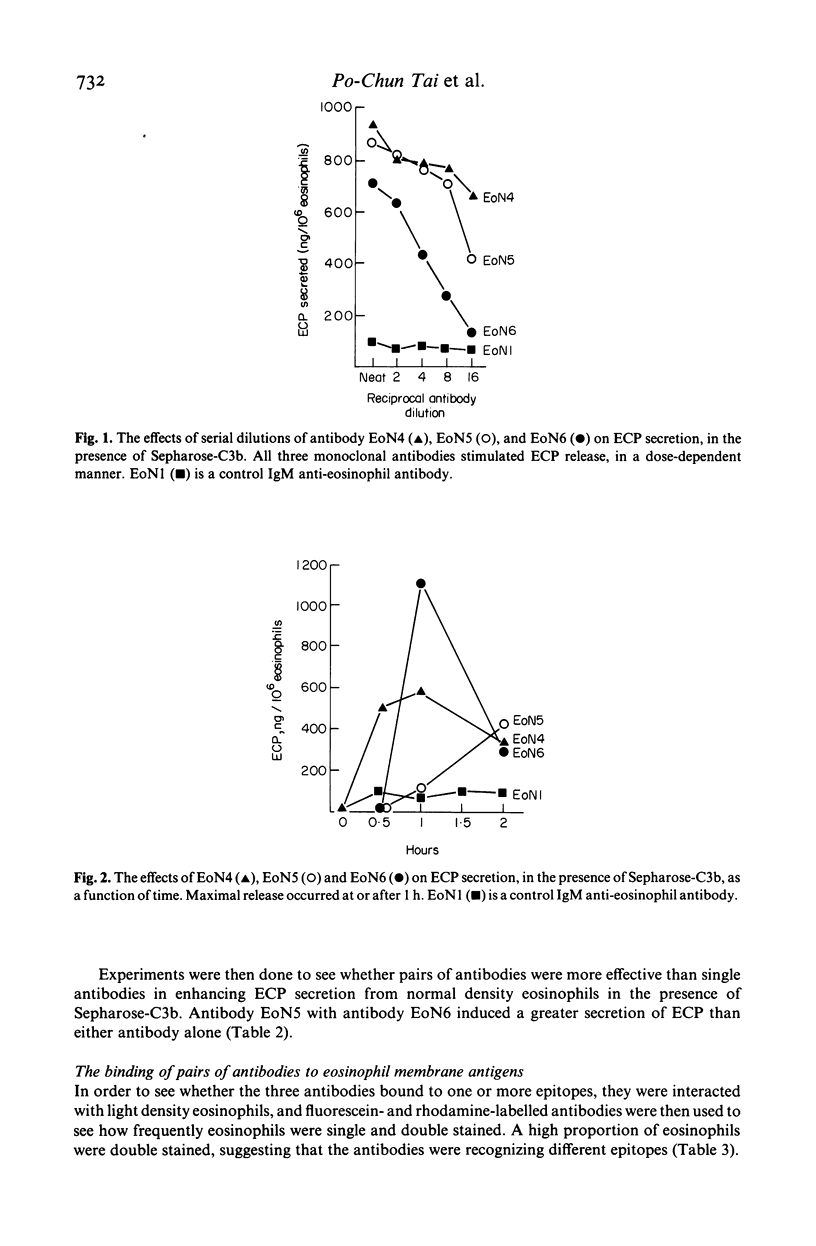
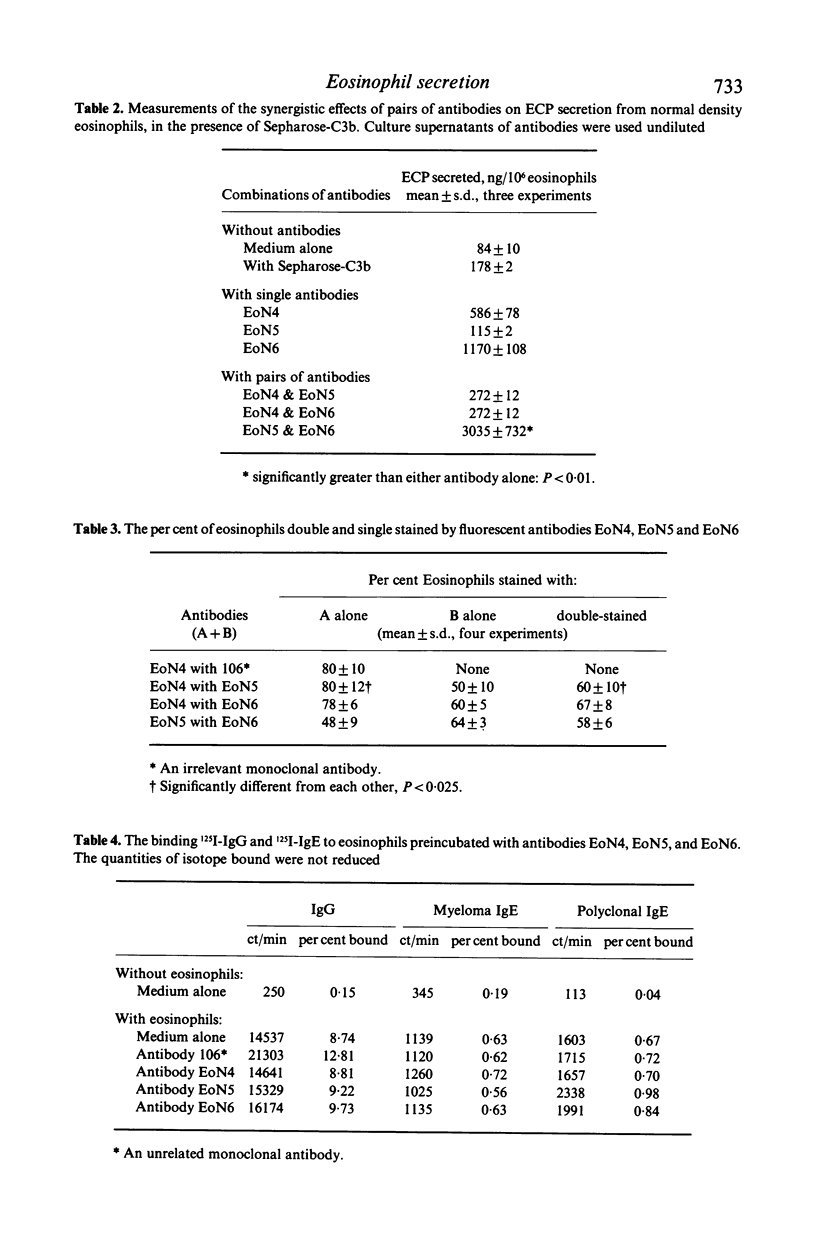




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G. Surface glycoproteins of human white blood cells. Analysis by surface labeling. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):57–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball E. D., Bernier G. M., Cornwell G. G., 3rd, McIntyre O. R., O'Donnell J. F., Fanger M. W. Monoclonal antibodies to myeloid differentiation antigens: in vivo studies of three patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1203–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga J. P., Guarnotta G., Harte A., Pryce G., Campbell M. A., Quartey-Papafio R., Lydyard P. M., Roitt I. M. A common epitope identified by a monoclonal antibody, MID 2, present on all leucocytes and associated with a group of high molecular weight glycopeptides. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jan;19(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Cruise K. M., Mitchell G. F., Watt S. M. Preparation and surface labeling of murine eosinophils. Exp Hematol. 1980 Jan;8(1):108–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Torpier G., Johansson S. G., Prin L. Fc receptors for IgE on human and rat eosinophils. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2087–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Spiegelberg H. L., Prin L., Bennich H., Butterworth A. E., Pierce R. J., Ouaissi M. A., Capron A. Role of IgE receptors in effector function of human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):462–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Henson P. M. Purification and characterization of an antigen involved in neutrophil chemotaxis and degranulation using a monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jul;14(7):605–609. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Fells G. A., Sun X. H., Gadek J. E., Venet A., Crystal R. G. Eosinophil-mediated injury to lung parenchymal cells and interstitial matrix. A possible role for eosinophils in chronic inflammatory disorders of the lower respiratory tract. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):269–278. doi: 10.1172/JCI111411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foon K. A., Buescher S., Kimball E. S., Huang L. C., Stevenson H. C., Clarke G., Gregorio T., Harley J. B. Monoclonal antibody to human eosinophils recognizing 95 kD surface membrane antigen. Hybridoma. 1983;2(4):393–402. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J. J., Rosner I. K., Davis A. E., 3rd, Zeiger R. S., Arnaout M. A., Colten H. R. Complement-dependent histaminase release from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1172/JCI109414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Mainardi C. L., Kang A. H. Type-specific collagen degradation by eosinophils. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2070621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Differentiation antigens on mouse eosinophils and neutrophils identified by monoclonal antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jul;57(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López A. F., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of human granulocyte function by monoclonal antibody WEM-G1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1818–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R. C., Glauert A. M., Thorne K. J. Mechanism of Fc-mediated interaction of eosinophils with immobilized immune complexes: I. Effects of inhibitors and activators of eosinophil function. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:337–356. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen E. G., Spry C. J. Relation between eosinophilia and endomyocardial disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;27(4):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(85)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Ong R. R. Degranulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes is induced by multivalent cross-linking of wheat germ agglutinin binding site(s) on cell membrane. Inflammation. 1984 Sep;8(3):277–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00916416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podestá E. J., Solano A. R., Attar R., Sánchez M. L., Molina y Vedia L. Receptor aggregation induced by antilutropin receptor antibody and biological response in rat testis Leydig cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3986–3990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Bakes D. M., Barkans J. R., Spry C. J. Plasma membrane antigens on light density and activated human blood eosinophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):427–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Hayes D. J., Clark J. B., Spry C. J. Toxic effects of human eosinophil products on isolated rat heart cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):75–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2040075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Enzymes altering the binding capacity of human blood eosinophils for IgG antibody-coated erythrocytes (EA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):206–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J., Peterson C., Venge P., Olsson I. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish between storage and secreted forms of eosinophil cationic protein. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):182–184. doi: 10.1038/309182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Studies on blood eosinophils. I. Patients with a transient eosinophilia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):415–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Franks D. Surface proteins of the human eosinophil. I. Isolation of eosinophil IgG binding proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):464–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Free J., Franks D., Oliver R. C. The mechanism of Fc-mediated interaction of eosinophils with immobilized immune complexes. II. Identification of two membrane proteins, modified by the interaction. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:357–369. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Oliver R. C., Glauert A. M. Eosinophil interaction with antibody-coated, non-phagocytosable surfaces: changes in cell surface proteins. J Cell Sci. 1980 Apr;42:367–378. doi: 10.1242/jcs.42.1.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Oliver R. C., Glauert A. M. Eosinophil membrane changes during interaction with antibody-coated non-phagocytosable surfaces. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Feb;9(1):71–71. doi: 10.1042/bst0090071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Richardson B. A., Butterworth A. E. Surface proteins of the human eosinophil. II. Effects of Schistosoma mansoni larvae on eosinophil surface proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith M. C., Butterworth A. E. Enhancement of human eosinophil-mediated killing of Schistosoma mansoni larvae by mononuclear cell products in vitro. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1828–1843. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist I., Olofsson T., Olsson I. Mechanisms for eosinophil degranulation; release of the eosinophil cationic protein. Immunology. 1984 Jan;51(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Colten H. R. Histaminase release from human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):540–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., McNamara P., Thomas M., Smart I. J., Bradley J. The preparation and properties of monoclonal antibodies against human granulocyte membrane antigens. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jul;48(3):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]