Abstract
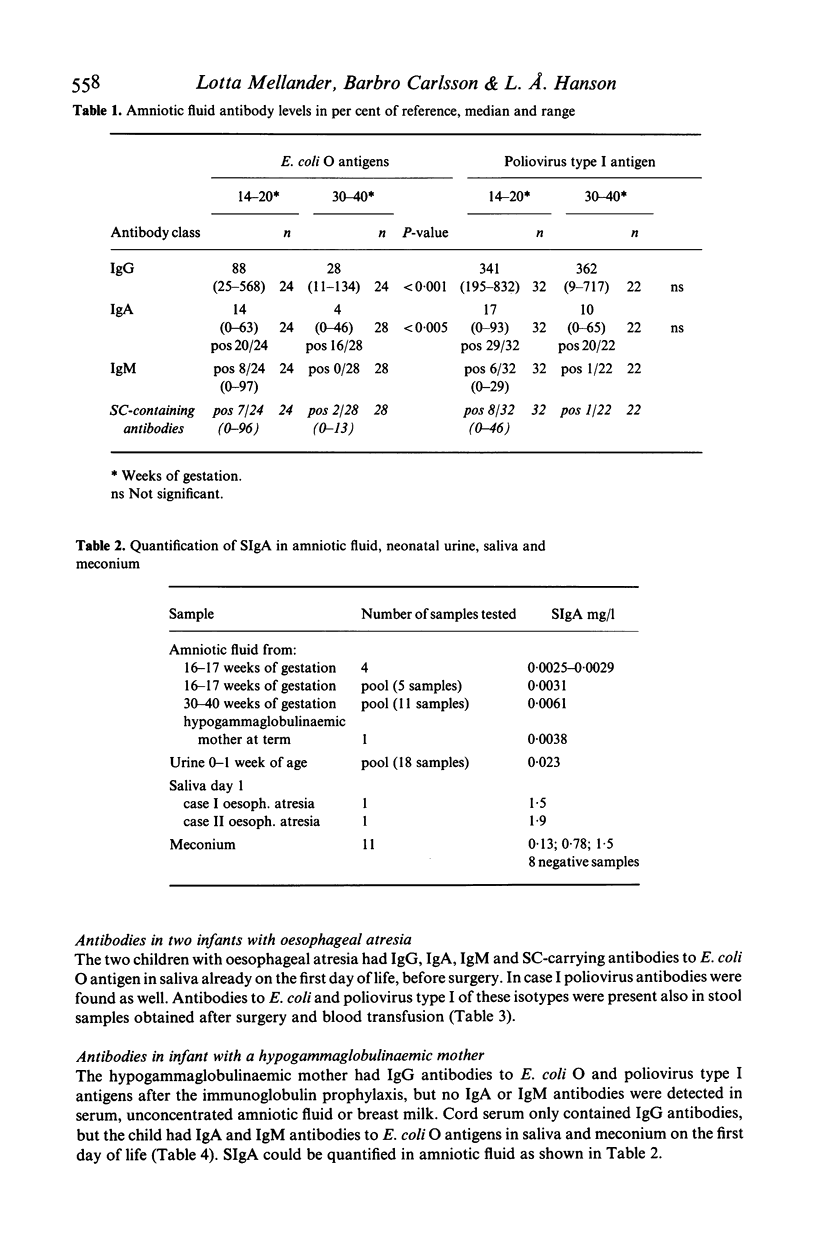
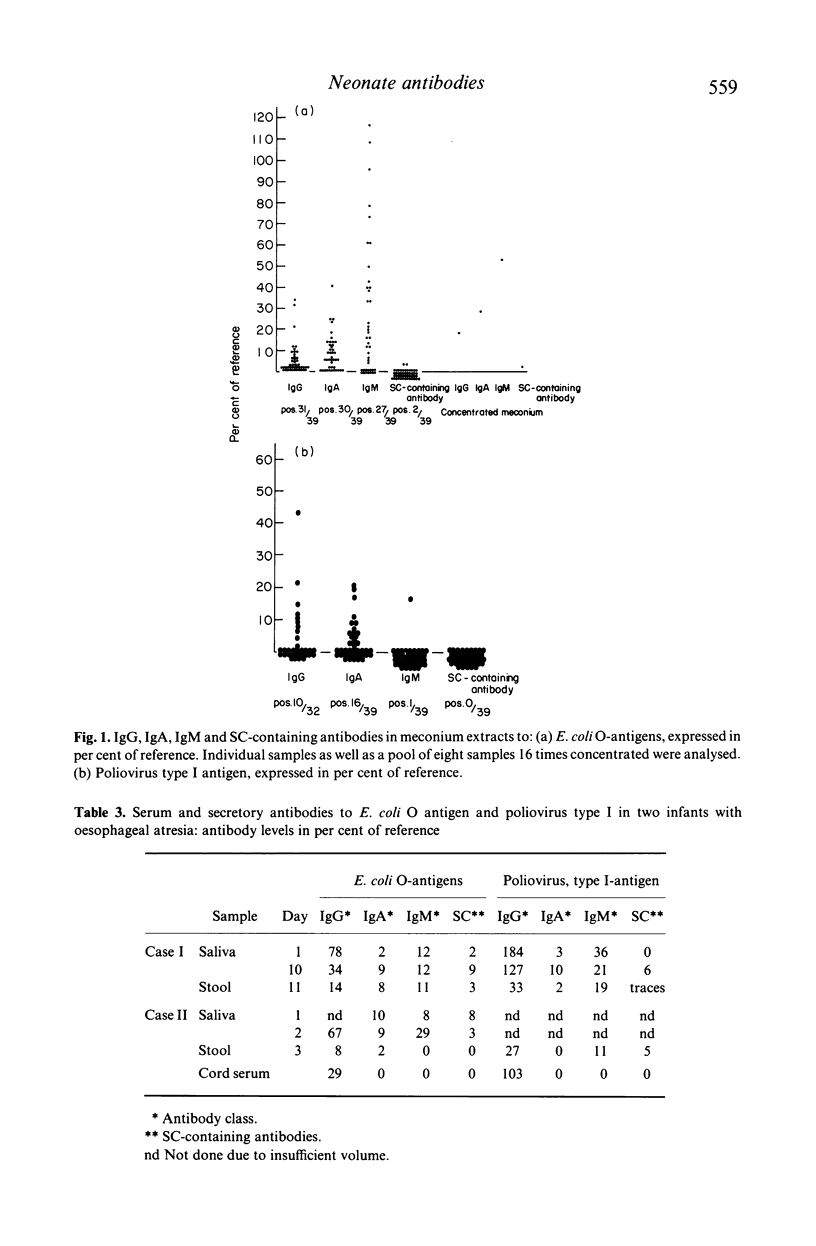
Antibodies to E. coli O-antigens and poliovirus type I antigen as well as total SIgA were analysed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), in amniotic fluid and in meconium, urine and saliva from neonates. Secretory IgA and IgM antibodies to E. coli and poliovirus antigens were found in saliva as well as in most meconium samples taken during the first day of life. SIgA could be quantified in all types of samples including amniotic fluid. The finding of secretory IgA and IgM antibodies to E. coli and poliovirus type I antigens in early samples from an infant of a hypogammaglobulinaemic mother, given regular intravenous (i.v.) immunoglobulin prophylaxis, but still lacking IgA and IgM antibodies, supports a fetal origin for at least part of the secretory antibodies detected in the different samples. Since it is unlikely that the fetus has been exposed to poliovirus, which is rare in Sweden, it is hypothesized that the stimulus inducing the SIgA and IgM antibodies found in the neonate could be anti-idiotypic antibodies from the mother.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerlund A. S., Hanson L. A., Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B. A sensitive method for specific quantitation of secretory IgA. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1275–1282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger P., Marquis G., Dallaire L., Montplaisir S., Ghoubril S. Natural occurrence of a humoral response to Candida in human amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Apr 15;136(8):1075–1079. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson B., Zaman S., Mellander L., Jalil F., Hanson L. A. Secretory and serum immunoglobulin class-specific antibodies to poliovirus after vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1238–1244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederqvist L. L., Ewool L. C., Bonsnes R. W., Litwin S. D. Detectability and pattern of immunoglobulins in normal amniotic fluid throughout gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Jan 15;130(2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(78)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederqvist L. L., Litwin S. D. Production of alpha 1 and alpha 2 immunoglobulin heavy chains during fetal life. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1605–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curl C. W. Immunoglobulin levels in amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Feb 1;109(3):408–410. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERRINGTON M. M., SOOTHILL J. F. An immunochemical study of the proteins of amniotic fluid and of maternal and foetal serum. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961 Oct;68:755–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1961.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H. GM GENES AND GAMMA-G-GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN FETUS. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Biasucci A. Development of gamma G, gamma A, gamma M, beta IC-beta IA, C 1 esterase inhibitor, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, hemopexin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, alpha 1-antitrypsin, orosomucoid, beta-lipoprotein, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and prealbumin in the human conceptus. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1433–1446. doi: 10.1172/JCI106109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T. Meconium in health and disease. Br Med Bull. 1978 Jan;34(1):75–78. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidin-Janson G., Hanson L. A., Kaijser B., Lincoln K., Lindberg U., Olling S., Wedel H. Comparison of Escherichia coli from bacteriuric patients with those from feces of healthy schoolchildren. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):346–353. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellander L., Carlsson B., Hanson L. A. Appearance of secretory IgM and IgA antibodies to Escherichia coli in saliva during early infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;104(4):564–568. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall H. W. Serum protein concentrations in pregnancy. II. Concentrations in cord serum and amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Feb 15;106(4):581–585. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. C., Galinha A., Salomon J. C. Immunoglobulins in the intestinal content of the human fetus with special reference to IgA. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jun;3(6):373–375. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein L. J., Goldberg B., Hiernaux J., Stein K. E., Bona C. A. Idiotype-antiidiotype regulation. V. The requirement for immunization with antigen or monoclonal antiidiotypic antibodies for the activation of beta 2 leads to 6 and beta 2 leads to 1 polyfructosan-reactive clones in BALB/c mice treated at birth with minute amounts of anti-A48 idiotype antibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1129–1144. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rule A. H., Lawrence D., Hager H. J., Hyslop N., Jr, Shwachman H. IgA: presence in meconium obtained from patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1971 Oct;48(4):601–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Söderström T. Neonatal administration of idiotype or antiidiotype primes for protection against Escherichia coli K13 infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1001–1011. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Bjursten L. M., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H. False positive results in class-specific rheumatoid factor (RF) assays due to interaction between RF and Fc fragments of anti-immunoglobulin indicator reagents. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 11;58(1-2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The immunological development of the human fetus. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1173–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


