Abstract
Mitochondria have the capacity to integrate environmental signals and, in animals with active stem cell populations, trigger responses in terms of growth and growth form. Colonial hydroids, which consist of feeding polyps connected by tube-like stolons, were treated with avicins, triterpenoid electrophiles whose anti-cancer properties in human cells are mediated in part by mitochondria. In treated hydroids, both oxygen uptake and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species were diminished relative to controls, similar to that observed in human cells exposed to avicins. While untreated colonies exhibit more stolon branches and connections in the centre of the colony than at the periphery, treated colonies exhibit the opposite: fewer stolon branches in the centre of the colony than at the periphery. The resulting growth form suggests an inversion of the normal pattern of colony development mediated by mitochondrial and redox-related perturbations. An as-yet-uncharacterized gradient within the colony may determine the ultimate phenotypic effect of avicin perturbation.
Keywords: avicins, cancer, hydroids, Podocoryna, reactive oxygen species, redox state
1. Introduction
An increasing number of roles for redox state in general, and mitochondria in particular, have been found in cell differentiation and death (e.g. Coffman et al. 2004; Green & Kroemer 2004; Irwin et al. 2003; Wood et al. 2003). Mitochondria may integrate environmental information and, depending on the circumstances, trigger differential cellular responses. Avicins, derived from Acacia victoria plants, are a case in point. This newly discovered family of triterpenoid electrophiles has been found to regulate the innate stress response in human cells (Haridas et al. 2004, submitted). For example, in cancer cells the avicins induce apoptosis by direct perturbation of the mitochondria, activating the intrinsic caspase pathway (Haridas et al. 2001, submitted), while in normal cells a minimal effect is seen (Mujoo et al. 2001). In addition, avicins induce a cytoprotective mechanism by the redox regulation of Nrf2, resulting in the enhancement of cell detoxification and antioxidant effects (Haridas et al. 2004, submitted). Generally, the avicins represent a new class of metabolites that regulate redox balance in human and mammalian cells through a coordinated system's response to stress, and much of this response involves mitochondria or related redox pathways. Such mitochondrion-related signalling pathways are arguably an ancient component of eukaryotic cells (Blackstone & Kirkwood 2003; Nedelcu et al. 2004). Here we examine the effects of avicin-related perturbations in an early-evolving animal, the colonial marine hydroid Podocoryna carnea. As with many simple animals, these hydroids have active stem cell populations at all stages of the life cycle (Holstein et al. 2003). Mitochondrion-related responses can thus have broad effects on cell proliferation and differentiation, and such effects are of clear interest with regard to anti-cancer selection (Galis & Metz 2003).
2. Material and methods
(a) Study animals and culture conditions
Colonial hydroids encrust a surface with branching and anastomosing stolons that connect feeding polyps. Variation in branching patterns characterizes both between-species and within-species differences (Buss & Blackstone 1991). ‘Sheet-like’ species show closely spaced polyps with short stolonal connections; ‘runner-like’ species exhibit widely spaced polyps with long stolonal connections. Colonies of P. carnea and other species shift from a runner-like growth form to a sheet-like one as they encrust and cover a surface. Thus, the central region of a large colony will show relatively closely spaced polyps and short stolon connections as compared with peripheral regions of the same colony. A number of mitochondrial perturbations result in clear effects on branching patterns that are uniform throughout the colony, e.g. stolons are more closely branched throughout the entire colony or more widely branched throughout the entire colony (Blackstone 2003).
Podocoryna (=Podocoryne) carnea colonies of a single clone were cultured using standard methods (e.g. Blackstone 1999; the same clone, P3, has been used extensively in previous investigations). For measures of oxygen uptake, colonies were grown from single-polyp explants on 12 mm diameter round glass cover-slips; for various measures of polyp and stolon development, explants were grown on 18 mm diameter round glass cover-slips; for measures of reactive oxygen species (ROS), explants were grown on 15 mm diameter round glass cover-slips. Growth of the colonies was confined to one side of the cover-slips by daily scraping with a razor blade. All experiments were carried out at 20.5 °C.
(b) Measures of oxygen uptake
Five treated and five control colonies were assayed using standard methods (Blackstone 2003). For each of these assays, a P. carnea colony on a 12 mm diameter cover-slip was attached with a drop of silicone grease to a cover-slip cemented to a small magnet. This assembly was contained in a 13 mm diameter sealed glass chamber (Strathkelvin RC300) with 0.7 ml of seawater (filtered to 0.2 μm). Chamber temperature was held constant (20.5±0.02 °C) using an external circulation water bath (Neslab RTE-100D), and the rate of decline in oxygen concentration over a 30 min period was measured (using a Strathkelvin 1302 electrode and a 781 oxygen metre) with stirring (by slowly spinning the magnet, cover-slips and colony). The chamber was then opened, a small volume of seawater removed, an equivalent amount of the stock solution of avicin extracts in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to achieve the target concentration of 10 μg ml−1, the solution mixed and aerated thoroughly with a small pipette, and the chamber resealed (this procedure took approximately ∼7 min). For the controls, DMSO was added to the same concentration as used in the avicin treatments. The rate of decline in oxygen concentration was then measured over another 30 min period. These assays were performed 3–5 h after the feeding of the subject colony as part of the normal feeding schedule. For each colony, the before/after difference in the rate of decline in oxygen concentration over a 30 min period was calculated, where this decline was measured by the least-squared slope of oxygen concentration versus time. An overall trend in these differences for the five colonies was analysed using a paired-comparison t-test.
(c) Comparisons of ROS
Hydrogen peroxide represents a major component of ROS under physiological conditions (Chance et al. 1979), and measures of H2O2 were taken using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (H2DCFDA; Nishikawa et al. 2000; Pei et al. 2000). This non-fluorescent dye is freely permeable to living cells. Once inside a cell, the acetate groups are removed by intracellular esterases. In turn, H2DCF is oxidized by peroxides, usually in the presence of peroxidase, cytochrome c, or Fe2+, to form 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein, which can then be visualized with fluorescent microscopy. The activation of H2DCF may be relatively specific for the detection of H2O2 as well as secondary and tertiary peroxides; alternatively, this may be regarded as a general, semi-quantitative assay of ROS (Finkel 2001). Stock solutions of H2DCFDA and avicin extracts were prepared in anhydrous DMSO. Six hydroid colonies (24 h after feeding) were incubated in 10 μg ml−1 avicins. Within 1 h, H2DCFDA was added to a concentration of 10 μmol−1 and colonies were incubated for an additional hour in the dark prior to measurement. Six control colonies were similarly treated, except only DMSO to the same concentration was added. Using a Hamamatsu Orca-100 cooled-CCD camera and a Zeiss Axiovert 135, ROS (as indicated by H2DCFDA-derived 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein) were imaged for a ∼50×150 μm contractile region at the base of three polyps per colony (excitation 450–490 nm, emission 515–565 nm). At these wavelengths, negative controls show that there is little native fluorescence. These regions were also imaged for native fluorescence of NAD(P)H (excitation 365 nm, emission>420 nm), which is a general measure of redox state (Chance 1991). These contractile regions contain the mitochondrion-rich epitheliomuscular cells (EMCs) of the colony (Blackstone et al. 2004).
Images with 12-bit depth (4096 grey levels) were thus obtained and were analysed using Image-Pro Plus software. In such images, fluorescence is visible from many ∼10 μm2 sized clusters of mitochondria from EMCs at polyp–stolon junctions (Blackstone et al. 2004). The luminance and area for each of these fluorescent objects was measured by: (i) selecting the object and an equivalent area of its immediate surroundings (background) as a circular region of interest, (ii) allowing the software to identify the area and luminance of the foreground ‘bright’ region (i.e. the area of fluorescent signal), (iii) exporting these measures to file, (iv) automatically identifying the area and luminance of the complementary background ‘dark’ region and exporting these measures to file. The area of each cluster was thus calculated, and the luminance of the cluster was adjusted for the background luminance by subtraction. These measures were analysed by a nested ANOVA: clusters nested within polyps, polyps nested within clonal replicates, and replicates within treatments.
(d) Comparisons of colony growth and development
Stock solutions of avicin extracts were prepared in anhydrous DMSO. Seven colonies treated with avicin extracts at 10 μg ml−1 and seven control colonies, treated with DMSO to the same concentration, were used. Each group was treated with the appropriate solution for approximately ∼4–6 h d−1. As each colony was nearly covering the surface of the 18 mm cover-slip (up to 60 days after explanting), that colony was imaged. Images were processed to facilitate automatic measurement using Image-Pro Plus software. The grey level of some image objects (i.e. background, stolons or polyps) was adjusted using Corel Photo-Paint software (background grey level=10, stolon=201, polyp=255). Processed images were checked against the original images to ensure accuracy. Each colony was divided up into a central region, arbitrarily defined as 30% of the total area (range 29.8–30.4%) centred on the original explant; and a peripheral region, defined as the remaining 70% of the colony. The central and peripheral regions of each processed image were measured in Image-Pro Plus software for areas of unencrusted cover-slip. These unencrusted areas provide an indication of stolon branching and anastomosis—large areas indicate a low rate of stolon branching and anastomosis, while small areas indicate a high rate. The boundary between the central and peripheral regions was used to assign unencrusted areas to the respective regions. The perimeter of the colony was used to distinguish unencrusted areas within the peripheral region from unencrusted areas outside the colony. Total colony area was measured as well. Using PC-SAS software, natural log-transformed data for unencrusted areas in the central region and in the peripheral region were compared between treated colonies and controls using univariate (ANOVA) and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA).
3. Results
(a) Measures of oxygen uptake
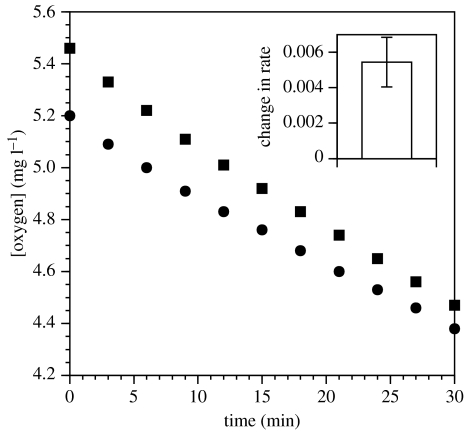
Treatment with avicins shows an immediate (within 10 min) inhibition of oxygen uptake (figure 1; paired comparison t-test of before and after slopes of oxygen concentration versus time, t=3.884, p<0.02, n=5), compared to the controls in seawater and DMSO at the same concentration (t=0.080 36, p>0.40, n=5).
Figure 1.
Rate of decline in oxygen concentration for a P. carnea colony before (squares) and after (circles) treatment with avicin extracts (10 μg ml−1). For five colonies of each treatment, inset plot shows the mean±s.e.m. of the before/after difference in the rate of decline in oxygen concentration, where this decline is measured by the least-squares slope of oxygen concentration versus time. This difference in rate was significantly positive, i.e. the oxygen uptake decreased after treatment.
(b) Comparisons of ROS
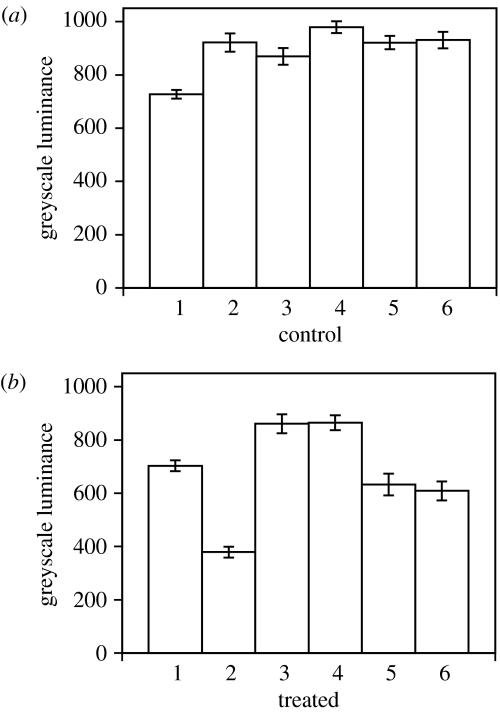
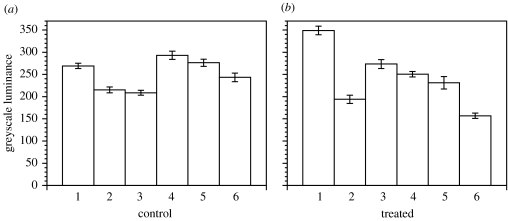
Within 2 h, avicins show an effect on peroxide and perhaps other ROS, as indicated by H2DCFDA-derived 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (figure 2; F1,10=7.02, p<0.05, n=6). Previous studies suggest that mitochondria are the principal source of these peroxides (Blackstone et al. 2004). Nevertheless, avicins do not seem to be acting as uncouplers or inhibitors of mitochondria, since no clear effect is observed on redox state as indicated by native fluorescence of NAD(P)H (figure 3; F1,10=0.08, p<0.70). A more general cellular antioxidant response is thus suggested.
Figure 2.
Mean±s.e.m. luminance (greyscale from 0 to 4095) for three polyps per replicate colony after incubation in H2DCFDA. ROS are thus visualized. (a) Control, (b) colonies treated with avicin extracts (10 μg ml−1).
Figure 3.
Mean±s.e.m. luminance (greyscale from 0 to 4095) for three polyps per replicate colony. Native fluorescence of NAD(P)H is measured. (a) Control, (b) colonies treated with avicin extracts (10 μg ml−1).
(c) Comparisons of colony growth and development
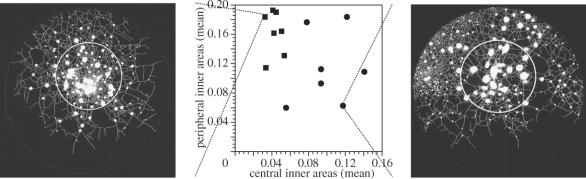
In typical growth of P. carnea colonies, stolons branch more in the centre of a colony, resulting in smaller mean sizes for unencrusted areas (figure 4). On the other hand, closer to the periphery of the colony, stolons branch less and mean sizes for unencrusted areas are larger. This pattern is nearly completely reversed in colonies treated with avicins (figure 4). Treated colonies tend to branch less in the centre of the colony and more on the periphery. There was no significant difference in total colony area (F1,12=0.61, p>0.45). Differences between control and treated colonies were significant for central inner areas (F1,12=36, p≪0.001), for peripheral inner areas (F1,12=5.3, p<0.05), and for both variables analysed simultaneously (MANOVA, F2,11=23, p≪0.001).
Figure 4.
Each data point represents a colony of P. carnea; circles are treated colonies (avicin extracts at 10 μg ml−1), and squares are the controls. Images of two highly divergent colonies are shown. Peripheral and central inner areas are distinguished by region of interest (shown on images by a circle) that was 30% of the total area.
4. Discussion
While the physiology and molecular biology of cancer are becoming well understood, the evolution of cancer remains less well known (Galis & Metz 2003). In this regard, studies of early-evolving animals can provide insight. A central innovation in the evolution of multicellularity is the appropriate downregulation of cell division (Szathmary & Wolpert 2003). Cancer is a general term for the abrogation of such downregulation. Nevertheless, animals such as cnidarians, which exhibit agametic, asexual reproduction and have active stem cells at all stages of the life cycle, show only modest endogenous downregulation of cell division. In this respect, are there fundamental differences between cnidarians and more derived animals?
Certainly, cnidarian cell division and differentiation seems highly responsive to environmental signals. A variety of environmental perturbations affect growth and the growth form of hydroids colonies (Dudgeon & Buss 1996; Buss 2001; Blackstone 2003). Aspects of the gastrovascular system may detect and integrate the environmental inputs and produce an altered pattern of system-level behaviour, ultimately transduced by local, cell-level receptors (Buss 2001). At least in some hydroids, regions of mitochondrion-rich EMCs may have a central role in such colony-wide responses (Blackstone et al. 2004). In the early-evolving animals, mitochondria may thus have a greater role as integrators of information and environmental signalling than in more derived animals. Nevertheless, the environmental perturbations that have been studied to date all show uniform effects, e.g. sheets are converted to runners or vice-versa, rather than differential effects, e.g. some regions of a colony become more sheet-like, while other regions become more runner-like.
Hydroids exhibit some interesting parallels to mammals in their response to avicins, a novel anti-cancer therapeutic treatment. In human cells, avicins cause a differential response, triggering apoptosis in cancer cells as well as activating a general stress response by redox regulation of Nrf2 (Haridas et al. 2004, submitted). In hydroid colonies, avicins diminish both oxygen uptake and ROS, the source of which appears to be mitochondrial (Blackstone et al. 2004). This is consistent with the decrease in both oxygen consumption and ROS (Haridas et al. 2004, submitted) seen in avicin-treated Jurkat cells, a human T-cell leukaemia line. Remarkably, the treatment of hydroid colonies with avicins causes a differential response between the central and peripheral regions of the colonies such that the central region becomes more runner-like, while the peripheral region becomes more sheet-like. At this time, it is difficult to account for these differential morphological changes. Certainly, there are numerous central/peripheral differences in a hydroid colony, including among others age, density of endodermal vacuoles, cell division rates, elasticity, rate and direction of gastrovascular flow and density of mitochondrion-rich contractile regions.
Tissue morphogenesis is driven by integrating signals to determine cell fate and phenotype. Even cells close to each other can enter different mutually exclusive cellular states: proliferation, differentiation, quiescence or apoptosis. One or more of the above central/peripheral differences apparently contributes to spatial variation within a hydroid colony. For instance, the peripheral regions of a colony may be less metabolically active, since mitochondrion-rich EMCs are more abundant at the base of large polyps, which tend to be centrally located (figure 4). In peripheral regions, avicins may thus induce the regression of stolons via cell death, leading to greater branching and the conversion from a runner-like to a sheet-like morphology. On the other hand, in the metabolically active centre of the colony, containing many mitochondrion-rich EMCs, avicins may simulate low metabolic demand and cause mitochondria to enter the resting state. Such an effect has been shown to convert a sheet-like morphology to a runner-like one (Blackstone 2003). The data suggest that this differential effect is mediated by mitochondrial perturbations (as in human cells), and the avicins appear to be acting as an oxidomimetic. Nevertheless, as with other patterning events (e.g. Coffman et al. 2004), the mechanisms by which mitochondria affect development remain obscure. Plausibly, both human cancer and normal cells differ in redox state, as do different regions in the hydroid colony. These differences in the initial conditions predicate the differential response to avicins, i.e. apoptosis versus cytoprotective effect on human cells, and branching or lack of branching in hydroid colony regions. These differential effects on growth may be hallmarks of effective anti-cancer therapeutics in general.
Acknowledgments
Two anonymous reviewers provided useful comments. K. Cherry provided invaluable help with analyses and graphics. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation (IBN-00-90580) and the Clayton Foundation for Research.
References
- Blackstone N.W. Redox control in development and evolution: evidence from colonial hydroids. J. Exp. Biol. 1999;202:3541–3553. doi: 10.1242/jeb.202.24.3541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone N.W. Redox signaling in the growth and development of colonial hydroids. J. Exp. Biol. 2003;206:651–658. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone N.W, Kirkwood T.B.L. Mitochondria and programmed cell death: “slave revolt” or community homeostasis? In: Hammerstein P, editor. Genetic and cultural evolution of cooperation. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 2003. pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone N.W, Cherry K.S, Glockling S.L. Structure and signaling in polyps of a colonial hydroid. Invert. Biol. 2004;123:42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Buss L.W. Growth by intussusception in hydractiniid hydroids. In: Jackson J.B.C, Lidgard S, McKinney F.K, editors. Evolutionary patterns. University of Chicago Press; Chicago, IL: 2001. pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Buss L.W, Blackstone N.W. An experimental exploration of Waddington's epigenetic landscape. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 1991;332:49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chance B. Optical method. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1991;20:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B, Sies H, Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol. Rev. 1979;59:527–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman J.A, McCarthy J.J, Dickey-Sims C, Robertson A.J. Oral–aboral axis specification in the sea urchin embryo. II. Mitochondrial distribution and redox state contribute to establishing polarity in Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev. Biol. 2004;273:160–171. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon S.R, Buss L.W. Growing with the flow: on the maintenance and malleability of colony form in the hydroid Hydractinia. Am. Nat. 1996;147:667–691. [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T. Reactive oxygen species and signal transduction. IUBMB Life. 2001;52:3–6. doi: 10.1080/15216540252774694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galis F, Metz J.A.J. Anti-cancer selection as a source of developmental and evolutionary constraints. Bioessays. 2003;25:1035–1039. doi: 10.1002/bies.10366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D.R, Kroemer G. The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 2004;305:626–629. doi: 10.1126/science.1099320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haridas V, Arntzen C.J, Gutterman J.U. Avicins, a family of triterpenoid saponins from Acacia victoriae (Bentham), inhibit activation of nuclear factor-κB by inhibiting both its nuclear localization and ability to bind DNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:11 557–11 562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191363498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haridas V, Hanausek M, Nishimura G, Soehnge H, Gaikwad A, Narog M, Spears E, Zoltaszek R, Walaszek Z, Gutterman J.U. Triterpenoid electrophiles (avicins) activate the innate stress response by redox regulation of a gene battery. J. Clin. Invest. 2004;113:65–73. doi: 10.1172/JCI18699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haridas, V., Li, X., Higuchi, M., Colombini, M. & Gutterman, J. U. Submitted. Triterpenoid electrophiles (avicins) induce apoptosis by VDAC closure and energy regulation. FEBS Lett.
- Holstein T.W, Hobmayer E, Technau U. Cnidarians: an evolutionarily conserved model system for regeneration. Dev. Dyn. 2003;226:257–267. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin W.A, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in myopathic mice with a collagen VI deficiency. Nat. Genet. 2003;35:367–371. doi: 10.1038/ng1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujoo K, et al. Triterpenoid saponins from Acacia victoriae (Bentham) decrease tumor cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5486–5490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedelcu A.M, Marcu O, Michod R.E. Sex as a response to oxidative stress: a twofold increase in cellular reactive oxygen species activates sex genes. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2004;271:1591–1596. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T, et al. Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature. 2000;404:787–790. doi: 10.1038/35008121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z.-M, Murata Y, Benning G, Thomine S, Klüsener B, Allen G.J, Grill E, Schroeder J.I. Calcium channels activated by hydrogen peroxide mediate abscisic acid signalling in guard cells. Nature. 2000;406:731–734. doi: 10.1038/35021067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szathmary E, Wolpert L. The transition from single cells to multicellularity. In: Hammerstein P, editor. Genetic and cultural evolution of cooperation. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 2003. pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- Wood Z.A, Poole L.B, Karplus P.A. Peroxiredoxin evolution and the regulation of hydrogen peroxide signaling. Science. 2003;300:650–653. doi: 10.1126/science.1080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]