Abstract
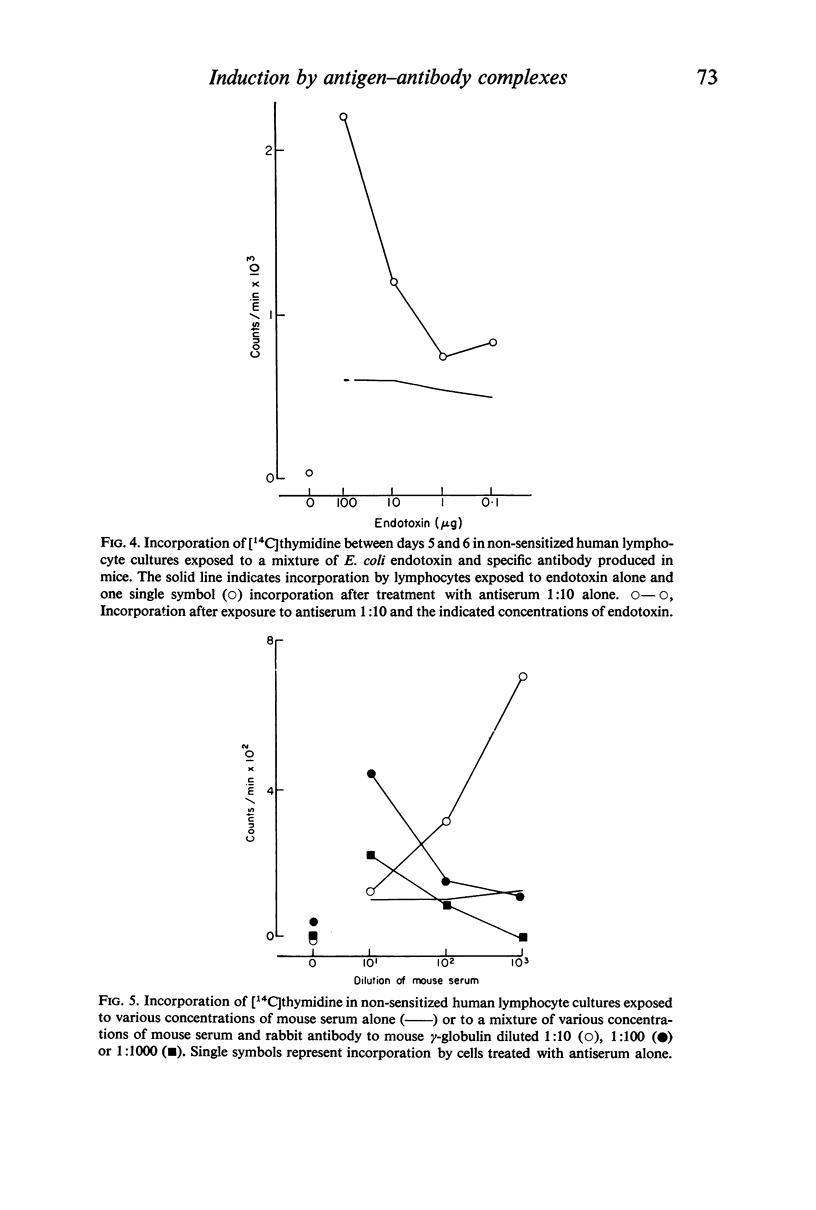
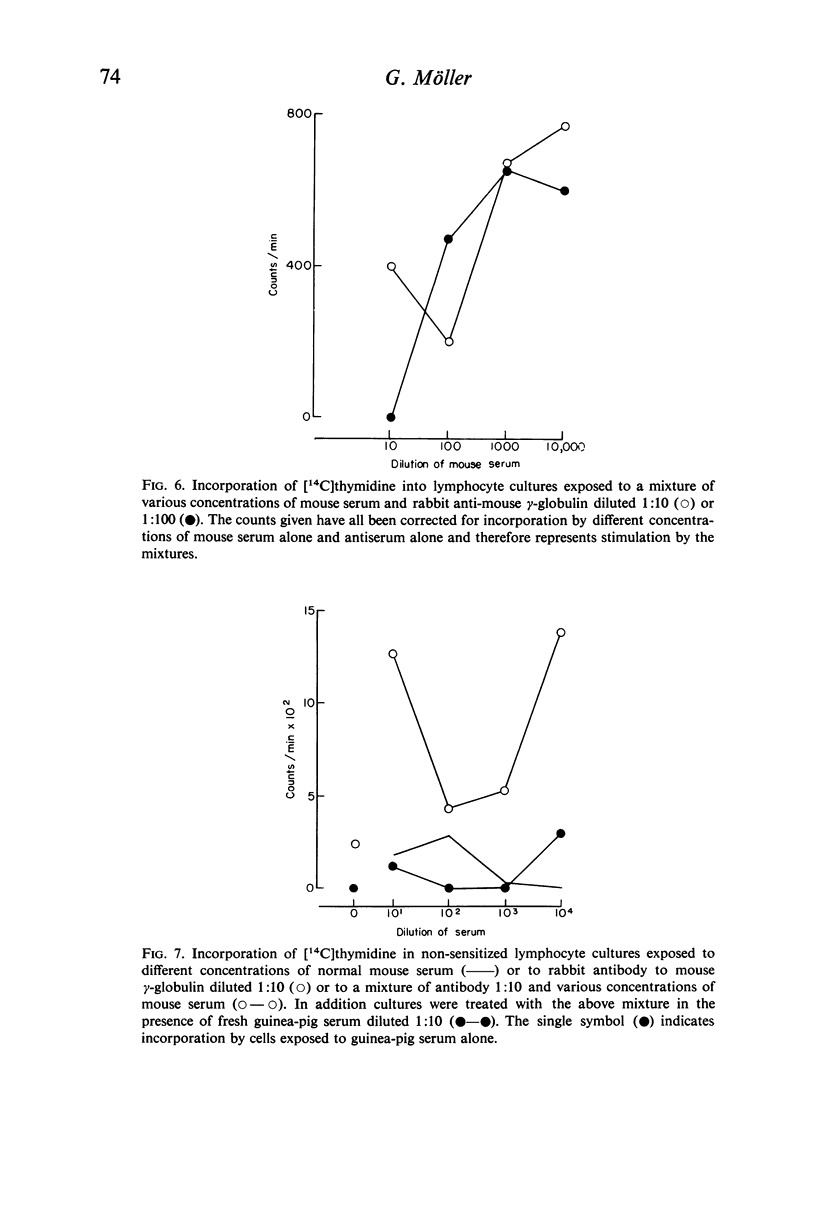
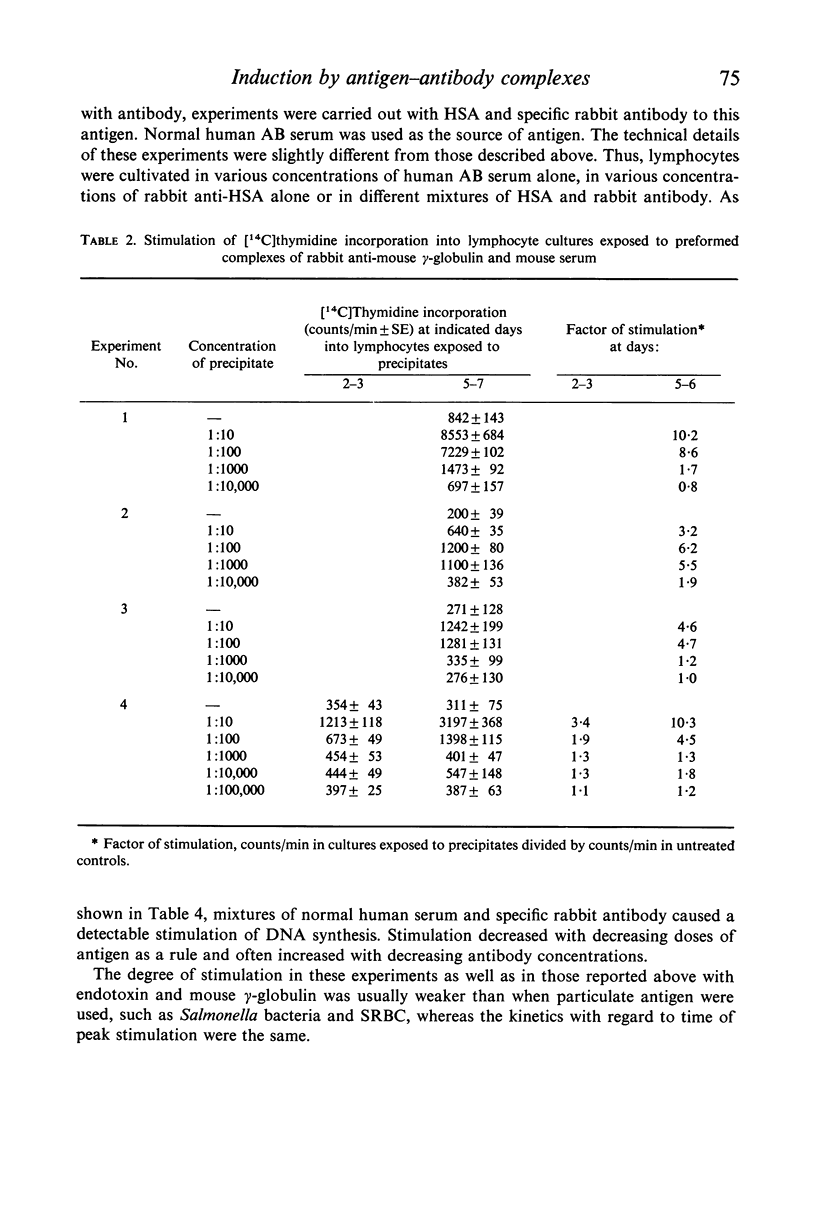
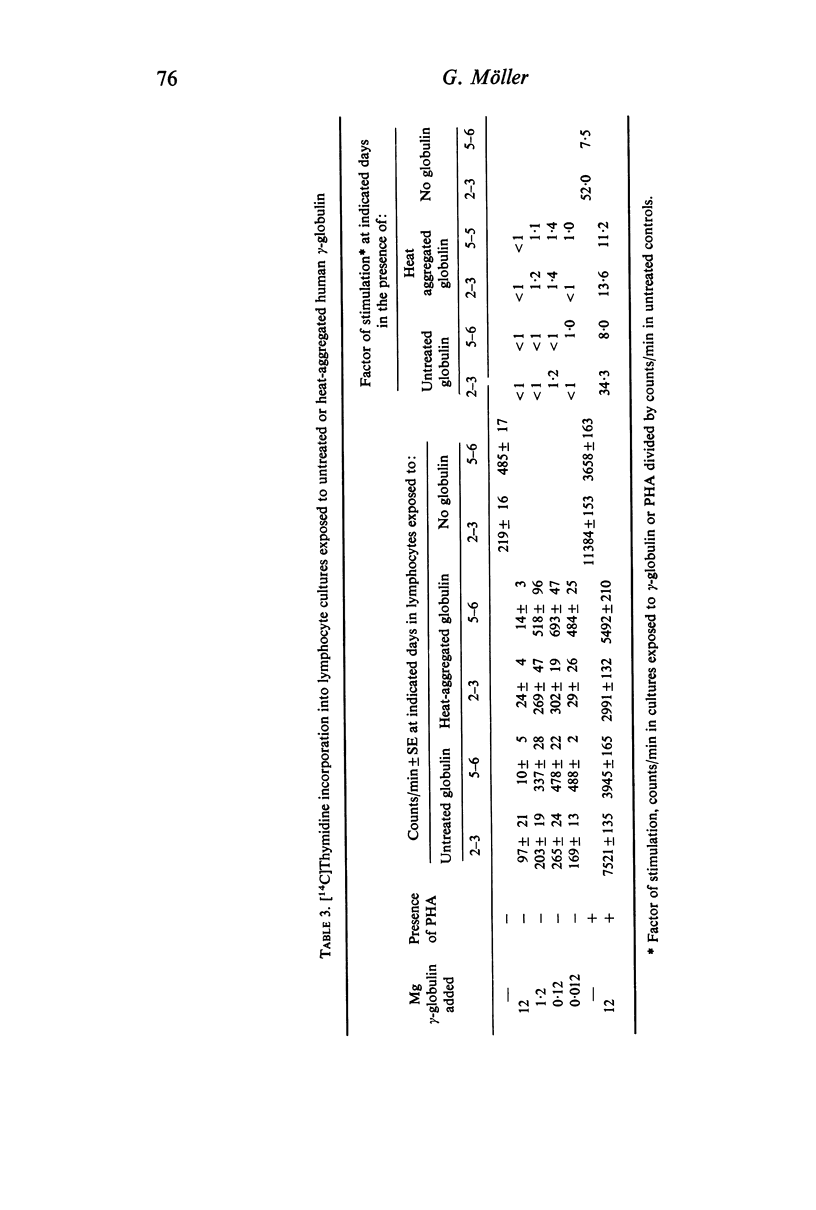
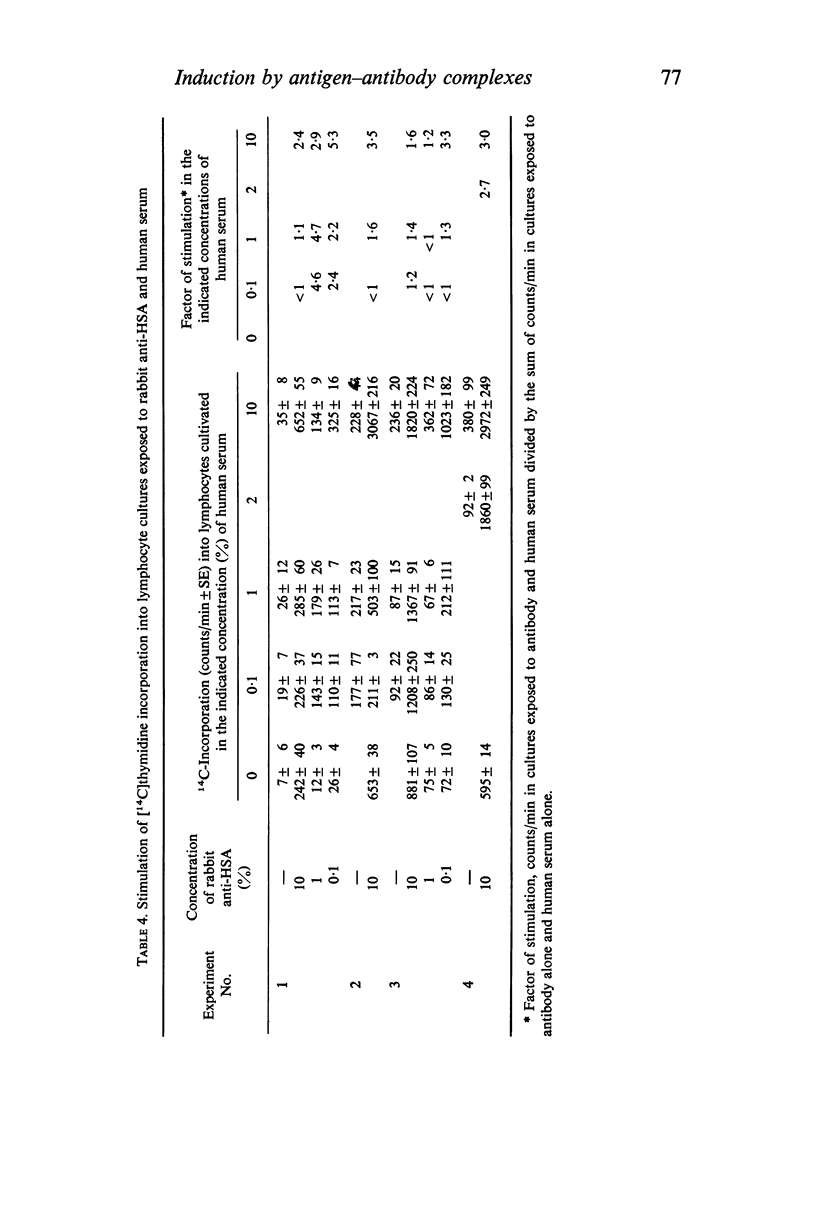
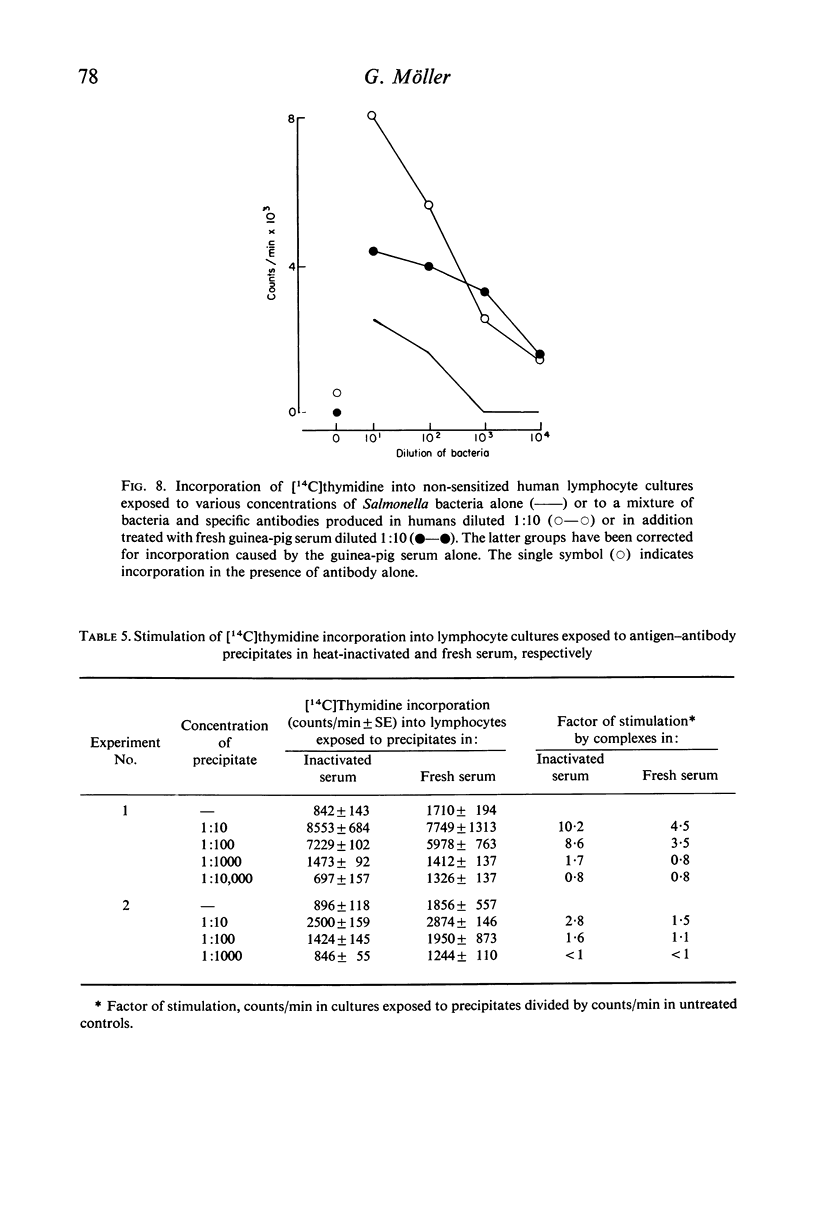
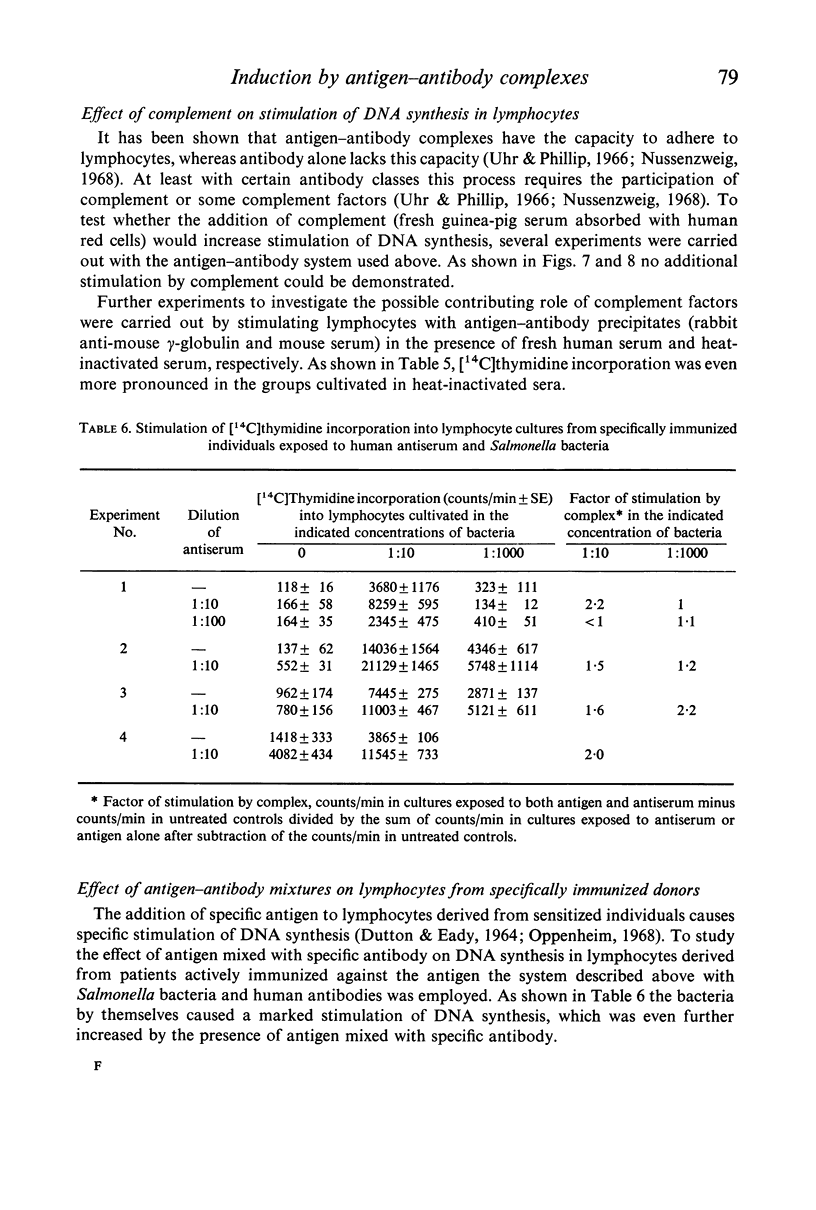
Antibodies were produced in various species against particulate (sheep red blood cells and Salmonella bacteria) or soluble (E. coli endotoxin, human serum albumin and mouse γ-globulin) antigens. Antibody mixed with the corresponding antigen stimulated DNA synthesis in normal human lymphocytes cultivated in vitro, whereas antibody alone or antigen alone had no or a negligible effect. The species origin of the antibody did not seem to influence the results. Maximal stimulation of DNA synthesis occurred after 5–6 days. Preformed antigen–antibody complexes were also stimulatory, whereas heat-aggregated γ-globulin had no effect. The addition of fresh complement did not increase DNA stimulation. The degree of stimulation of DNA synthesis after contact between lymphocytes from immunized individuals and the specific antigen was even further increased when humoral antibody was introduced.
The present findings suggest a mechanism by which non-committed lymphoid cells of host origin are activated by a small proportion of antibody-producing cells to participate in various cell-mediated immune reactions, in particular since it was found that lymphocytes stimulated by antigen–antibody complexes acquired the capacity to kill allogeneic and autochthonous fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUTTON R. W., EADY J. D. AN IN VITRO SYSTEM FOR THE STUDY OF THE MECHANISM OF ANTIGENIC STIMULATION IN THE SECONDARY RESPONSE. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:40–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLM G., PERLMANN P., WERNER B. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ-INDUCED CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF NORMAL LYMPHOID CELLS ON CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Nature. 1964 Aug 22;203:841–843. doi: 10.1038/203841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Cytotoxic potential of stimulated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):721–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxic action of unsensitized immunologically competent cells on allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue culture cells. Nature. 1965 Aug 21;207(999):818–821. doi: 10.1038/207818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G. The in vitro cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes: the effect of metabolic inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Nov;48(2):334–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren G., Zukoski C. F., Möller G. Differential effects of human granulocytes and lymphocytes on human fibroblasts in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Oct;3(8):817–836. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLUSKEY R. T., BENACERRAF B., MCCLUSKEY J. W. STUDIES ON THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CELLULAR INFILTRATE IN DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Mar;90:466–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAJARIAN J. S., FELDMAN J. D. Passive transfer of transplantation immunity. I. Tritiated lymphoid cells. II. Lymphoid cells in millipore chambers. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:1083–1093. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J. Relationship of in vitro lymphocyte transformation to delayed hypersensitivity in guinea pigs and man. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):21–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Waksman B. H. Cytotoxic effect of lymphocyte-antigen interaction in delayed hypersensitivity. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1060–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Studies on rabbit lymphocytes in vitro. VI. The induction of blast transformation with sheep antisera to rabbit IgA and IgM. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):393–400. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



