Abstract
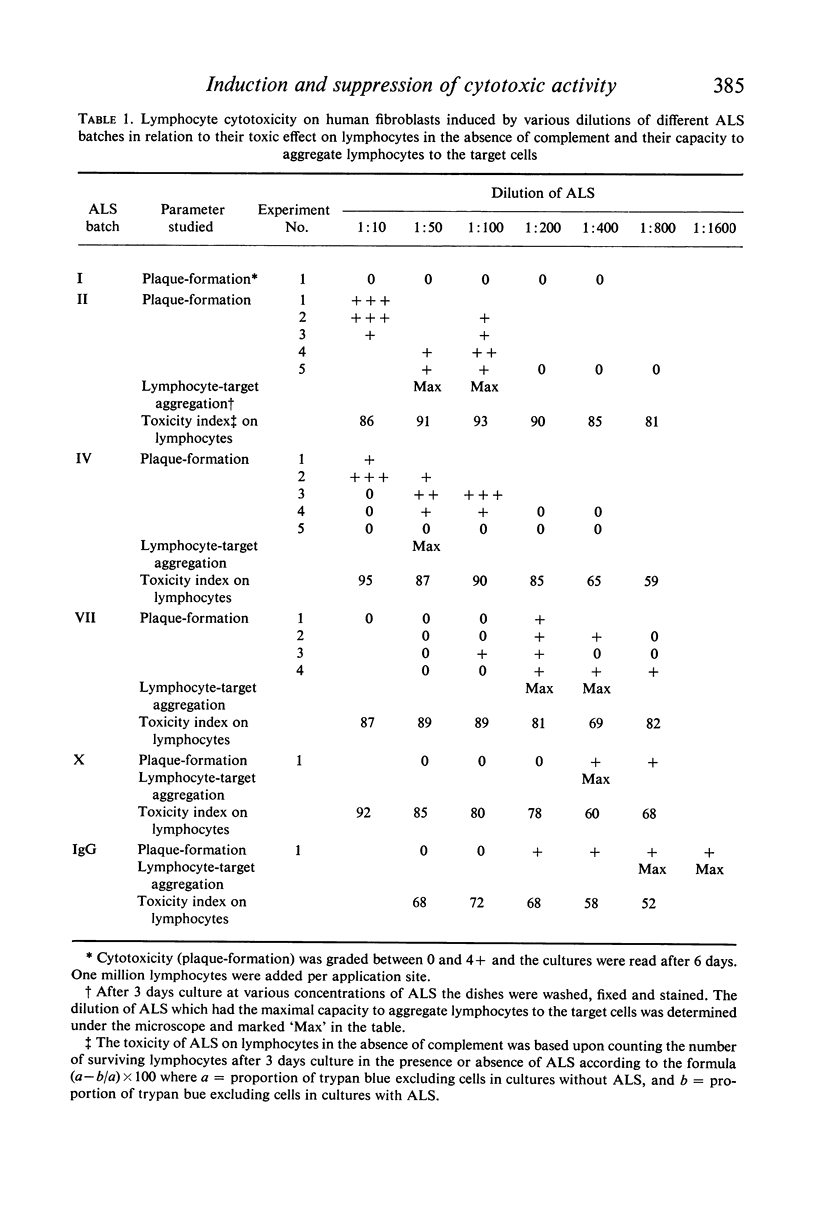
Heterologous anti-lymphocyte sera were demonstrated to induce a cytotoxic potential in normal non-immunized human lymphocytes against allogeneic fibroblast target cells. The cytotoxicity-inducing capacity was restricted to certain dilutions of anti-lymphocytic serum above and below which no cytotoxic effect was obtained. This optimal concentration shifted towards higher dilutions in sera taken late during the immunization course. The antisera were shown to stimulate the DNA-synthesis in lymphocytes and to aggregate the lymphocytes to the target cells. The DNA-synthesis and the aggregation as well were maximal at the same dilution of anti-lymphocytic serum which induced cytotoxicity. No cytotoxic effect was demonstrable on sheep fibroblasts. It is, therefore, suggested that the anti-lymphocytic serum antibody induces lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against allogeneic fibroblasts in a two step manner: it stimulates the lymphocytes into a cytotoxic state; it aggregates the human lymphocytes to the human fibroblasts by virtue of its bivalent structure.
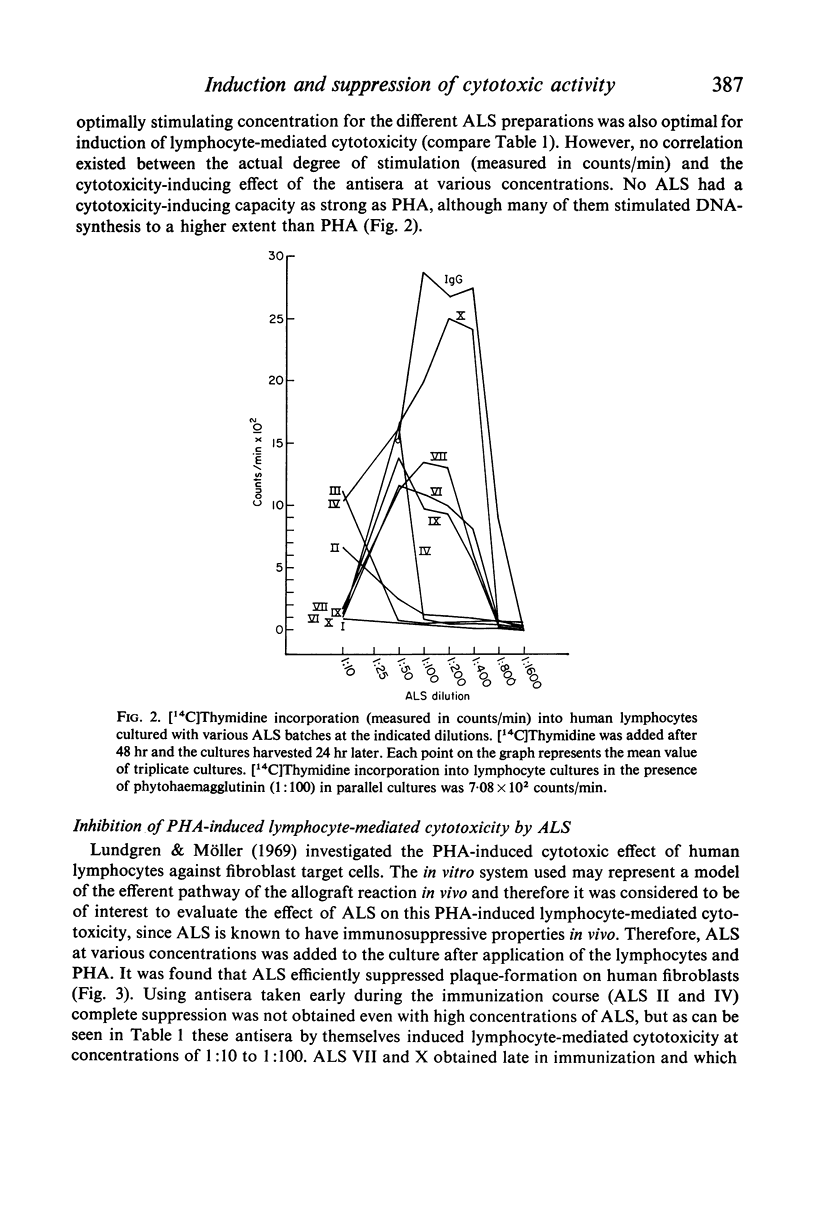
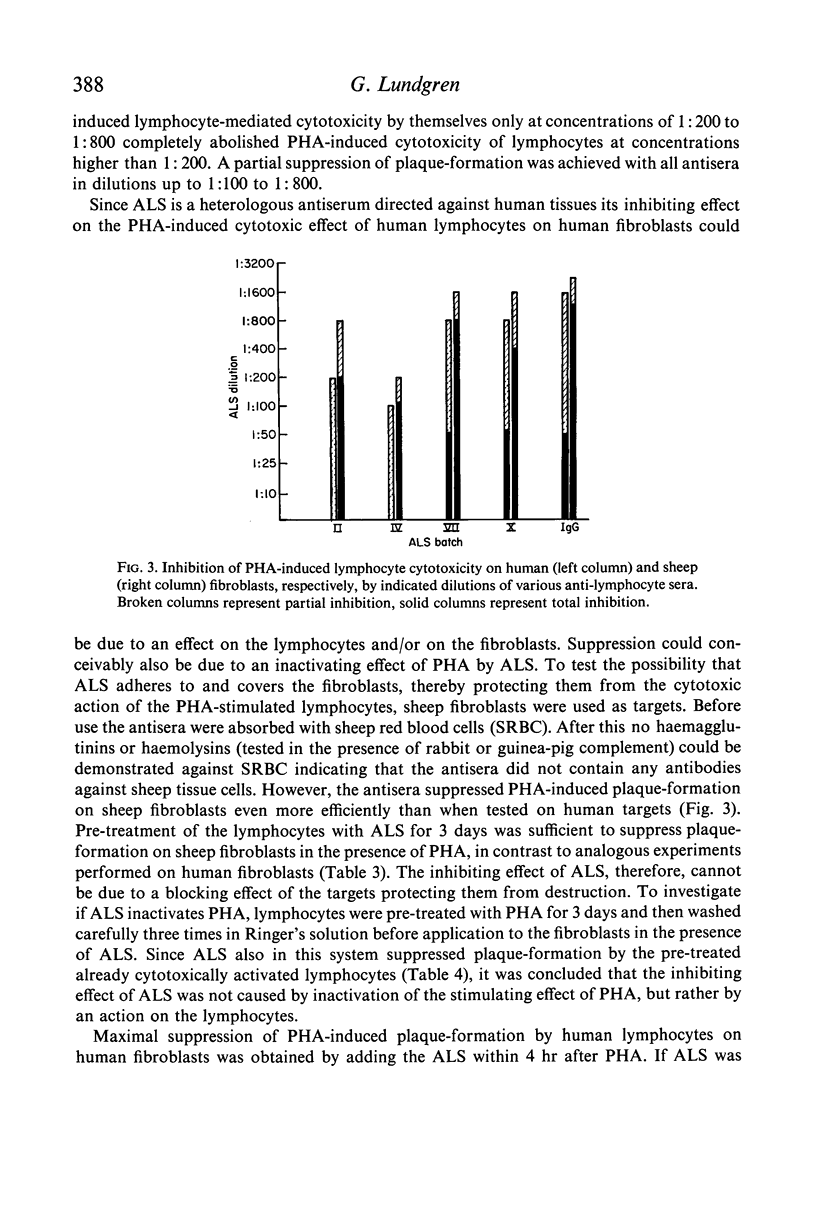
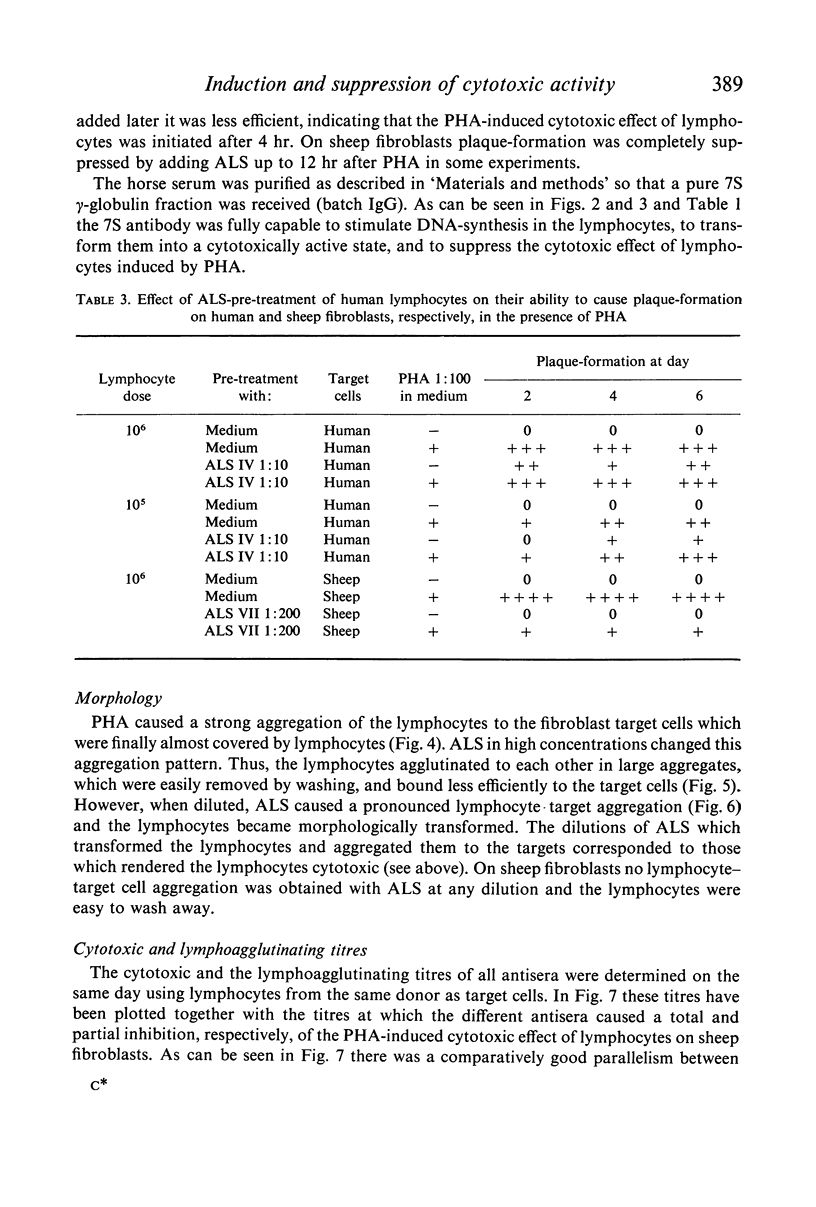
Anti-lymphocytic serum was also found to suppress the cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes induced by various non-specific agents, such as phytohaemagglutinin, streptolysin O and anti-lymphocytic serum itself. The mechanism for this inhibition is extensively discussed and it is suggested that anti-lymphocytic serum suppresses the reaction by coating the lymphocytes, thereby preventing the intimate contact between effector and target cell. A similar mechanism may operate in vivo and could be a partial explanation of the in vivo immunosuppressive effect of anti-lymphocytic serum. Purified 7S γ-globulin possessed all activities of the whole antiserum.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. F., James K., Woodruff M. F. Effect of acid treatment on the immunosuppressive properties of anti-lymphocytic IgG. Nature. 1968 May 25;218(5143):771–773. doi: 10.1038/218771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent L., Courtenay T., Gowland G. Immunological reactivity of lymphoid cells after treatment with anti-lymphocytic serum. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1461–1464. doi: 10.1038/2151461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., NORDMAN C., DELACHAPELLE A. MITOGENIC ACTION OF ANTILEUCOCYTE IMMUNE SERUM ON PERIPHERAL LEUCOCYTES IN VITRO. Lancet. 1963 Aug 24;2(7304):385–386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)93062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLM G., PERLMANN P., WERNER B. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ-INDUCED CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF NORMAL LYMPHOID CELLS ON CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Nature. 1964 Aug 22;203:841–843. doi: 10.1038/203841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Inhibition of cytotoxic lymphocytes by anti-lymphocytic serum. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):420–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H., Medawar P. B. Further experiments on the action of antilymphocytic antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):470–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H., Medawar P. B. Nature and mode of action of antilymphocytic antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1130–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren G., Collste L., Möller G. Cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes: antagonism between inducing processes. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):289–291. doi: 10.1038/220289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren G., Möller G. Non-specific induction of cytotoxicity in normal human lymphocytes in vitro: studies of mechanism and specificity of the reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):435–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren G., Zukoski C. F., Möller G. Differential effects of human granulocytes and lymphocytes on human fibroblasts in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Oct;3(8):817–836. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosedale B., Felstead K. J., Parke J. A. The effect of anti-lymphocyte serum on the response of human and mouse lymphocytes to PHA. Nature. 1968 Jun 8;218(5145):983–984. doi: 10.1038/218983a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perper R. J., Okimoto J. T., Cochrum K. C., Ramsey N., Najarian J. S. A rapid method for purification of large quantities of anti-lymphocytic serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):575–580. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Effect of actinomycin D on cellular nucleic acid synthesis and virus production. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):556–557. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H., Cantell K. Production of interferon by human leukocytes in vitro. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1966;44(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traeger J., Carraz M., Fries D., Perrin J., Saubier E., Bernhardt J. P., Revillard J. P., Bonnet P., Archimbaud J. P., Brochier J. Studies of anti-lymphocyte globulins made from thoracic duct lymphocytes. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):455–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODRUFF M. F., ANDERSON N. A. EFFECT OF LYMPHOCYTE DEPLETION BY THORACIC DUCT FISTULA AND ADMINISTRATION OF ANTILYMPHOCYTIC SERUM ON THE SURVIVAL OF SKIN HOMOGRAFTS IN RATS. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:702–702. doi: 10.1038/200702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]