Abstract
Antibodies to calf thymus nuclei, nucleoprotein, DNA, soluble nucleoprotein and hydrazide (hydrallazine and isoniazid)-altered nucleoprotein were investigated by a standard complement-fixation method in 214 tuberculous patients receiving isoniazid. Findings were compared to those on thirty-seven sera from lupus patients receiving neither steroids nor immunosuppressants and on sixty-six sera from normal controls.
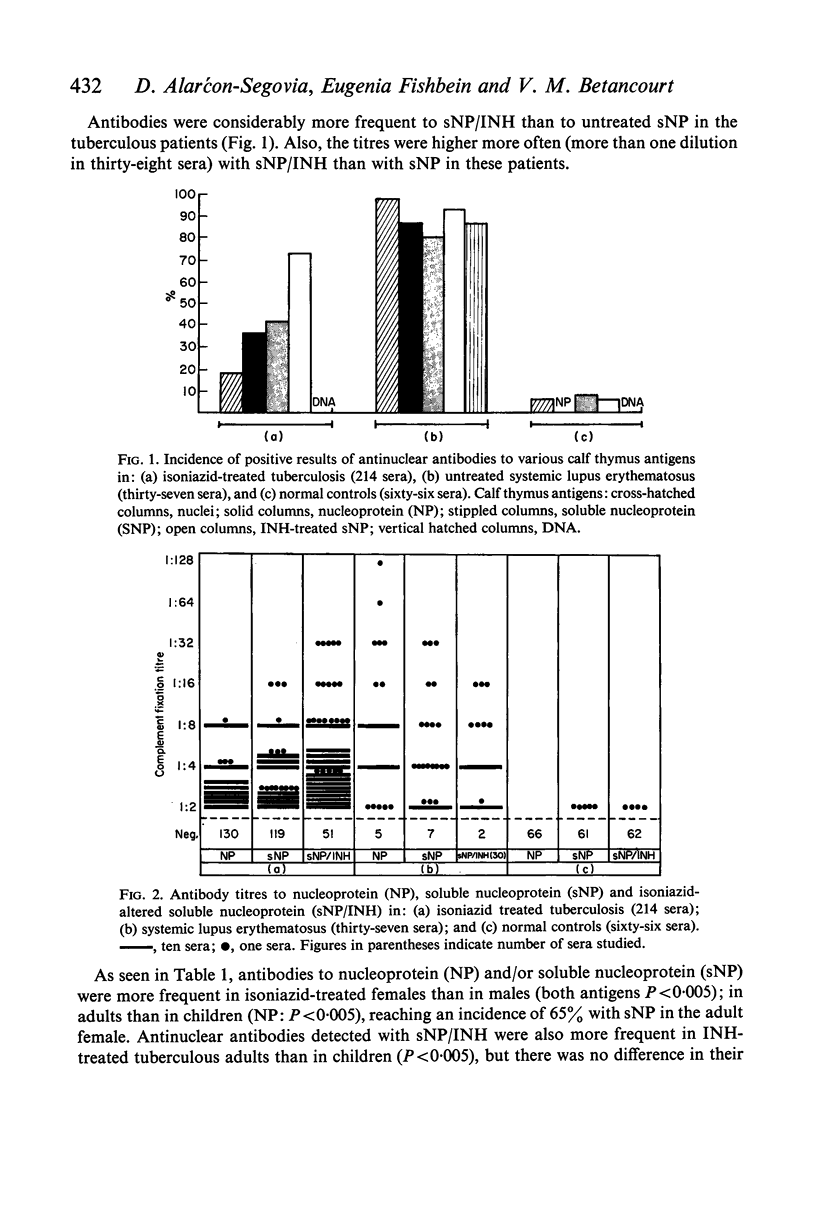
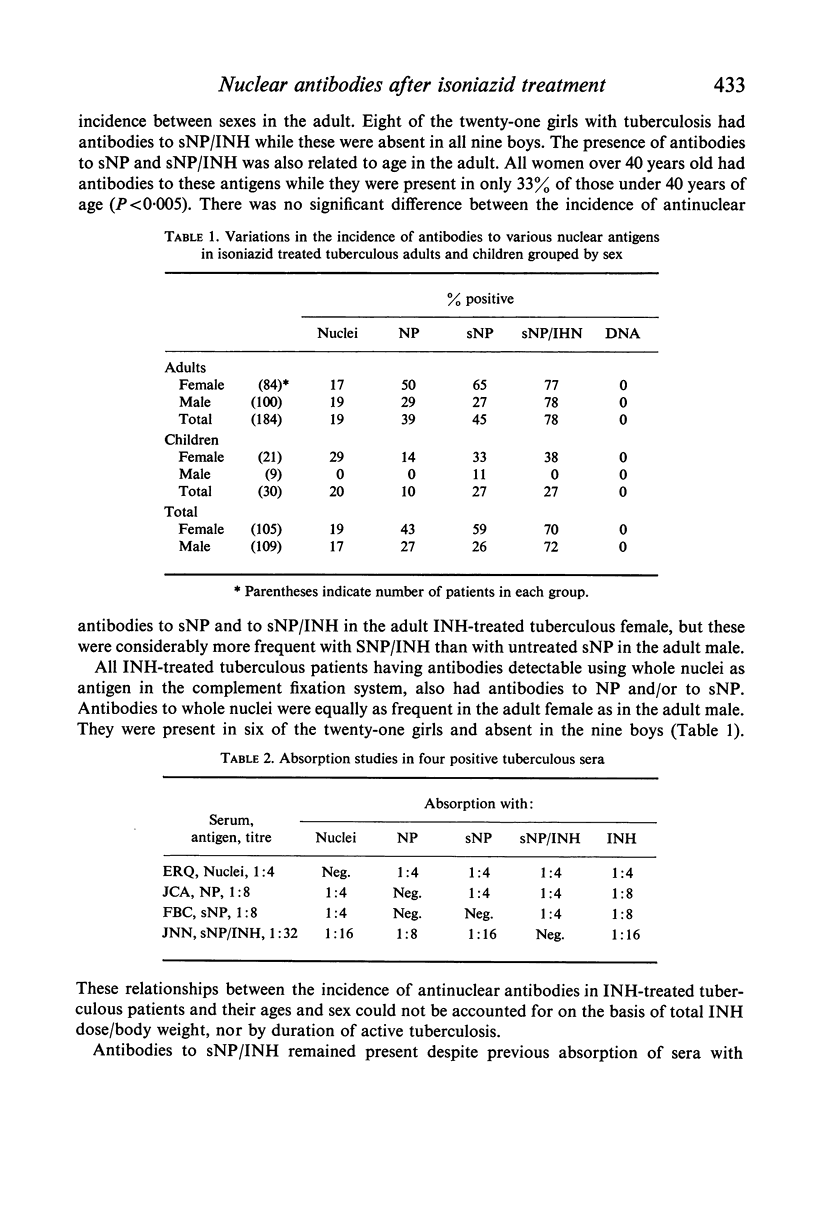
The incidence of antibodies to all antigens studied except DNA was significantly higher in isoniazid-treated tuberculous patients than in the normal controls, but lower than in the lupus patients. Unlike lupus there were no detectable DNA antibodies in the tuberculous or in the control sera. Antibodies to nucleoprotein (soluble and insoluble) and particularly to hydrazide-altered nucleoprotein were the most frequently found in the isoniazid-treated tuberculous patients. In general, antinuclear antibodies were more frequent in the isoniazid-treated tuberculous female than in the male; in the adult than in the child.
It is suggested that hydrazides may cause in vivo similar alteration of nucleoprotein to that which they cause in vitro. Hydrazide-altered nucleoprotein probably elicits the production of antinuclear antibodies which in turn may activate systemic lupus erythematosus in otherwise predisposed individuals.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALARCON SEGOVIA D., WORTHINGTON J. W., WARD L. E., WAKIM K. G. LUPUS DIATHESIS AND THE HYDRALAZINE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Mar 4;272:462–466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196503042720905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLFREY V. G., LITTAU V. C., MIRSKY A. E. METHODS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF THYMUS NUCLEI AND THEIR APPLICATION TO STUDIES OF NUCLEAR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Cell Biol. 1964 May;21:213–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón Segovia D. Papel de diversas drogas en la activación del lupus eritematoso generalizado. Rev Invest Clin. 1966 Jul-Dec;18(3):445–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannat A., Seligmann M. Induction by isoniazid and hydrallazine of antinuclear factors in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jan;3(1):99–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannat A., Seligmann M. Possible induction of antinuclear antibodies by isoniazid. Lancet. 1966 Jan 22;1(7430):185–187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90704-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAMESHEK W. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a complex auto-immune disorder. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Apr;48(4):707–730. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-48-4-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS E. L., TUFFANELLI D. L. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF 520 CASES. JAMA. 1964 Oct 12;190:104–111. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070150014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeyre N., Kahn M. F., de Sèze S. Les syndromes lupoïdes après absorption d'isoniazide. Etude de 6 cas. Sem Hop. 1967 Nov 26;43(49):3063–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost P. G., Lachmann P. J. The relationship of desoxyribonuclease inhibitor levels in human sera to the occurrence of antinuclear antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jun;3(5):447–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUDIE R. B., ANDERSON J. R., GRAY K. G. Complement-fixing antithyroid antibodies in hospital patients with asymptomatic thyroid lesions. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(2):389–400. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACKETT E., BEECH M., FORBES I. J. Thyrogloubulin antibodies in patients without clinical disease of the thyroid gland. Lancet. 1960 Aug 20;2(7147):402–404. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92842-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMER R., LEVIN F. M., RUDD E. GLOBULINS RESEMBLING RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN SERUM OF THE AGED. Am J Med. 1963 Aug;35:175–181. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLEY H. L. EVIDENCE FOR A PREDISPOSITION TO RHEUMATIC DISEASES IN FAMILIES OF PATIENTS DEVELOPING DRUG-INDUCED SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. Arthritis Rheum. 1964 Dec;7:684–686. doi: 10.1002/art.1780070608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Davies S. H., Teitelbaum S., Delamore I. W., Williams A. W. The clinical and pathological significance of gastric parietal cell antibody. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(2):657–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb18993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappat E. J., Cawein M. J. A familial study of procainamide-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. A question of pharmacogenetic polymorphism. Am J Med. 1968 Dec;45(6):846–852. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Rivero I., Siegel M. Activation of systemic lupus erythematosus by drugs. Arch Intern Med. 1966 May;117(5):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Ziff M. Natural antibodies to procaine amide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Nov;3(9):901–909. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M., Lee S. L., Peress N. S. The epidemiology of drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Oct;10(5):407–415. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svec K. H., Veit B. C. Age-related antinuclear factors: immunologic characteristics and associated clinical aspects. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Dec;10(6):509–516. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. An immunologic precipitin system between soluble nucleoprotein and serum antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):735–745. doi: 10.1172/JCI105574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINGALE S. B., MINZER L., ROSENBERG B., LEE S. L. Drug induced lupus-like syndrome. Clinical and laboratory syndrome similar to systemic lupus erythematosus following antituberculous therapy: report of a case. Arch Intern Med. 1963 Jul;112:63–66. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1963.03860010109012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



