Abstract
A modification of the charcoal method for the detection and titration of antibody to intrinsic factor in serum and for the assay of intrinsic factor in human gastric juice is described. The antibody was detected in a titre greater than 5 ng units/ml in 52% of the sera of 162 patients with Addisonian pernicious anaemia. False positive results may occur if the serum is withdrawn within 24 hr of the parenteral administration of normal therapeutic doses of vitamin B12.
In the analysis of human gastric juice, the charcoal method of immunoassay clearly distinguishes between intrinsic factor and other vitamin B12 binding substances. A good correlation was observed between the gastric acid secretion, the ability to absorb oral radioactive vitamin B12 in the Schilling test, and the assay of intrinsic factor in the gastric juice. Intrinsic factor as an antigen is stable in acid and alkali media but is destroyed by incubation at 56°C for 30 min. A secretion of less than 100 ng units intrinsic factor in the gastric juice during the post-histamine hour is not compatible with adequate vitamin B12 absorption and is indicative of Addisonian pernicious anaemia.
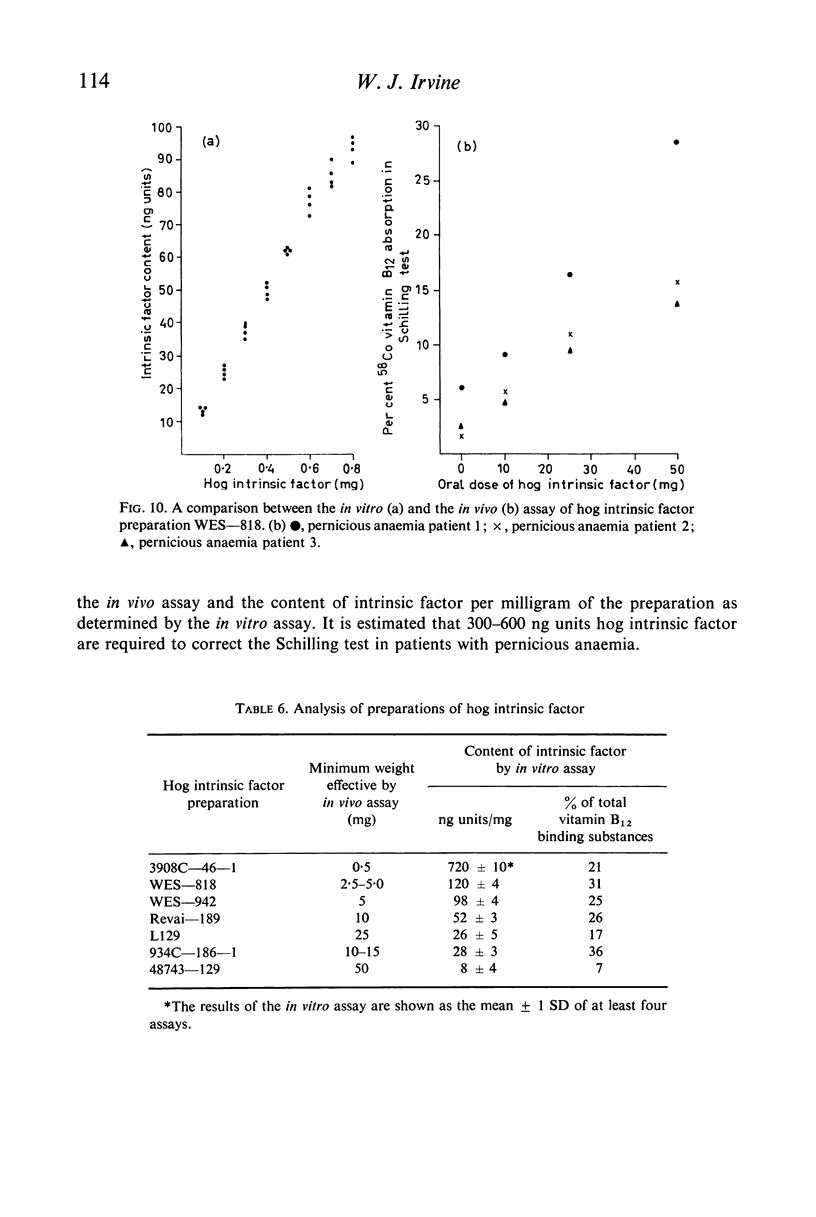
A good correlation was observed between the immunoassay and the biological activity of preparations of hog intrinsic factor. To correct the absorption of oral vitamin B12 in the Schilling test in patients with pernicious anaemia 300–600 ng units hog intrinsic factor are required. It is suggested that hog intrinsic factor preparations should be defined in terms of nanogram units intrinsic factor per milligram.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELS J., BOUMA W., JANSZ A., WOLDRING M. G., BAKKER A., NIEWEG H. O. Experiments on the intrinsic factor antibody in serum from patients with pernicious anemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jun;61:893–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARDEMAN S., CHANARIN I. A METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF HUMAN GASTRIC INTRINSIC FACTOR AND FOR THE DETECTION AND TITRATION OF ANTIBODIES AGAINST INTRINSIC FACTOR. Lancet. 1963 Dec 28;2(7322):1350–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90736-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARDEMAN S., CHANARIN I., DOYLE J. C. STUDIES ON SECRETION OF GASTRIC INTRINSIC FACTOR IN MAN. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 5;2(5409):600–603. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5409.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRDWOOD R. H. Microbiological methods of assay in clinical medicine with particular reference to the investigation of deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Scott Med J. 1960 Jan;5:10–22. doi: 10.1177/003693306000500103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. Divalent cation and pH dependence of rat intrinsic factor action in everted sacs and mucosal homogenates of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI104423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., GOTTLIEB C., LAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R. INTRINSIC-FACTOR ASSAY. Lancet. 1964 Nov 7;2(7367):1017–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90975-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVINE W. J., DAVIES S. H., HAYNES R. C., SCARTH L. SECRETION OF INTRINSIC FACTOR IN RESPONSE TO HISTAMINE AND TO GASTRIN IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF ADDISONIAN PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. Lancet. 1965 Aug 28;2(7409):397–401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90754-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVINE W. J. EFFECT OF GASTRIN I AND II ON SECRETION OF INTRINSIC FACTOR. Lancet. 1965 Apr 3;1(7388):736–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVINE W. J. IMMUNOLOGIC ASPECTS OF PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. N Engl J Med. 1965 Aug 19;273:432–438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196508192730807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES G. H., HOSKINS D. W., SLEISENGER M. H. Antibody to intrinsic factor in serum from patients with pernicious anemia. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1106–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI104562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES G. H., SLEISENGER M. H. The immunologic identification and quantitation of human intrinsic factor in gastric secretions. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:442–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI104732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY A. W. Effect of large doses of histamine on gastric secretion of HCI; an augmented histamine test. Br Med J. 1953 Jul 11;2(4827):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4827.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRIE J. H., SMITH G. M., FORREST A. P. THE HISTAMINE-INFUSION TEST. Lancet. 1964 Aug 8;2(7354):270–273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)93043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING R. F. Intrinsic factor studies II. The effect of gastric juice on the urinary excretion of radioactivity after the oral administration of radioactive vitamin B12. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Dec;42(6):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS E. W., WILSON T. H. Factors controlling B12 uptake by intestinal sacs in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:103–107. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN L. W., HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. IN VITRO ASSAY FOR HUMAN INTRINSIC FACTOR. J Clin Invest. 1963 Sep;42:1443–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI104829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANGEL A. G., CALLENDER S. T. EFFECT OF GASTRIN I AND II ON THE SECRETION OF INTRINSIC FACTOR. Br Med J. 1965 May 29;1(5447):1409–1411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5447.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


