Abstract
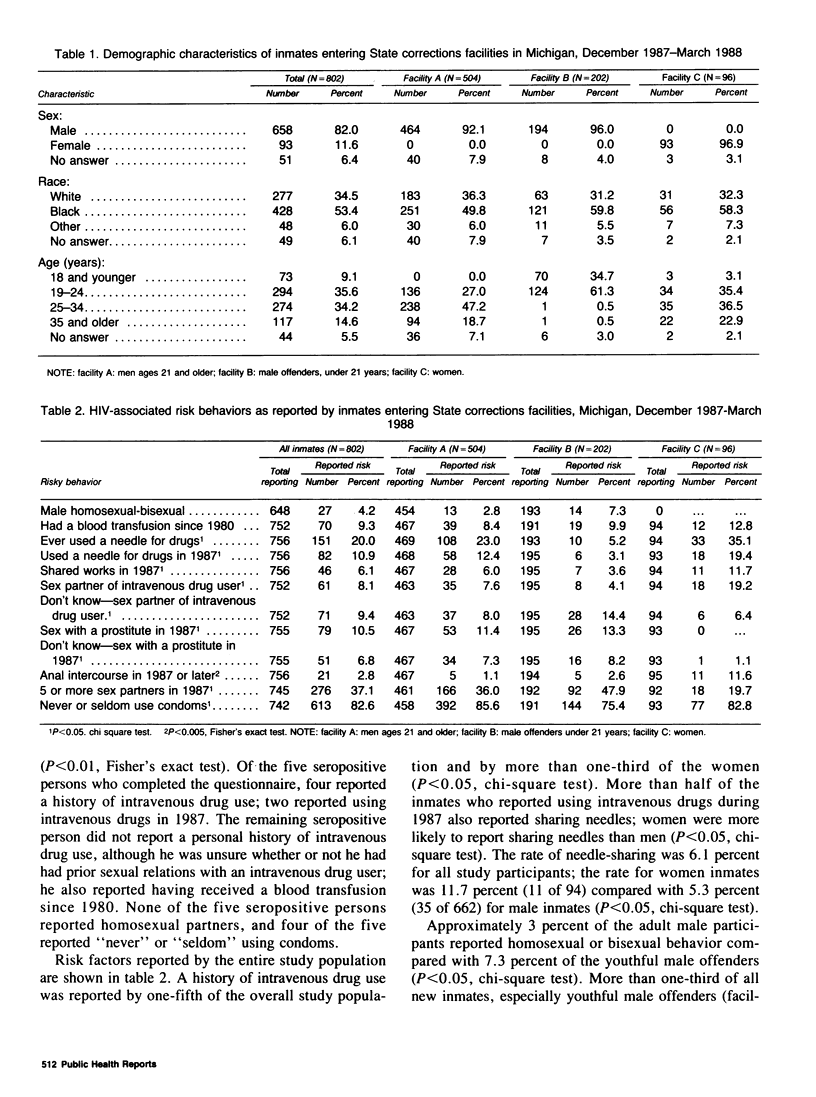
Seroprevalence surveys of incoming inmates provide useful sentinel information on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection rates among groups that practice HIV-associated high-risk behaviors. In addition, such data are beneficial to corrections officials in the formulation of institutional policies to prevent HIV infection. Inmates entering the Michigan corrections system from December 1987 to March 1988 participated in blind, anonymous serosurveys for HIV infection. Eight of 802 entering inmates (1.0 percent) were seropositive; most seropositive persons reported intravenous drug use. The most common risk behaviors reported by study participants were intravenous drug use (20.0 percent), multiple sexual partners (37.1 percent), and infrequent (that is, never or seldom) use of condoms (82.6 percent). Women reported the highest rates of intravenous drug use (35.1 percent) and needle-sharing (19.4 percent). Results from this study indicate that in spite of wide-spread HIV-associated risk behaviors, the extent of HIV-seropositivity among incoming inmates in Michigan is relatively low. Such data suggest that there is still time to impact the course of the AIDS epidemic among high-risk groups in States where the prevalence of HIV infection is relatively low. The data also indicate that the potential for HIV spread in correctional facilities is noteworthy and that HIV prevention education and substance abuse treatment services are needed in corrections facilities.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anda R. F., Perlman S. B., D'Alessio D. J., Davis J. P., Dodson V. N. Hepatitis B in Wisconsin male prisoners: considerations for serologic screening and vaccination. Am J Public Health. 1985 Oct;75(10):1182–1185. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.10.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Bernard E. Aerosol pentamidine. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):852–854. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M. H., Joseph J. G. AIDS and behavioral change to reduce risk: a review. Am J Public Health. 1988 Apr;78(4):394–410. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.4.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Moss A. R., Onishi R., Osmond D., Carlson J. R. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in heterosexual intravenous drug users in San Francisco. Am J Public Health. 1987 Feb;77(2):169–172. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. D., Vaughn W. K., Brodie J. S., Hutcheson R. H., Jr, Schaffner W. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis B in Tennessee prisoners. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):450–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Dickinson G. M., La Voie L. Safety and efficacy of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in AIDS. JAMA. 1988 Feb 26;259(8):1185–1189. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.8.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass G. E., Hausler W. J., Loeffelholz P. L., Yesalis C. E., 3rd Seroprevalence of HIV antibody among individuals entering the Iowa Prison System. Am J Public Health. 1988 Apr;78(4):447–449. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S. AIDS commentary. Azidothymidine. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):427–431. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. W., Redfield R. R., Ward D. L., Burke D. S., Miller R. N. Prevalence and incidence of HTLV-III infection in a prison. JAMA. 1986 Oct 24;256(16):2198–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


