Abstract
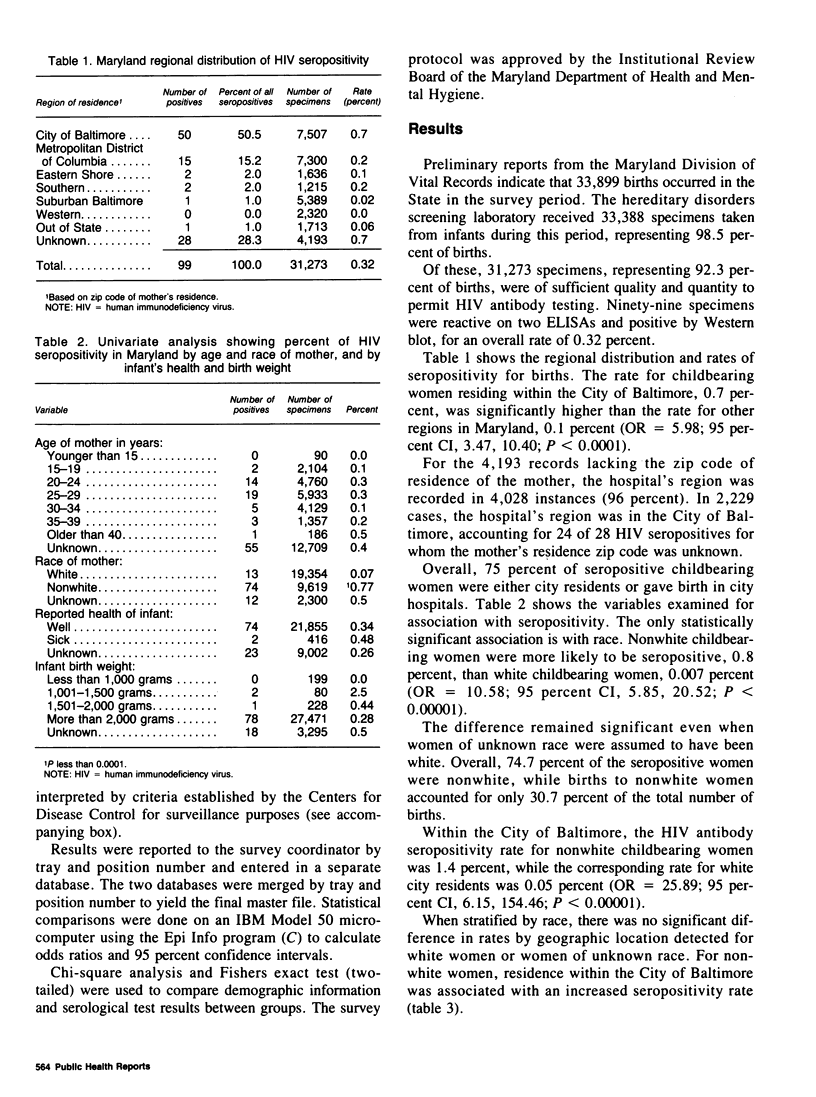
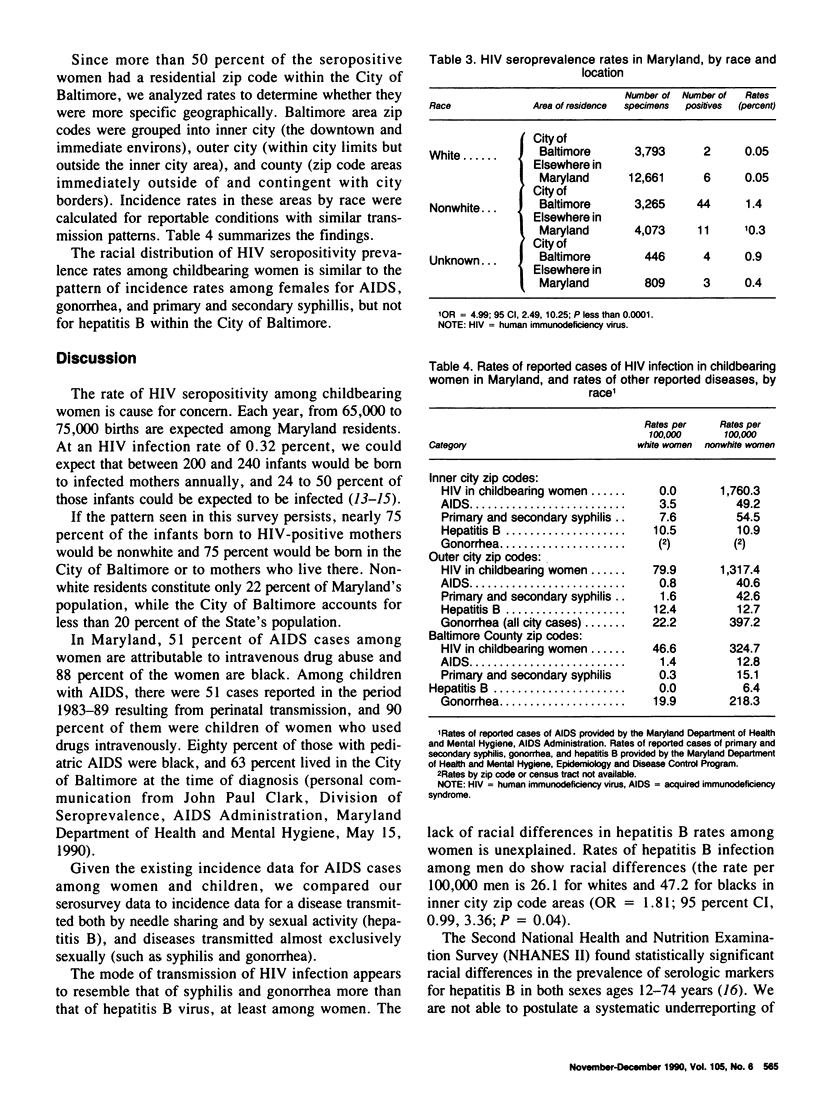
Because blood specimens from newborns reflect the antibody status of the mother, seroprevalence rates among childbearing women are obtainable from analysis of the specimens. A blinded survey of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody seroprevalence among childbearing women was conducted in Maryland. The survey used 31,273 dried filter paper blood spot specimens obtained from newborns screened for hereditary disorders. Overall, 99 specimens were positive on two enzyme-linked immunoassays and on Western blot, providing a seroprevalence rate of 0.32 percent. The rate for child-bearing women residing within the City of Baltimore, 0.7 percent, was significantly higher than the rate for those residing elsewhere in Maryland, 0.1 percent. The statewide rate for nonwhite women, 0.8 percent, was higher than for white women, 0.007 percent. No statistically significant associations were found with residence in an inner city area, as opposed to residence in other areas of the city; birth weight group; reported health of the infant; or the infant having received a transfusion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hoff R., Berardi V. P., Weiblen B. J., Mahoney-Trout L., Mitchell M. L., Grady G. F. Seroprevalence of human immunodeficiency virus among childbearing women. Estimation by testing samples of blood from newborns. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):525–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesman S., Minkoff H., Holman S., McCalla S., Sijin O. Serosurvey of human immunodeficiency virus infection in parturients. Implications for human immunodeficiency virus testing programs of pregnant women. JAMA. 1987 Nov 20;258(19):2701–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuszak D. L., Kotval I., Garg R., Patel J., Israel E., Glasser D. Prevalence of risk behaviors and HIV infection in Maryland STD clinics. Md Med J. 1989 Dec;38(12):1019–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick L. F., Berns D., Stricof R., Stevens R., Pass K., Wethers J. HIV seroprevalence in newborns in New York State. JAMA. 1989 Mar 24;261(12):1745–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Glasser D., Cannon R. O., Matuszak D. L., Dunning R. W., Kline R. L., Campbell C. H., Israel E., Fauci A. S., Hook E. W., 3rd Human immunodeficiency virus infection among patients attending clinics for sexually transmitted diseases. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jan 28;318(4):197–203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198801283180401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



