Abstract
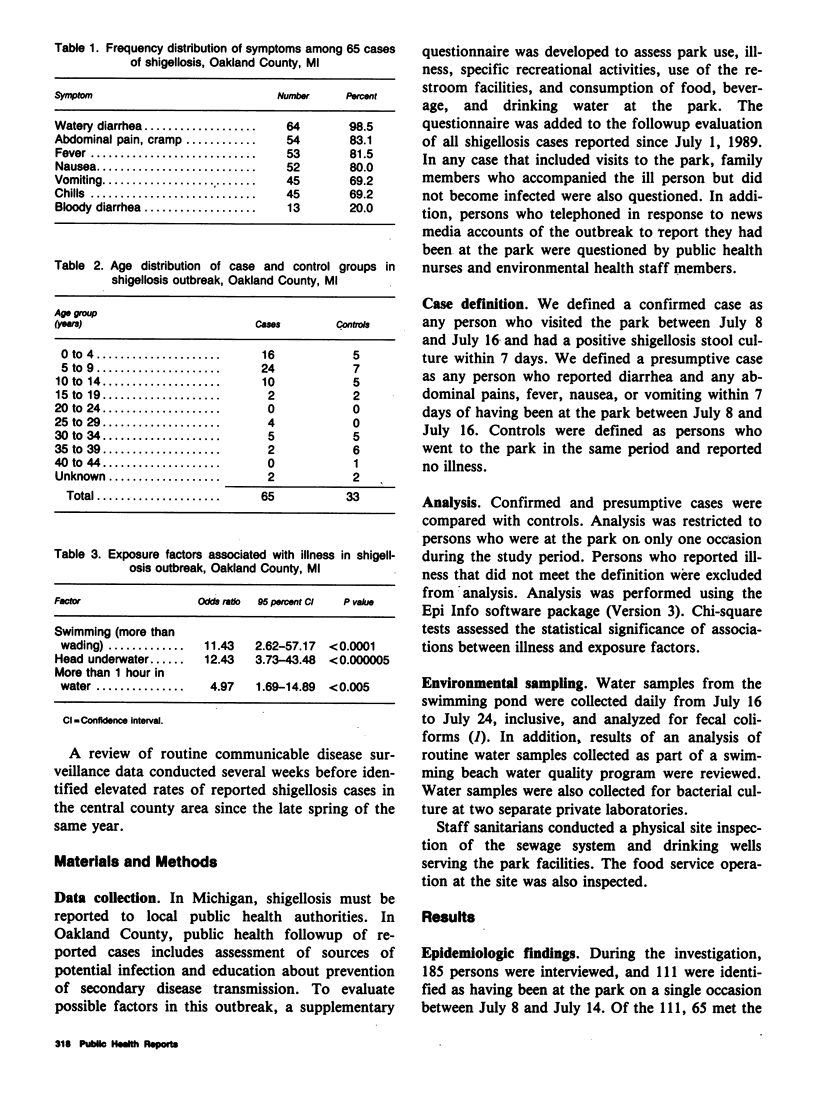
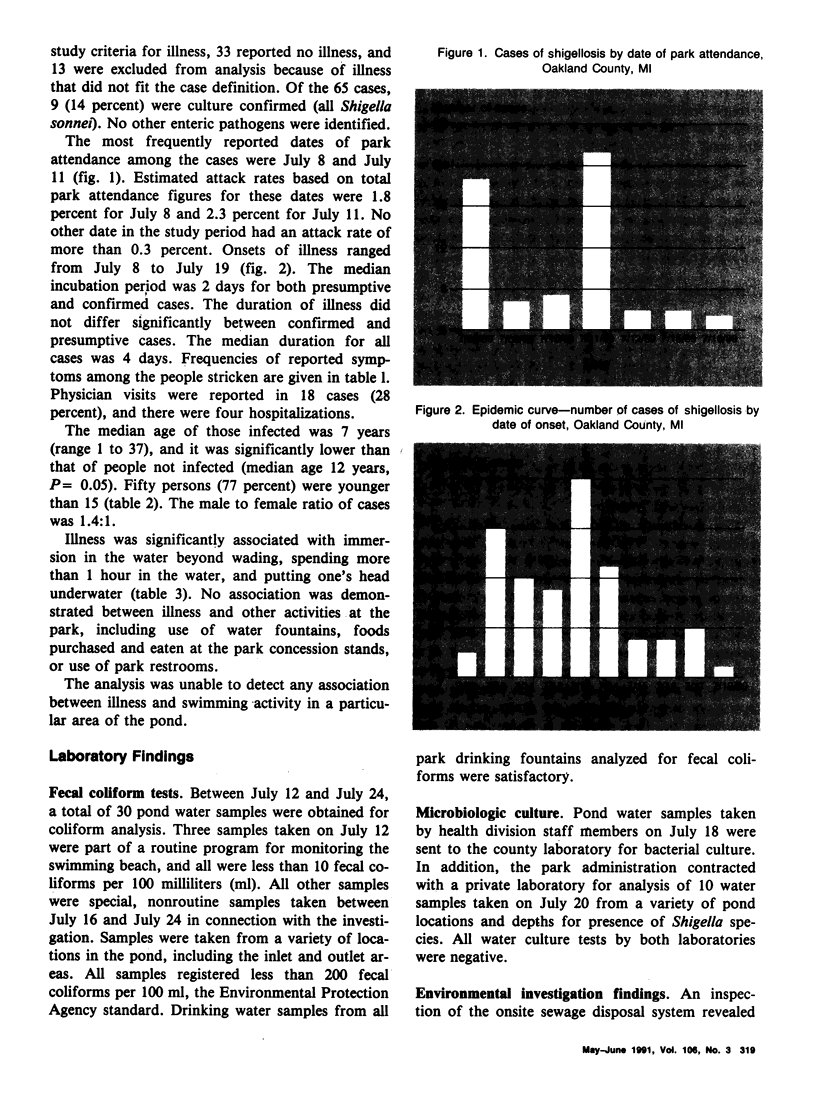
In July 1989 an outbreak of shigellosis occurred among visitors to a recreational park in Oakland County, MI. An epidemiologic investigation discovered an association between illness and swimming in a pond at the park, especially for those who had put their head underwater. No other factors were epidemiologically incriminated. A total of 65 cases were identified; nine were culture confirmed, all Shigella sonnei. Several water samples evaluated for fecal coliform counts shortly after the outbreak were found satisfactory. Cultures of water samples were negative for Shigella species. Inspection of the park's sewage disposal and toilet facilities found all equipment in proper working condition and no evidence of a sewage contamination event from these potential sources. No other commercial or residential sources of potential sewage contamination existed near the pond. Investigators concluded that Shigella contamination of the pond by a swimmer or swimmers on one or more occasions was a strong possibility. Factors supporting this conclusion included elevated incidence of S. sonnei in the community during the 2 months prior to the outbreak, greater use of the pond, warm water and air temperatures, and inadequate water exchange in the pond. This report adds one of the few documented outbreaks of shigellosis implicating bather contamination to the literature on the growing number of incidents that have been associated with recreational use of water.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Craun G. F., Blake P. A. Epidemiology of common-source outbreaks of shigellosis in the United States, 1961-1975. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Jul;108(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favero M. S. Microbiologic indicators of health risks associated with swimming. Am J Public Health. 1985 Sep;75(9):1051–1054. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.9.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makintubee S., Mallonee J., Istre G. R. Shigellosis outbreak associated with swimming. Am J Public Health. 1987 Feb;77(2):166–168. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Hazlet K. K., Schaefer J., Wells J. G., Pruneda R. C. Shigellosis from swimming. JAMA. 1976 Oct 18;236(16):1849–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo F. J., Waterman S. H., Vogt J. K., England B. Shigellosis associated with recreational water contact in Los Angeles County. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 May;38(3):613–617. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


