Abstract
A soluble antigen present in infectious tissue culture fluids was separated from the infective virus particle by ultracentrifugation of two serologically related strains of bovine viral diarrhea viruses, NADL-MD and Oregon C24V.
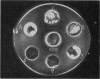
Neutralizing antibodies against the two viruses were absent in four hog cholera antisera, but present in significant titer in the commercially prepared antiserum. Precipitin tests utilizing the agar double diffusion technique formed a single line of identity between the concentrated soluble antigen of both viruses and NADL-MD and hog cholera antisera. No lines were observed using concentrated virus pellet and noninfected BEK cell antigens or control SPF calf and swine sera.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCCA M. A., CASEY H. L., WINN J. F. Method of concentration of viral diagnostic reagents using hydrophilic agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jun;104:247–250. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. H., BAKER J. A., McENTEE K. A cytopathogenic strain of virus diarrhea virus. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jan;50:73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEFFY B. E., COGGINS L., BAKER J. A. Relationship between hog cholera virus and virus diarrhea virus of cattle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Feb;109:349–352. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE G., COWAN K. M. Separation of the soluble antigens and infectious particles of rinderpest and canine distemper. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:209–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]