Abstract
Reduction in caloric intake to 400 a day for 72 hours resulted in a significant increase in the plasma bilirubin concentration in patients with Gilbert's syndrome and in normal subjects. This was due to an increase in unconjugated pigment. There was no significant increase in the bilirubin concentration in patients with liver disease or haemolytic anaemia.
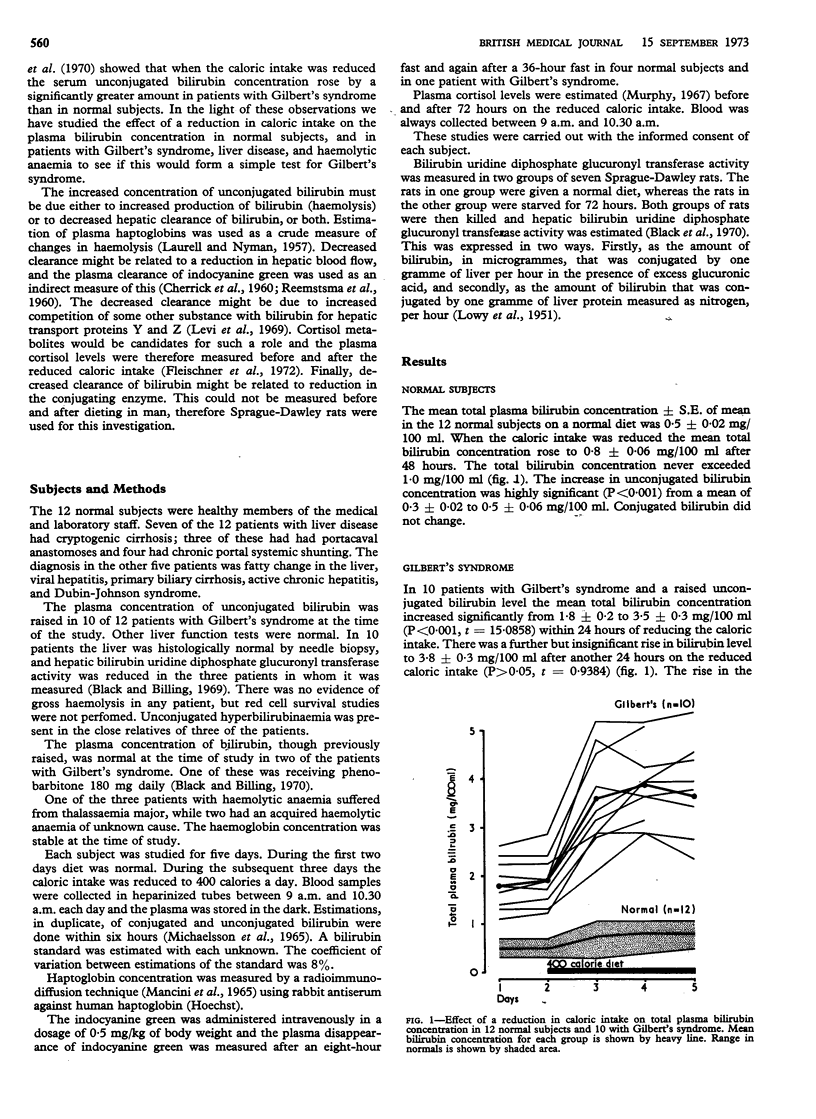
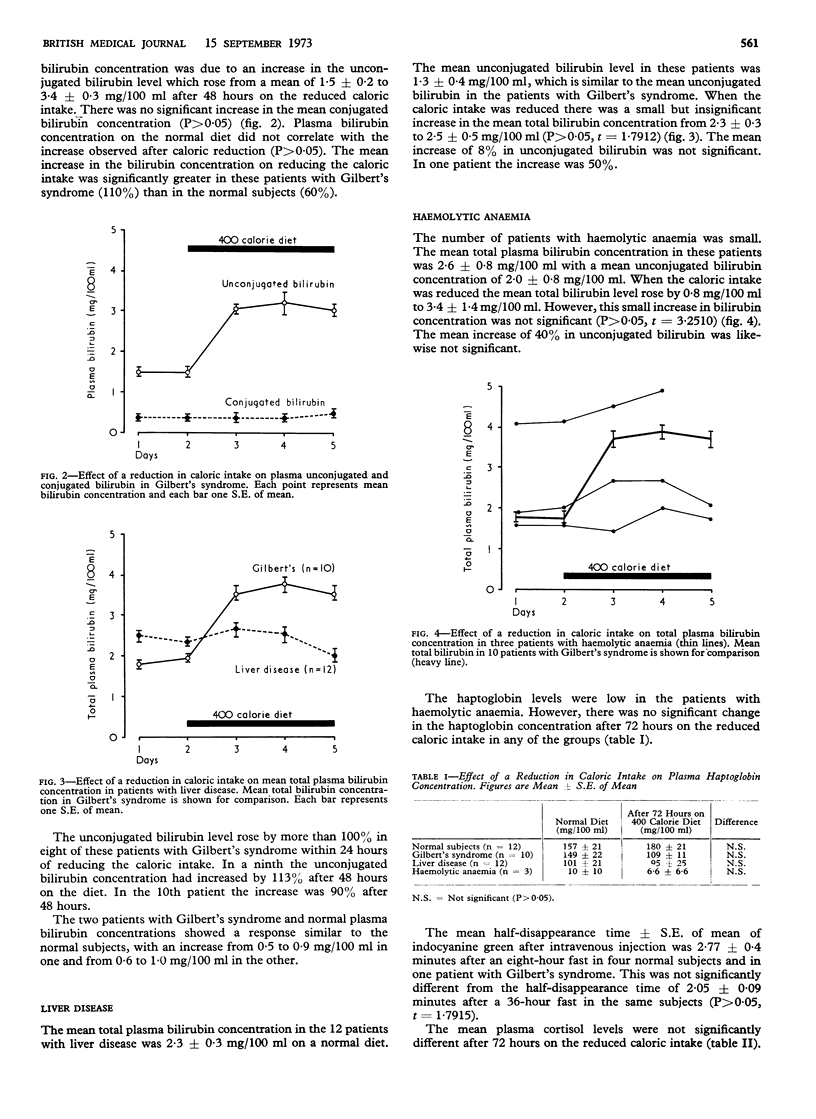
The increase in unconjugated bilirubin was signficantly greater in Gilbert's syndrome than in normals but only when the initial bilirubin concentration was raised. It was usually seen within 24 hours of reducing the caloric intake. An increase of 100% or more suggests that unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia is due to Gilbert's syndrome. In the normal subjects the unconjugated bilirubin level did not exceed 1·0 mg/100 ml.
The increase in unconjugated bilirubin concentration on reducing the caloric intake may be due to decreased hepatic bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronyl transferase activity, which was shown to be present in seven rats starved for 72 hours. The effect of a 400 calorie diet for 24 hours on the unconjugated bilirubin level may distinguish Gilbert's syndrome from other causes of unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARIAS I. M., LONDON I. M. Bilirubin glucuronide formation in vitro; demonstration of a defect in Gilbert's disease. Science. 1957 Sep 20;126(3273):563–564. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3273.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLING B. H., WILLIAMS R., RICHARDS T. G. DEFECTS IN HEPATIC TRANSPORT OF BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL HYPERBILIRUBINAEMIA: AN ANALYSIS OF PLASMA BILIRUBIN DISAPPEARANCE CURVES. Clin Sci. 1964 Oct;27:245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. F., Kyle L. H., Canary J. J. Comparative effects of caloric restriction and metabolic acceleration on body composition in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):273–278. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Bloomer J. R., Howe R. B., Berlin N. I. Constitutional hepatic dysfunction (Gilbert's syndrome). A new definition based on kinetic studies with unconjugated radiobilirubin. Am J Med. 1970 Sep;49(3):296–305. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Billing B. H., Heirwegh K. P. Determination of bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity in needle-biopsy specimens of human liver. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Jul;29(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Billing B. H. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 5;280(23):1266–1271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906052802303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Sherlock S. Treatment of Gilbert's syndrome with phenobarbitone. Lancet. 1970 Jun 27;1(7661):1359–1361. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Barrett P. V., Rodkey F. L., Berlin N. I. Studies on the mechanism of fasting hyperbilirubinemia. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):479–487. doi: 10.21236/ad0740975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERRICK G. R., STEIN S. W., LEEVY C. M., DAVIDSON C. S. Indocyanine green: observations on its physical properties, plasma decay, and hepatic extraction. J Clin Invest. 1960 Apr;39:592–600. doi: 10.1172/JCI104072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsher B. F., Rickard D., Redeker A. G. The reciprocal relation between caloric intake and the degree of hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 23;283(4):170–172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007232830403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischner G., Robbins J., Arias I. M. Immunological studies of Y protein. A major cytoplasmic organic anion-binding protein in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI106856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B., NYMAN M. Studies on the serum haptoglobin level in hemoglobinemia and its influence on renal excretion of hemoglobin. Blood. 1957 Jun;12(6):493–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Two hepatic cytoplasmic protein fractions, Y and Z, and their possible role in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin, sulfobromophthalein, and other anions. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2156–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAUELSSON M., NOSSLIN B., SJOELIN S. PLASMA BILIRUBIN DETERMINATION IN THE NEWBORN INFANT. A METHODOLOGICAL STUDY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE INFLUENCE OF HEMOLYSIS. Pediatrics. 1965 Jun;35:925–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Poppenhausen R. B., Ho W. K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science. 1972 Jul 7;177(4043):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4043.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEMSTSMA K., HOTTINGER G. C., DEGRAFF A. C., Jr, CREECH O., Jr The estimation of hepatic blood flow using indocyanine green. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1960 Mar;110:353–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


