Abstract
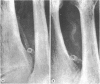
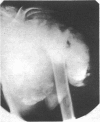
An objective radiographic study of erosions, fractures, and periarticular and vascular calcification was made in a series of 135 patients over 10 years of maintenance haemodialysis therapy. The four lesions progressed at different rates, consistent with variation in the response of tissues to a changing biochemical milieu and deficiency in vitamin D metabolites. The half time for development of individual radiographic signs was 3·4 years for vascular calcification, 9 years for fractures, 16 years for periarticular calcification, and 22·9 years for erosions. Calcification of the dorsalis pedis artery seen as a developing ring or tube was an early and valuable sign of disturbed calcium metabolism. In these patients renal osteodystrophy is a chronic condition with a prolonged time course.
Full text
PDF
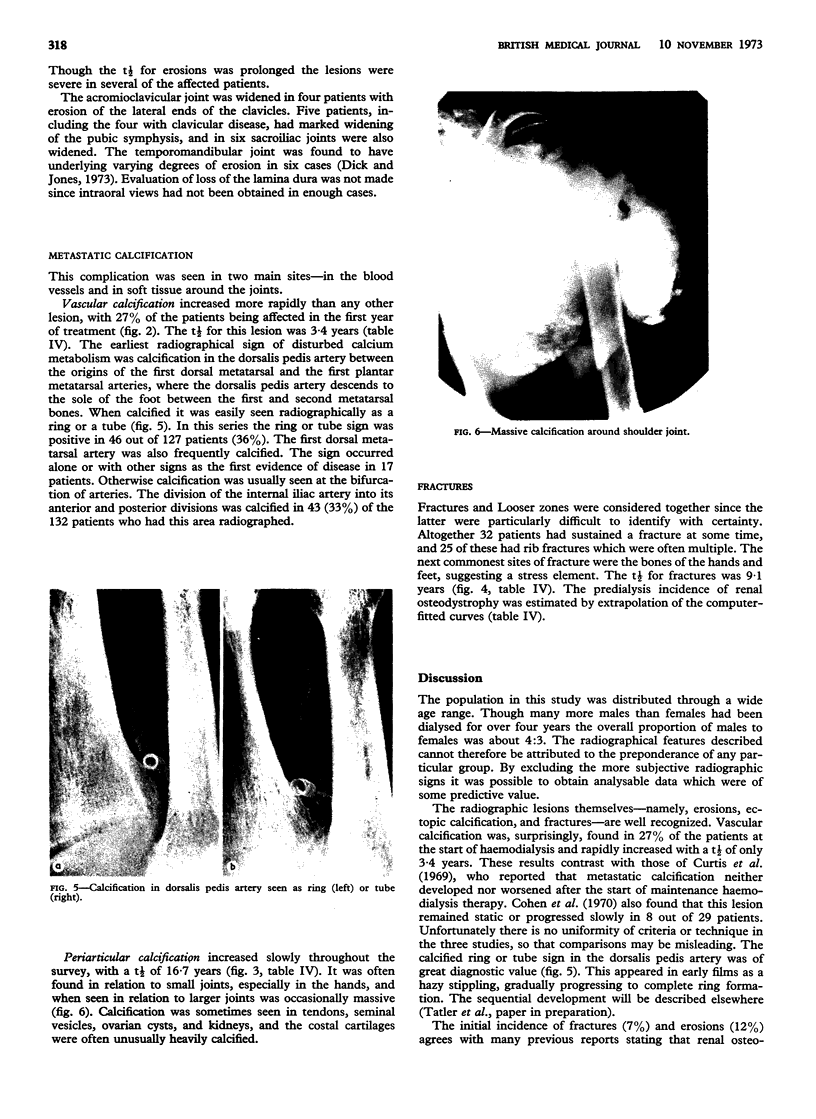

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baillod R. A., Ku G., Moorhead J. F. Home dialysis in children and adolescents. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1972;9:335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Cohen G. F., Ahad V., Kaye M. Renal osteodystrophy in patients on chronic haemodialysis. A radiological study. Clin Radiol. 1970 Apr;21(2):124–134. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(70)80099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craswell P. W., Hird V. M., Judd P. A., Baillod R. A., Varghese Z., Moorhead J. F. Plasma renin activity and blood pressure in 89 patients receiving maintenance haemodialysis therapy. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 30;4(5843):749–753. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5843.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick R., Jones D. N. Temporo-mandibular joint changes in patients undergoing chronic haemodialysis. Clin Radiol. 1973 Jan;24(1):72–76. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(73)80120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle F. H. Radiological patterns of bone disease associated with renal glomerular failure in adults. Br Med Bull. 1972 Sep;28(3):220–224. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzler A. M., Jaffe H. L. Osseous findings in chronic renal insufficiency in adults. Am J Pathol. 1941 May;17(3):293–302.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. Hemodialysis in the home--13 months' experience. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Feb;64(2):276–283. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-64-2-276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordan J. L., Page J., Kerr D. N., Walls J., Moorhead J., Crockett R. E., Franz H., Ritz E. Hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure and dialysis osteodystrophy. Q J Med. 1970 Jul;39(155):359–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt A. M., Massry S. G., Winfield A. C., DePalma J. R., Gordon A. Disordered calcium and phosphorus metabolism during maintenance hemodialysis. Correlation of clinical, roentgenographic and biochemical changes. Am J Med. 1971 Sep;51(3):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui J., Kerr D. N. Complications of renal failure and their response to dialysis. Br Med Bull. 1971 May;27(2):153–159. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin G., Klenerman L., Darby A., Bansal S. Tumoral calcinosis in England. Br Med J. 1973 Jan 20;1(5846):147–149. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5846.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese Z., Moorhead J. F., Tatler G. L., Baillod R. A., Wills M. R. Plasma hydroxyproline in renal osteodystrophy. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1973;10(0):187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing A. J. Optimum calcium concentration of dialysis fluid for maintenance haemodialysis. Br Med J. 1968 Oct 19;4(5624):145–149. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5624.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]