Abstract
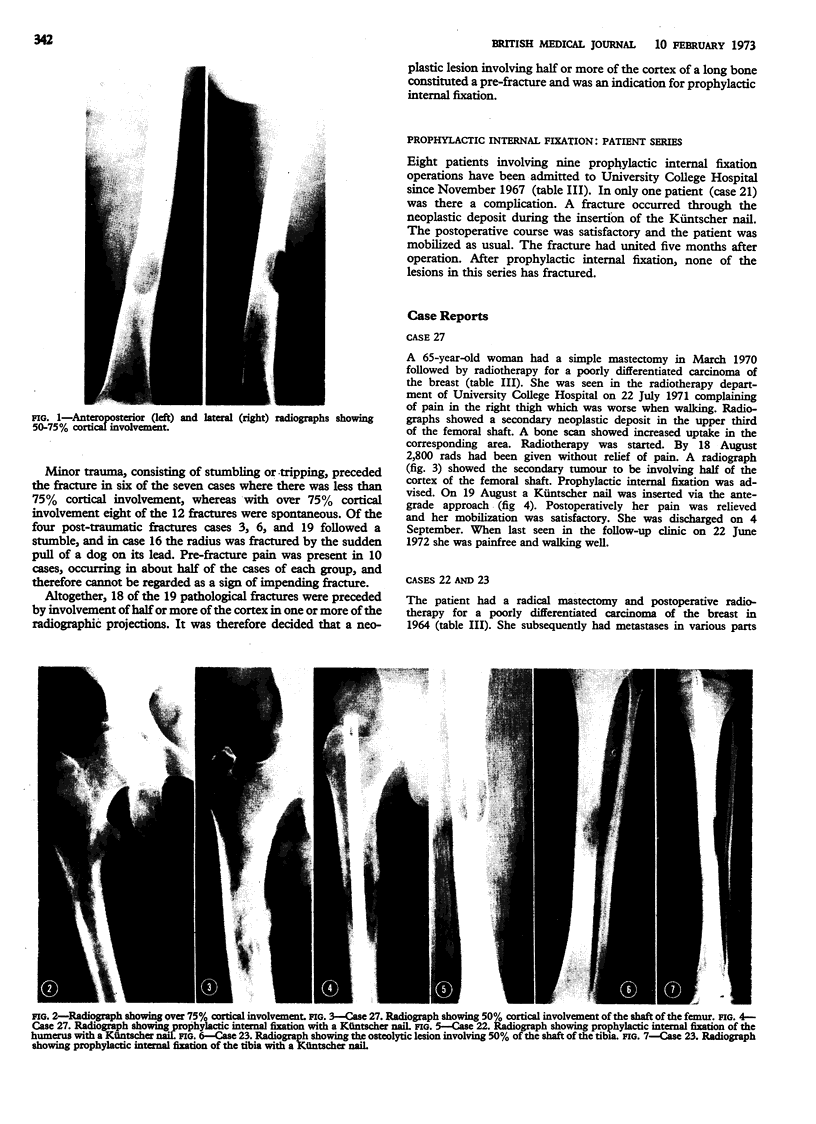
The notes and radiographs of 19 patients who had pathological fractures of long bones due to secondary neoplastic deposits were reviewed. Involvement of over half of the cortex is recommended as an indication for prophylactic internal fixation to prevent the development of a pathological fracture. Eight patients were treated successfully in this way. A notable secondary effect of prophylactic internal fixation was the considerable reduction in pain at the site of the lesion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BREMNER R. A., JELLIFFE A. M. The management of pathological fracture of the major long bones from metastatic cancer. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1958 Nov;40-B(4):652–659. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.40B4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coran A. G., Banks H. H., Aliapoulios M. A., Wilson R. E. The management of pathologic fractures in patients with metastatic carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1968 Dec;127(6):1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish F. F., Murray J. A. Surgical treatment for secondary neoplastic fractures. A retrospective study of ninety-six patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Jun;52(4):665–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]