Abstract
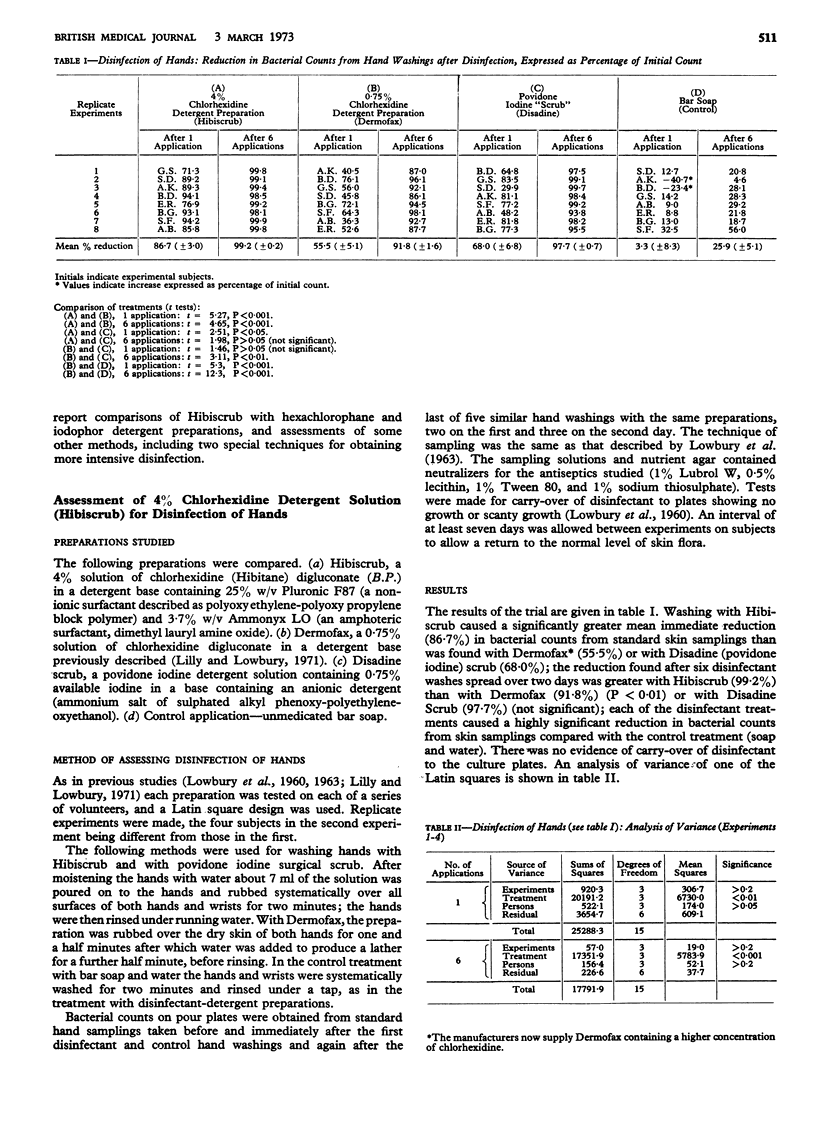
In a comparison of three antiseptic detergent preparations for hand washing, Hibiscrub, a 4% chlorhexidine detergent solution, caused a significantly greater estimated immediate reduction of skin flora (86·7% ± 3·0) than was obtained with Dermofax, a 0·75% chlorhexidine detergent solution (55·5% ± 5·1), or with Disadine scrub, a povidone iodine detergent preparation (68% ± 6·8). After six applications the mean estimated reductions of skin flora were 99·2% ± 0·2 for Hibiscrub, 97·7% ± 0·7 for povidone iodine, and 91·8% ± 1·6 for Dermofax.
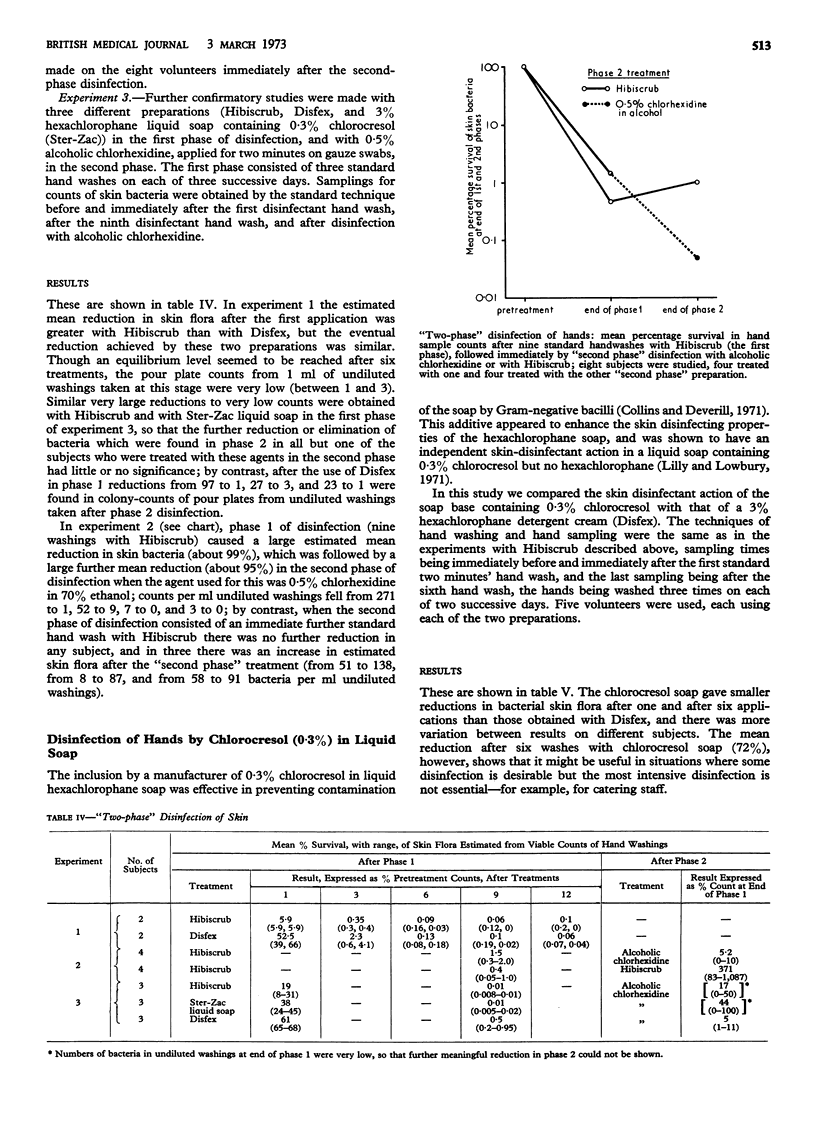
After a series of hand washings with Hibiscrub, as with a hexachlorophane detergent preparation, a further large reduction of skin flora, shown by bacterial counts of hand sampling, was obtained by a second phase of disinfection consisting of two minutes' application on gauze swabs of 0·5% chlorhexidine digluconate in 70% ethanol; a further wash with Hibiscrub, in place of alcoholic chlorhexidine, for the second phase of disinfection caused an increase rather than a reduction in the yield of bacteria on skin sampling. Unlike this “two-phase” disinfection, the application for 30 minutes of compresses soaked in 10% aqueous povidone iodine or in 0·5% aqueous chlorhexidine digluconate did not cause a greater reduction in skin flora than that obtained by the conventional two minutes' application on gauze of 0·5% chlorhexidine in 70% ethanol.
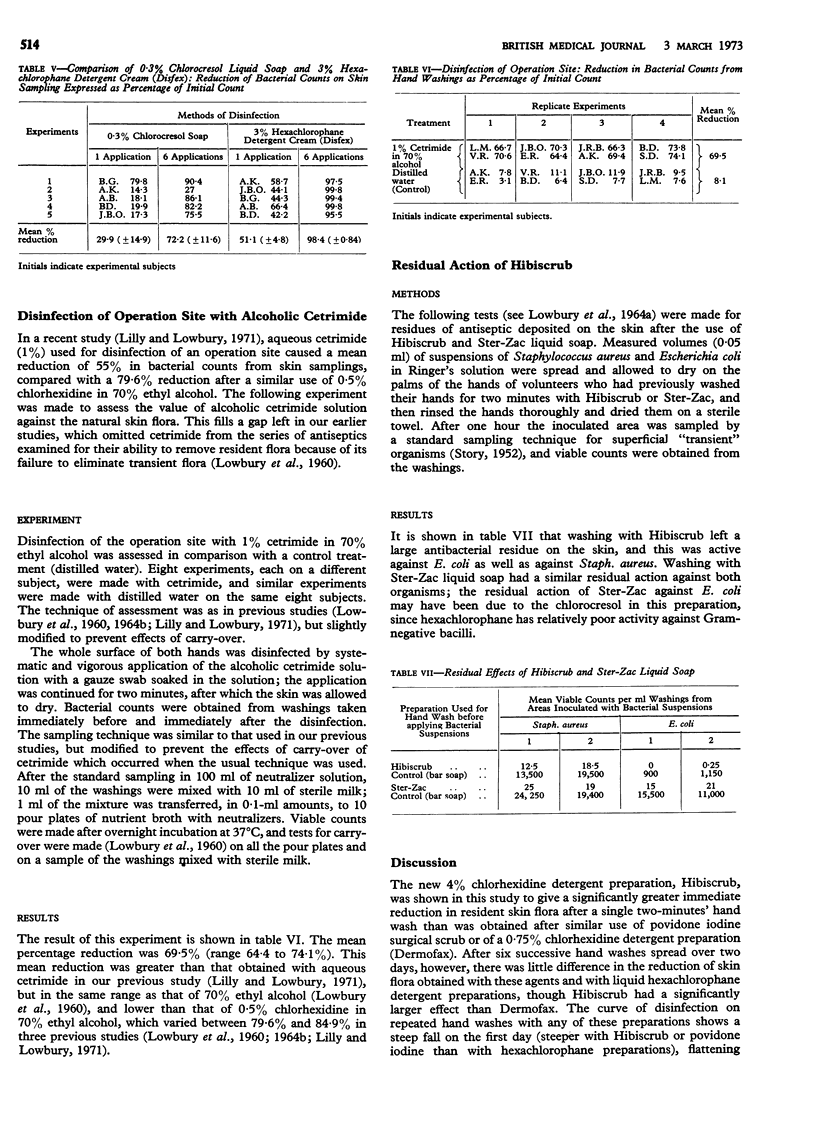
Chlorocresol (0·3%) liquid soap (the base used for Ster-Zac liquid hexachlorophane soap) caused a mean reduction of skin flora when used for hand washing of 29% after one application and 72% after six applications spread over two days. This formulation, though less active and more variable as a detergent skin antiseptic than chlorhexidine, hexachlorophane, or povidone iodine detergent preparations, is an inexpensive disinfectant soap which could be useful in catering establishments. Alcoholic cetrimide applied as for disinfection of an operation site caused a reduction of skin flora greater than that shown by aqueous cetrimide but comparable to that shown by 70% ethyl alcohol in previous experiments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curley A., Kimbrough R. D., Hawk R. E., Nathenson G., Finberg L. Dermal absorption of hexochlorophane in infants. Lancet. 1971 Aug 7;2(7719):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewett S. E., Tuke W., Payne D. J., Verdon P. E. Skin distribution of Clostridium welchii: use of iodophor as sporicidal agent. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1172–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forfar J. O., Gould J. C., Maccabe A. F. Effect of hexachlorophane on incidence of staphylococcal and gram-negative infection in the newborn. Lancet. 1968 Jul 27;2(7561):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92618-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. DISINFECTION OF HANDS: REMOVAL OF TRANSIENT ORGANISMS. Br Med J. 1964 Jul 25;2(5403):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5403.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. Disinfection of the skin of operation sites. Br Med J. 1960 Oct 8;2(5205):1039–1044. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5205.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. METHODS FOR DISINFECTION OF HANDS AND OPERATION SITES. Br Med J. 1964 Aug 29;2(5408):531–536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5408.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A. Disinfection of the hands of surgeons and nurses. Br Med J. 1960 May 14;1(5184):1445–1450. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5184.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J. Disinfection of the skin: an assessment of some new preparations. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 18;3(5776):674–676. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5776.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORY P. Testing of skin disinfectants. Br Med J. 1952 Nov 22;2(4794):1128–1130. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4794.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


