Abstract
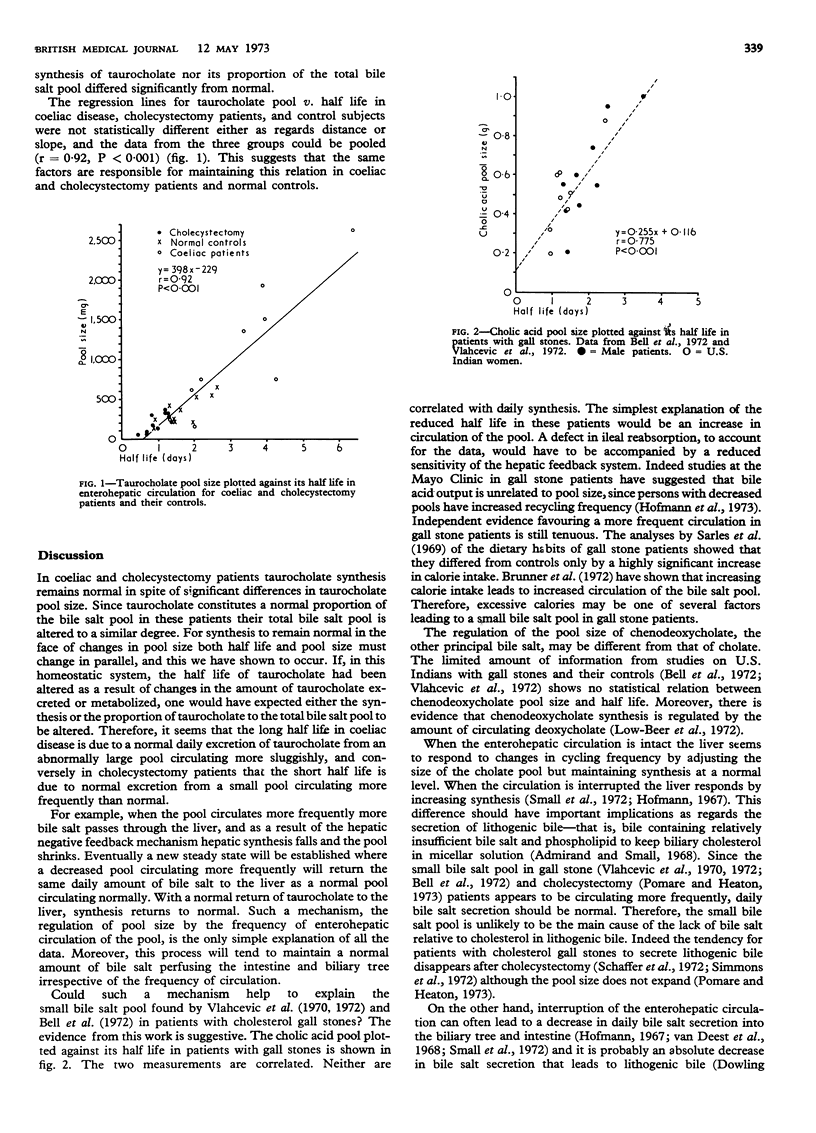
When the enterohepatic circulation is intact the size of the bile salt pool is largely determined by the frequency of its enterohepatic circulation. This hypothesis, derived from studies of cholate kinetics in coeliac, cholecystectomy, and gall stone patients, represents the simplest interpretation of the data. A corollary is that daily cholate secretion is likely to be normal in these conditions and that therefore the propensity of bile to form cholesterol gall stones is not likely to be directly related to bile salt pool size.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admirand W. H., Small D. M. The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1043–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI105794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austad W. I., Lack L., Tyor M. P. Importance of bile acids and of an intact distal small intestine for fat absorption. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. S., Eastwood M. A. Studies on the quantitative distribution of bile salts along the rat small intestine under varying dietary regimes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 10;152(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMagno E. P., Go W. L., Summerskill W. H. Impaired cholecystokinin-pancreozymin secretion, intraluminal dilution, and maldigestion of fat in sprue. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jul;63(1):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Bell G. D., White J. Lithogenic bile in patients with ileal dysfunction. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):415–420. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Metzger A. L., Adler R. D. Mechanisms of lithogenic bile formation in American Indian women with cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3026–3043. doi: 10.1172/JCI107130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. I. Cholylglycine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1889–1897. doi: 10.1172/JCI106991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Northfield T. C., Thistle J. L. Can a cholesterol-lowering diet cause gallstones? N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):46–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Kottke B. A., Poley J. R. Methods for the description of bile acid kinetics in man. Methods Med Res. 1970;12:149–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The syndrome of ileal disease and the broken enterohepatic circulation: cholerheic enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Heaton S. T., Read A. E. Gallbladder inertia and sluggish enterohepatic circulation of bile-salts in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1971 May 15;1(7707):991–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Pomare E. W., Read A. E. The effect of coeliac disease upon bile salts. Gut. 1973 Mar;14(3):204–208. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Pomare E. W., Morris J. S. Control of bile salt synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 16;238(85):215–216. doi: 10.1038/newbio238215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbach E. H. Hepatic synthesis of bile acids. Biochemical steps and mechanisms of rate control. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):478–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles H., Chabert C., Pommeau Y., Save E., Mouret H., Gérolami A. Diet and cholesterol gallstones. A study of 101 patients with cholelithiasis compared to 101 matched controls. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Aug;14(8):531–537. doi: 10.1007/BF02232927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Braasch J. W., Small D. M. Bile composition at and after surgery in normal persons and patients with gallstones. Influence of cholecystectomy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 28;287(26):1317–1322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212282872603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons F., Ross A. P., Bouchier I. A. Alterations in hepatic bile composition after cholecystectomy. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(3):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Dowling R. H., Redinger R. N. The enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):552–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Deest B. W., Fordtran J. S., Morawski S. G., Wilson J. D. Bile salt and micellar fat concentration in proximal small bowel contents of ileectomy patients. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1314–1324. doi: 10.1172/JCI105823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Bell C. C., Jr, Buhac I., Farrar J. T., Swell L. Diminished bile acid pool size in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1970 Aug;59(2):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Bell C. C., Jr, Gregory D. H., Buker G., Juttijudata P., Swell L. Relationship of bile acid pool size to the formation of lithogenic bile in female Indians of the southwest. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jan;62(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


