Abstract
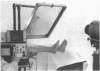
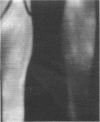
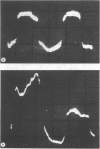
The possibility that subclinical increased heat of the limb may be an early and reliable sign in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis is being investigated using thermography. Of the 35 cases studied 17 have had early deep venous thrombosis confirmed on phlebography. Of these, 16 cases have been previously diagnosed using thermography.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES R. B. THERMOGRAPHY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Oct 9;121:34–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb13683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COON W. W., COLLER F. A. Clinicopathologic correlation in thromboembolism. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1959 Sep;109:259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COON W. W., WILLIS P. W. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: prediction, prevention and treatment. Am J Cardiol. 1959 Nov;4:611–621. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(59)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanc C., Kakkar V. V., Clarke M. B. The detection of venous thrombosis of the legs using 125-I-labelled fibrinogen. Br J Surg. 1968 Oct;55(10):742–747. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800551007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambie J. M., Mahaffy R. G., Barber D. C., Karmody A. M., Scott M. M., Matheson N. A. Diagnostic accuracy in venous thrombosis. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 18;2(5702):142–143. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5702.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrell M. T., Dunnill M. S. The post-mortem incdence of pulmonary embolism in a hospital population. Br J Surg. 1968 May;55(5):347–352. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800550506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negus D., Pinto D. J., Brown N. 125-I-labelled fibrinogen in the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis. Acta Chir Belg. 1969 Oct;68(7):507–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negus D., Pinto D. J., Le Quesne L. P., Brown N., Chapman M. 125-I-labelled fibrinogen in the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis and its correlation with phlebography. Br J Surg. 1968 Nov;55(11):835–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S., GALLAGHER N. G. Prevention of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in injured patients. A trial of anticoagulant prophylaxis with phenindione in middle-aged and elderly patients with fractured necks of femur. Lancet. 1959 Dec 5;2(7110):981–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S. Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Their prevention by oral anticoagulants. Am J Med. 1962 Nov;33:703–716. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHLAND H., GOLDBERG L. M. PULMONARY EMBOLISM: A COMMONLY MISSED CLINICAL ENTITY. Dis Chest. 1964 May;45:533–536. doi: 10.1378/chest.45.5.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]