Abstract
During the first few weeks of life many preterm infants develop flattened heads. We have shown that this deformity can be reduced by nursing preterm infants on soft, air filled mattresses of the type used for detecting apnoea.
Full text
PDF
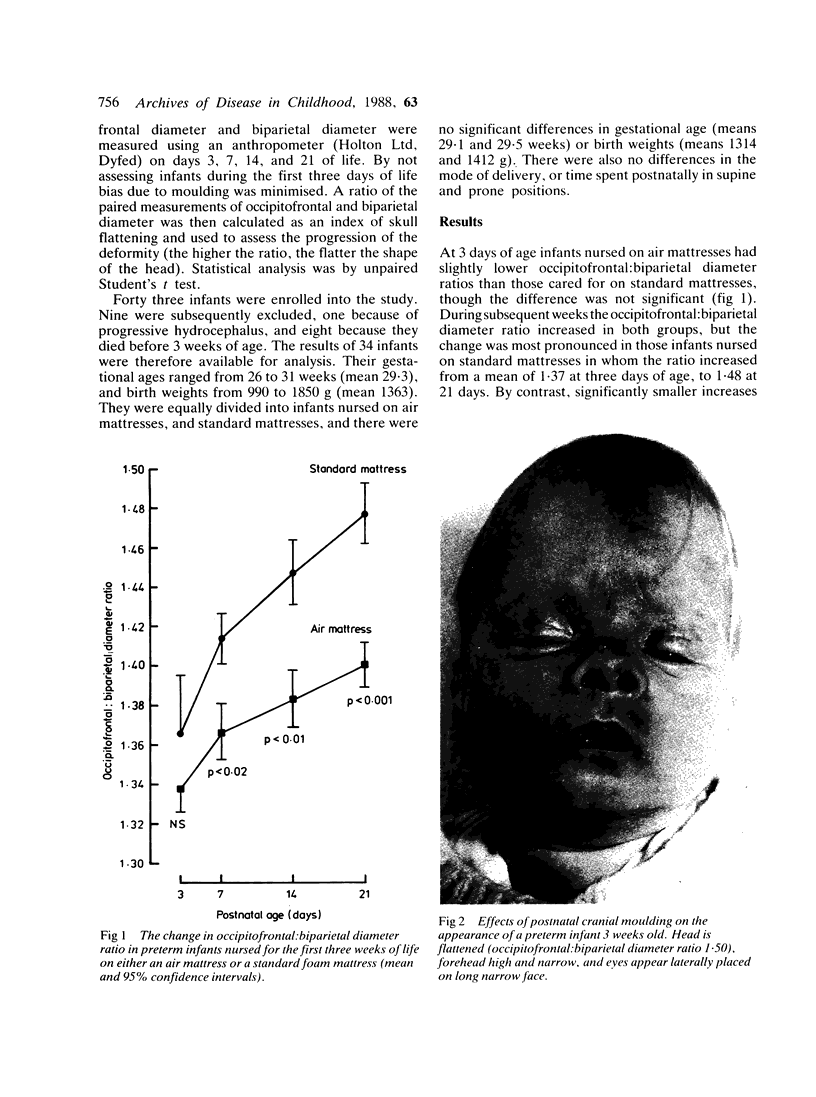

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum J. D., Searls D. Head shape and size of pre-term low-birthweight infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1971 Oct;13(5):576–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1971.tb08320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budreau G. K. Postnatal cranial molding and infant attractiveness: implications for nursing. Neonatal Netw. 1987 Apr;5(5):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer L. I., Pierpont M. E. Rocking waterbeds and auditory stimuli to enhance growth of preterm infants. Preliminary report. J Pediatr. 1976 Feb;88(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largo R. H., Duc G. Head growth and changes in head configuration in healthy preterm and term infants during the first sex months of life. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1978 Feb;32(6):431–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden D. J. Reduction of head flattening in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1980 Aug;22(4):507–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1980.tb04356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]