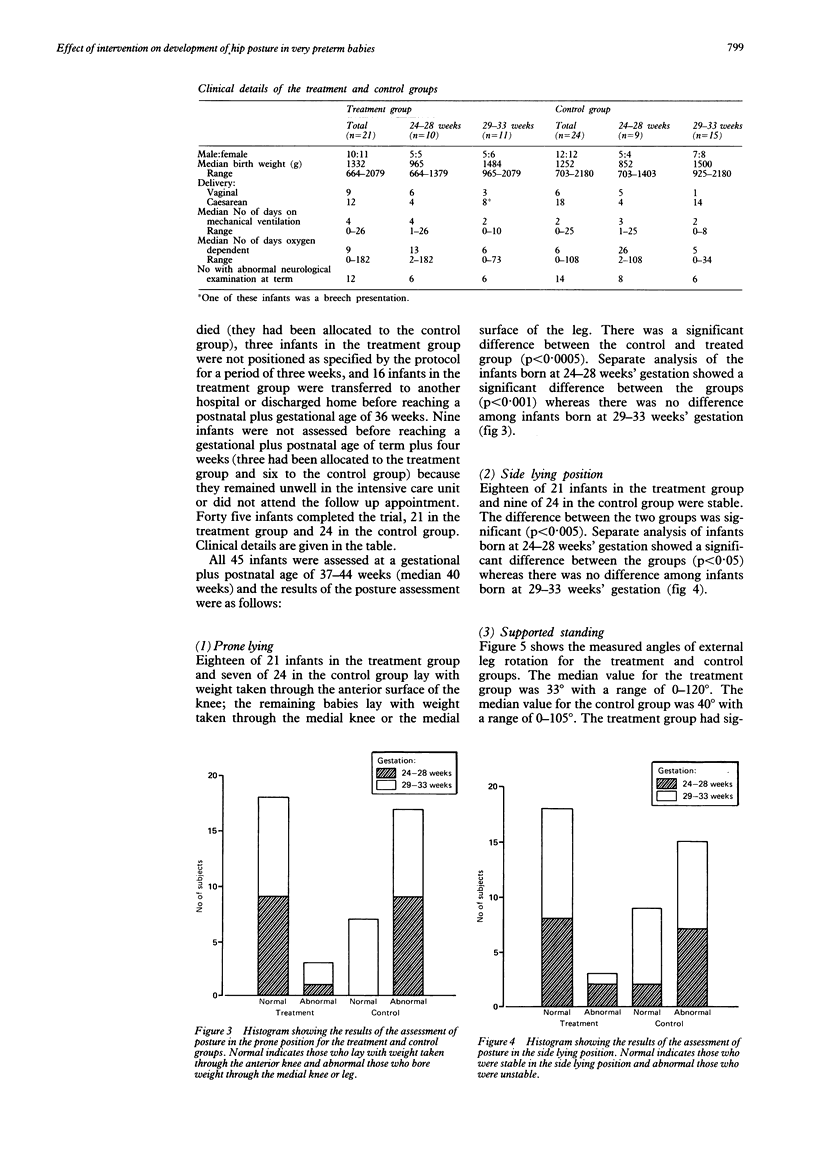
Abstract
Preterm babies are physiologically hypotonic, which causes their posture to be flattened when lying in the prone position. This flattened posture may persist beyond term. In a prospective, randomised, controlled, double blind trial of postural support carried out on 45 babies born at less than 33 weeks of gestation, we showed that infants positioned with specific hip support during the period of intensive care had significantly fewer features of flattened posture at the age equivalent to term.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grenier A. Prévention des déformations précoces de hanche chez les nouveau-nés à cerveau lésé. Maladie de Little sans ciseaux? Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1988 Jun;35(6):423–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J. L., Henderson-Smart D. J., Edwards D. A. A longitudinal study of early leg postures of preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990 Feb;32(2):151–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1990.tb16914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Reynolds E. O., Lipscomb A. P. Outcome for infants of very low birthweight: survey of world literature. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1038–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A., Hope P. L., Hamilton P., Costello A. M., Baudin J., Bradford B., Amiel-Tison C., Reynolds E. O. Prediction in very preterm infants of satisfactory neurodevelopmental progress at 12 months. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1988 Feb;30(1):53–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1988.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabary J. C., Tabary C., Tardieu C., Tardieu G., Goldspink G. Physiological and structural changes in the cat's soleus muscle due to immobilization at different lengths by plaster casts. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):231–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Updike C., Schmidt R. E., Macke C., Cahoon J., Miller M. Positional support for premature infants. Am J Occup Ther. 1986 Oct;40(10):712–715. doi: 10.5014/ajot.40.10.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]