Abstract
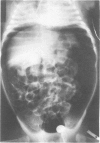
Three cases of gastroduodenal perforation and one case of ulceration and extreme thinning of the gastric wall occurred in preterm babies treated with dexamethasone for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. This complication of treatment with steroids has not to our knowledge previously been described in preterm infants. Urgent abdominal paracentesis was an essential part of the resuscitation in these cases, and this potentially serious side effect should be considered in all babies treated with steroids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dayton M. T., Kleckner S. C., Brown D. K. Peptic ulcer perforation associated with steroid use. Arch Surg. 1987 Mar;122(3):376–380. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400150130025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debas H. T., Cohen M. M., Holubitsky I. B., Harrison R. C. Caffeine-stimulated acid and pepsin secretion: dose-response studies. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(5):453–457. doi: 10.3109/00365527109180725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadul C. E., Lemann W., Thaler H. T., Posner J. B. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract in patients receiving steroids for neurologic disease. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):348–352. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss C., Schneider A. T., Chiaramonte L. T. Perforated gastric ulcer in an asthmatic treated with theophylline and steroids. Case report and literature review. Ann Allergy. 1986 Mar;56(3):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ReMine S. G., McIlrath D. C. Bowel perforation in steroid-treated patients. Ann Surg. 1980;192(4):581–586. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198010000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]