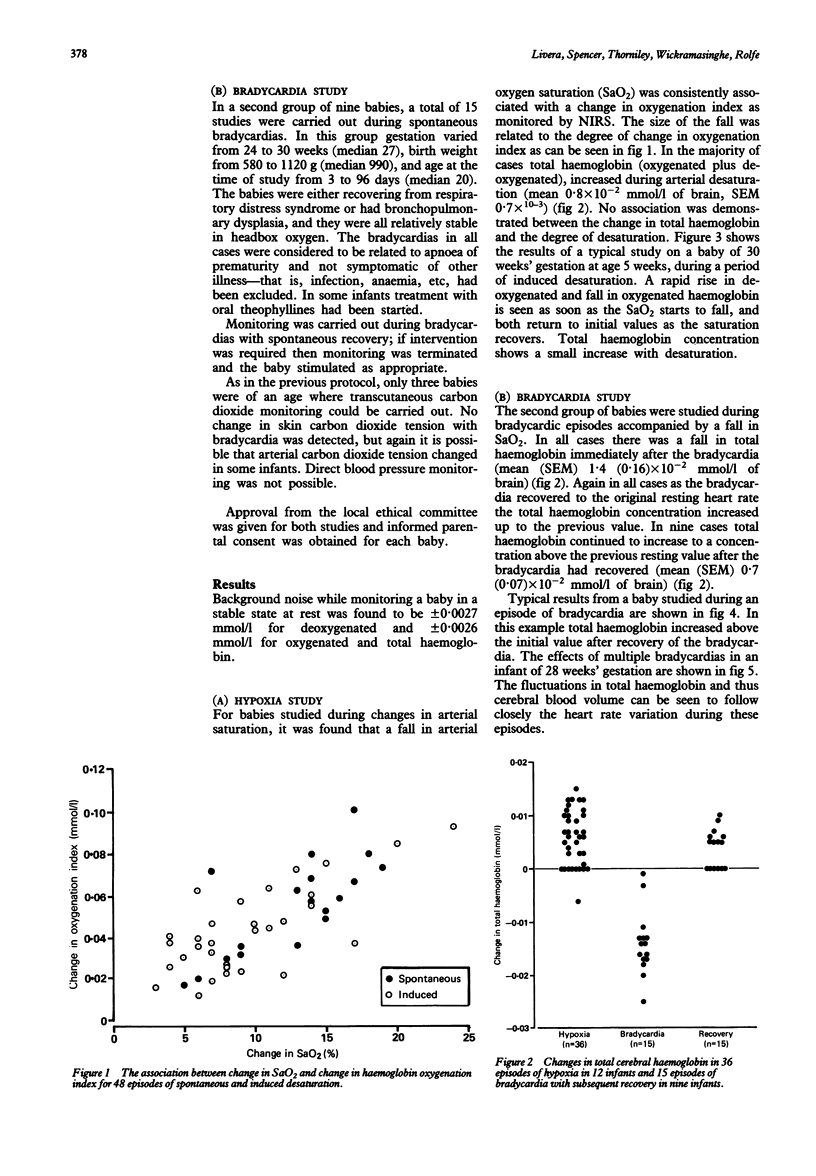
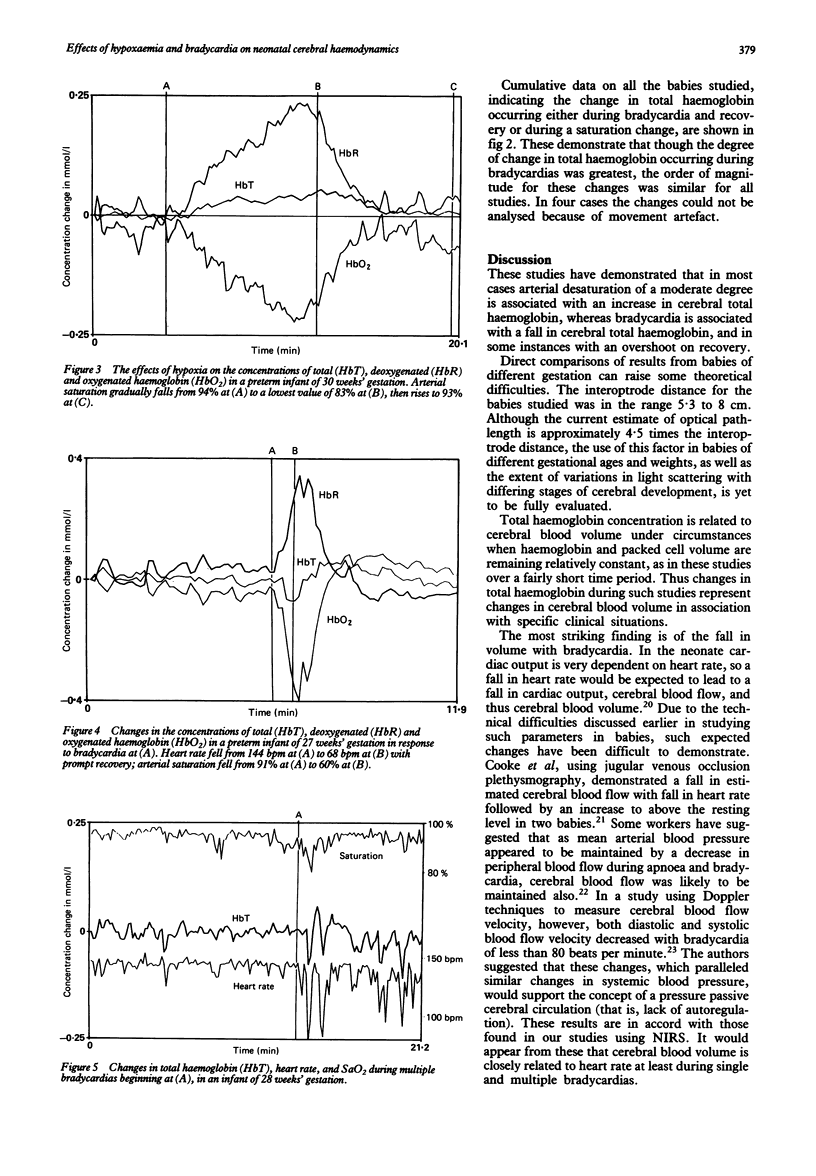
Abstract
Near infrared spectroscopy has been used to assess the effects of bradycardia and hypoxia on the cerebral circulation in the premature neonate. The technique is well tolerated and can be applied in almost any infant. Continuous monitoring of changes in cerebral oxygenated, deoxygenated, and total haemoglobin is possible. Total haemoglobin is analogous to cerebral blood volume; thus information on circulatory changes as well as oxygenation state can be obtained. Twenty five babies had cerebral monitoring carried out using this technique. During episodes of hypoxia, both spontaneous and induced, impairment of haemoglobin oxygenation within the brain was detected together with an overall increase in the total mean haemoglobin concentration, which was 0.8 x 10(-2) mmol/l. Bradycardia with apnoea also led to impairment of cerebral oxygenation, and to a rapid fall in the concentration of total mean haemoglobin to 1.4 x 10(-2) mmol/l, which was followed in some cases by an increase to above the resting value on recovery of the heart rate to a mean of 0.7 x 10(-2) mmol/l. These disturbances to total haemoglobin concentration represent abnormalities of cerebral blood volume that may be implicated in the pathogenesis of neonatal cerebral injury.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brazy J. E., Lewis D. V., Mitnick M. H., Jöbsis vander Vliet F. F. Noninvasive monitoring of cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants: preliminary observations. Pediatrics. 1985 Feb;75(2):217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert S. A., Hoskins E. M., Fong K. W., Forsyth S. C. Etiological factors associated with the development of periventricular leukomalacia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 Mar;76(2):254–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. W. Early and late cranial ultrasonographic appearances and outcome in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Sep;62(9):931–937. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.9.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpy D. T., Cope M., van der Zee P., Arridge S., Wray S., Wyatt J. Estimation of optical pathlength through tissue from direct time of flight measurement. Phys Med Biol. 1988 Dec;33(12):1433–1442. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisen G. Cerebral blood flow in preterm infants during the first week of life. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Jan;75(1):43–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jöbsis F. F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science. 1977 Dec 23;198(4323):1264–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.929199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen N. A. The luxury-perfusion syndrome and its possible relation to acute metabolic acidosis localised within the brain. Lancet. 1966 Nov 19;2(7473):1113–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou H. C. Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage and intraventricular hemorrhage. A pathogenetic model. Arch Neurol. 1980 Sep;37(9):585–587. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500580081017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlow N., D'Souza S. W., Chiswick M. L. Neurodevelopmental outcome in babies weighing less than 2001 g at birth. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jun 20;294(6587):1582–1586. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6587.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Duncan C. C., Ehrenkranz R. A., Lange R. C., Taylor K. J., Kleinman C. S., Scott D. T., Sivo J., Gettner P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm neonate: timing and cerebral blood flow changes. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miall-Allen V. M., de Vries L. S., Whitelaw A. G. Mean arterial blood pressure and neonatal cerebral lesions. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):1068–1069. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., McMenamin J. B., Volpe J. J. Fluctuating cerebral blood-flow velocity in respiratory-distress syndrome. Relation to the development of intraventricular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 28;309(4):204–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307283090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., Volpe J. J. Episodes of apnea and bradycardia in the preterm newborn: impact on cerebral circulation. Pediatrics. 1985 Sep;76(3):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Crowe J., Wickramasinghe Y., Rolfe P. Non-invasive optical methods for the study of cerebral metabolism in the human newborn: a technique for the future? J Med Eng Technol. 1985 Jul-Aug;9(4):160–166. doi: 10.3109/03091908509032600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs C. N. Cardiovascular effects of apnoea in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jul;52(7):534–540. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.7.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trounce J. Q., Shaw D. E., Levene M. I., Rutter N. Clinical risk factors and periventricular leucomalacia. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Jan;63(1):17–22. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S., Cope M., Delpy D. T., Wyatt J. S., Reynolds E. O. Characterization of the near infrared absorption spectra of cytochrome aa3 and haemoglobin for the non-invasive monitoring of cerebral oxygenation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 30;933(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(88)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. S., Cope M., Delpy D. T., Wray S., Reynolds E. O. Quantification of cerebral oxygenation and haemodynamics in sick newborn infants by near infrared spectrophotometry. Lancet. 1986 Nov 8;2(8515):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90467-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


