Abstract
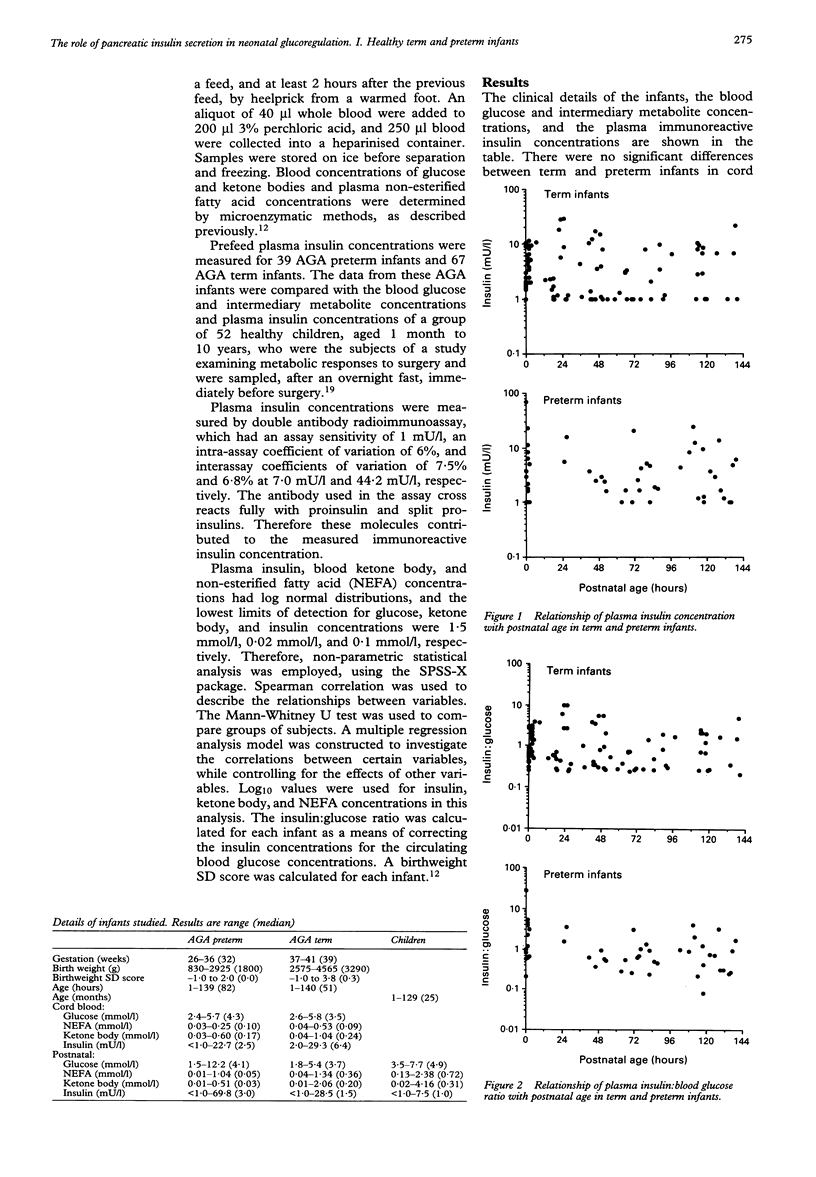
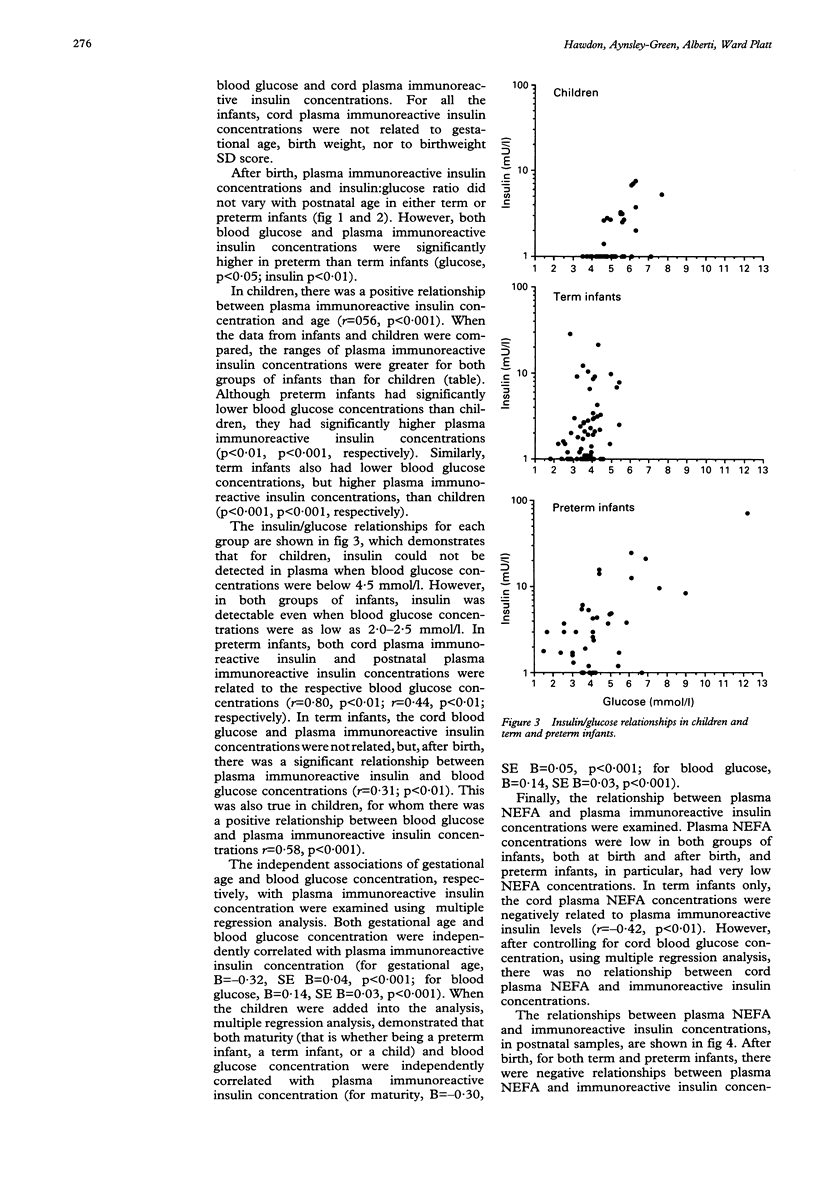
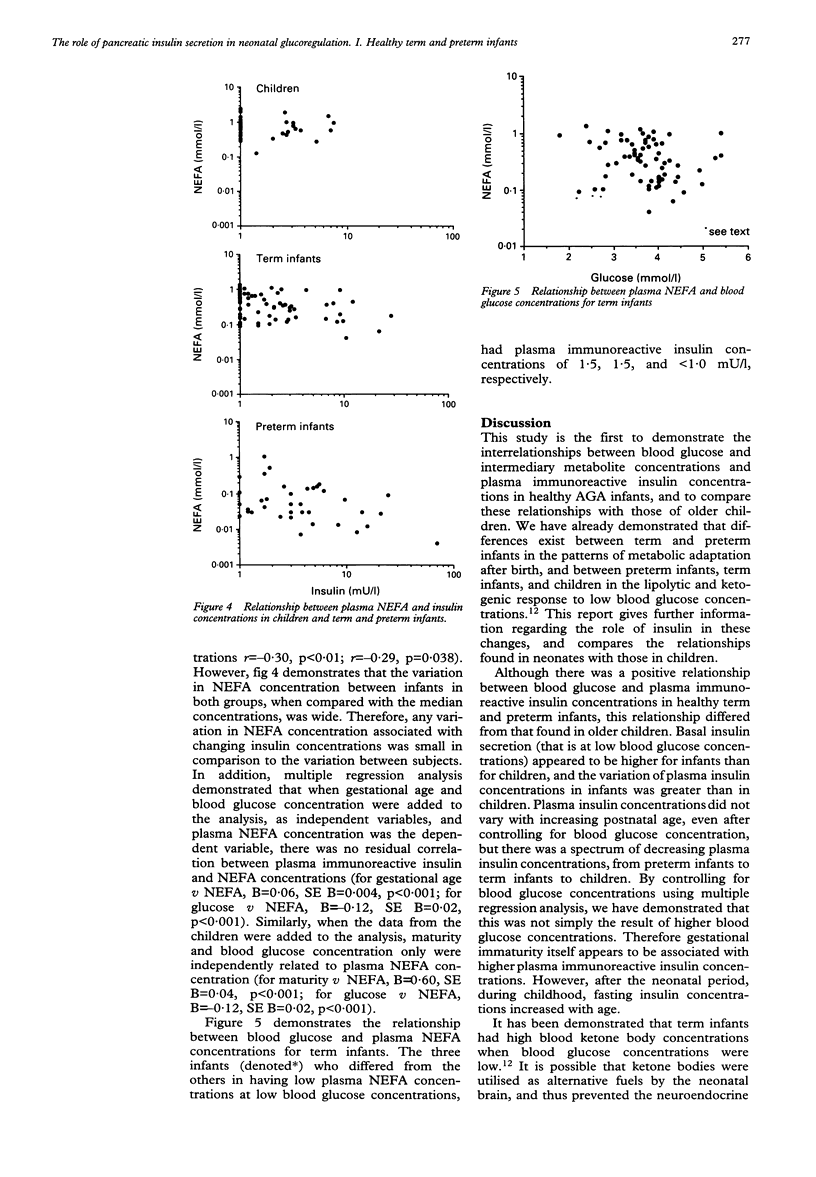
The glucoregulatory role of insulin in adult subjects is undisputed. However, less is known about the secretion of insulin and its actions in the neonatal period, either for healthy subjects, or for those at risk of disordered blood glucose homoeostasis. The relationships between blood glucose and plasma immunoreactive insulin concentrations were therefore examined in 52 healthy children (aged 1 month-10 years), 67 appropriate birth weight for gestational age (AGA) term infants, and 39 AGA preterm neonates. In children and AGA neonates, plasma immunoreactive insulin concentration was positively related to blood glucose concentration. However, although both groups of neonates had significantly lower blood glucose concentrations than children, plasma immunoreactive insulin concentrations were significantly higher in both term and preterm neonates, when compared with children. The variation in plasma immunoreactive insulin concentrations was greater for neonates than for children. These data suggest, that compared with older subjects, plasma immunoreactive insulin concentrations are high in newborn babies and that neonatal pancreatic insulin secretion is less closely linked to circulating blood glucose concentrations. There are important implications for the interpretation of studies in hypoglycaemic and hyperglycaemic neonates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aynsley-Green A., Jenkins P., Tronier B., Heding L. G. Plasma proinsulin and C-peptide concentrations in children with hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 May;73(3):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb17748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A. Metabolic and endocrine interrelations in the human fetus and neonate. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Feb;41(2 Suppl):399–417. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Gough M. H., Keeling J., Ashcroft S. J., Turner R. C., Baum J. D. Nesidioblastosis of the pancreas: definition of the syndrome and the management of the severe neonatal hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jul;56(7):496–508. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.7.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick S. K., Lewandowski C. Prolonged hyperinsulinism and hypoglycemia. In an asphyxiated, small for gestation infant. Case management and literature review. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1989 Dec;28(12):575–578. doi: 10.1177/000992288902801205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Leonard J. V. Hyperinsulinism in asphyxiated and small-for-dates infants with hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):311–313. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92685-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Leonard J. V., Teale D., Marks V., Williams D. M., Kennedy C. R., Hall M. A. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in small for dates babies. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Oct;65(10):1118–1120. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.10.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowett R. M., Tenenbaum D. Hepatic response to insulin in control of glucose kinetics in the neonatal lamb. Metabolism. 1987 Nov;36(11):1021–1026. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falorni A., Fracassini F., Massi-Benedetti F., Maffei S. Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in the newborn infant. Comparisons between the responses observed the first and seventh day of life to intravenous and oral glucose tolerance tests. Diabetes. 1974 Mar;23(3):172–178. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.3.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawdon J. M., Aynsley-Green A., Bartlett K., Ward Platt M. P. The role of pancreatic insulin secretion in neonatal glucoregulation. II. Infants with disordered blood glucose homoeostasis. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Mar;68(3 Spec No):280–285. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.3_spec_no.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawdon J. M., Ward Platt M. P., Aynsley-Green A. Patterns of metabolic adaptation for preterm and term infants in the first neonatal week. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Apr;67(4 Spec No):357–365. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.4_spec_no.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawdon J. M., Weddell A., Aynsley-Green A., Ward Platt M. P. Hormonal and metabolic response to hypoglycaemia in small for gestational age infants. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Mar;68(3 Spec No):269–273. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.3_spec_no.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G., Persson B., Stangenberg M. B-cell function in newborn infants of diabetic mothers. Diabetologia. 1980 Nov;19(5):427–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00281821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenka H. M., Seager J. Hyperinsulinism in asphyxiated and small-for-dates infants with hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1984 Oct 27;2(8409):975–975. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A. Ontogeny of gut hormones and hormone-related substances. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1989;351:80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb11215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Foster D. W. Hormonal control of ketogenesis. Biochemical considerations. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Apr;137(4):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. E., Brunner M. R., Duckworth W. C., Hooker C. S., Frank B. H. Receptor binding and biological potency of several split forms (conversion intermediates) of human proinsulin. Studies in cultured IM-9 lymphocytes and in vivo and in vitro in rats. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):13989–13994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccà L., Sherwin R., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of continuous physiologic hyperinsulinemia on glucose kinetics and counterregulatory hormones in normal and diabetic humans. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):849–857. doi: 10.1172/JCI109384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley H. J., Bassett J. M., Milner R. D. Control of carbohydrate metabolism in the fetus and newborn. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):37–43. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling M. A., Grajwer L. A., Leake R., Fisher D. A. Role of glucagon in perinatal glucose homeostasis. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1385–1386. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A., Anday E. K., Baker L., Delivoria-Papadopolous M. Metabolic fuel and hormone responses to fasting in newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1979 Nov;64(5):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple R. C., Carrington C. A., Luzio S. D., Owens D. R., Schneider A. E., Sobey W. J., Hales C. N. Insulin deficiency in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):293–295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Johnson P. C. Suppression of insulin release by fish-insulin-induced hypoglycaemia: with reference to the diagnosis of insulinomas. Lancet. 1973 Jun 30;1(7818):1483–1485. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91817-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward Platt M. P., Tarbit M. J., Aynsley-Green A. The effects of anesthesia and surgery on metabolic homeostasis in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr Surg. 1990 May;25(5):472–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(90)90553-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


