Abstract
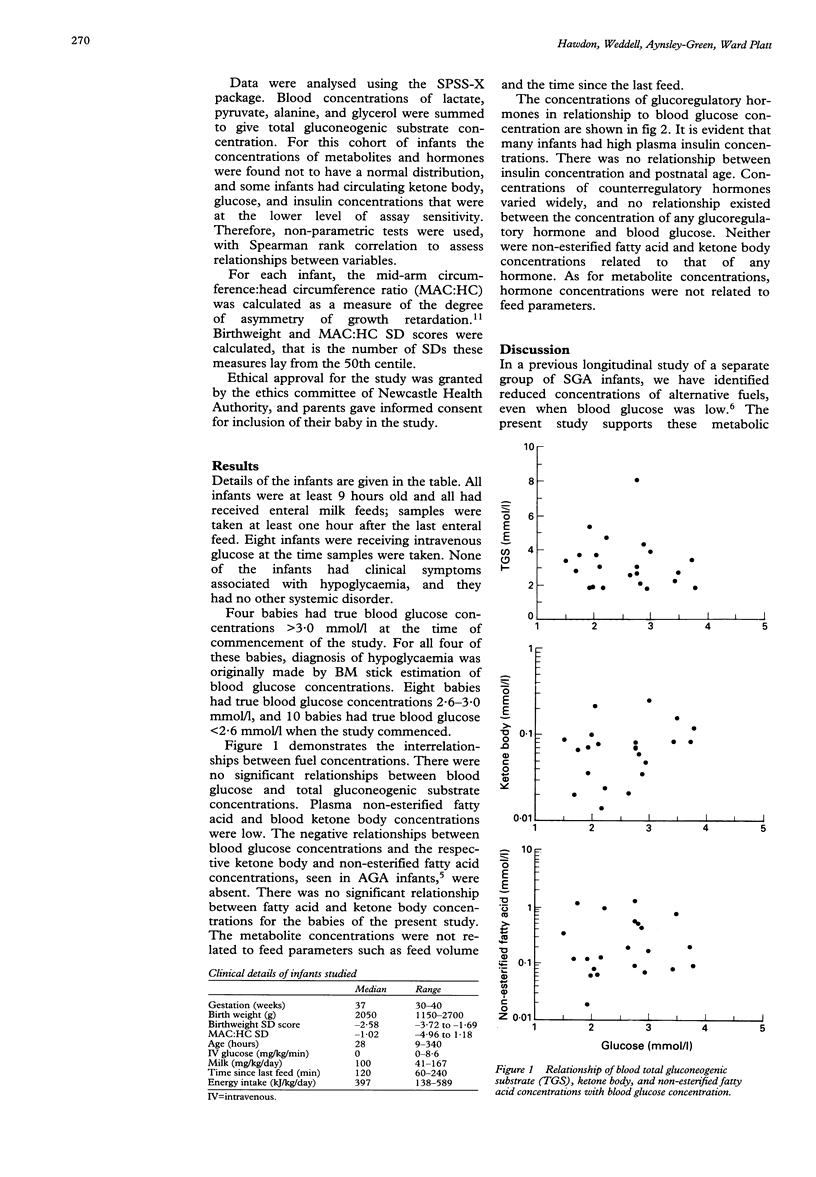
Little is known of the ability of hypoglycaemic infants who are small for gestational age (SGA) to mount the coordinated hormonal and metabolic counterregulatory response that is seen in healthy older subjects during glycopenia. This response was studied in 22 SGA infants (birth weight < 10th centile) by measuring the blood concentrations of glucose, intermediary metabolites, and glucoregulatory hormones. Plasma non-esterified fatty acid and blood ketone body concentrations were low, even when blood glucose concentrations were low. Plasma insulin and glucagon varied widely (< 1.0-53.1 mU/l and 16.6-87.1 pmol/l, respectively). Concentrations of noradrenaline and glucagon were raised, but cortisol and adrenaline were lower than those found in hypoglycaemic adults. There was no relationship between the concentration of any hormone and blood glucose concentration. We postulate that hypoglycaemia and the failure to mobilise alternative fuels in some SGA infants is secondary both to a poorly coordinated counterregulatory hormone response and to a peripheral insensitivity to the actions of the hormones. Those infants, who fail to mount a counterregulatory response, should be identified by accurate and reliable blood glucose monitoring, and an adequate exogenous supply of energy, either enteral or parenteral, should be ensured.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostakis D. E., Lardinois R. Urinary catecholamine excretion and plasma NEFA concentration in small-for-date infants. Pediatrics. 1971 Jun;47(6):1000–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick S. K., Lewandowski C. Prolonged hyperinsulinism and hypoglycemia. In an asphyxiated, small for gestation infant. Case management and literature review. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1989 Dec;28(12):575–578. doi: 10.1177/000992288902801205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Jenner D. A. Novel double-isotope technique for enzymatic assay of catecholamines, permitting high precision, sensitivity and plasma sample capacity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Nov;61(5):591–598. doi: 10.1042/cs0610591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Leonard J. V., Teale D., Marks V., Williams D. M., Kennedy C. R., Hall M. A. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in small for dates babies. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Oct;65(10):1118–1120. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.10.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowett R. M., Susa J. B., Oh W., Schwartz R. Glucose kinetics in glucose-infused small for gestational age infants. Pediatr Res. 1984 Jan;18(1):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerr H. G., Versmold H. T., Bidlingmaier F., Sippell W. G. Adrenocortical steroids in small-for-gestational-age term infants during the early neonatal period. Pediatr Res. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–118. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198902000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J., Davis J., Lorenzi M., Rizza R., Bohannon N., Karam J., Lewis S., Kaplan R., Schultz T., Cryer P. Hormonal mechanisms of recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):E380–E385. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.4.E380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. Gluconeogenesis in late fetal and early neonatal life. Biol Neonate. 1986;50(5):237–258. doi: 10.1159/000242605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawdon J. M., Ward Platt M. P., Aynsley-Green A. Patterns of metabolic adaptation for preterm and term infants in the first neonatal week. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Apr;67(4 Spec No):357–365. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.4_spec_no.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawdon J. M., Ward Platt M. P. Metabolic adaptation in small for gestational age infants. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Mar;68(3 Spec No):262–268. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.3_spec_no.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetenyi G., Jr, Cowan J. S. Glucoregulation in the newborn. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;58(8):879–888. doi: 10.1139/y80-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Murphy J. F., Dyas J., Robinson J. A., Riad-Fahmy D., Hughes I. A. Blood spot glucocorticoid concentrations in ill preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):1014–1018. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantto O., Lindbäck B., Aakvaag A., Damkjaer-Nielsen M., Pomoell U. M., Björkhem I. Assay of cortisol with a radioimmunoassay method calibrated by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. A Nordic collaborative study. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;43(5):433–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Bartolome J. V., Bartolome M. B., Slotkin T. A. Central and sympatho-adrenal responses to insulin in adult and neonatal rats. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;433(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Dune M. A. Intravenous glucose tolerance and plasma insulin studies in small-for-dates infants. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Feb;47(251):111–114. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.251.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Adrian T. E., Aynsley-Green A., Bloom S. R. Iatrogenic hyperinsulinism at birth. Lancet. 1980 Jan 19;1(8160):144–145. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90619-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Role of glucagon, catecholamines, and growth hormone in human glucose counterregulation. Effects of somatostatin and combined alpha- and beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma glucose recovery and glucose flux rates after insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):62–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI109464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokicki W., Forest M. G., Loras B., Bonnet H., Bertrand J. Free cortisol of human plasma in the first three months of life. Biol Neonate. 1990;57(1):21–29. doi: 10.1159/000243148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salle B. L., Ruiton-Ugliengo A. Effects of oral glucose and protein load on plasma glucagon and insulin concentrations in small for gestational age infants. Pediatr Res. 1977 Feb;11(2):108–112. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197702000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M., Fowden A. L., Knox J., Ousey J. C., Franco R., Rossdale P. D. Sympathoadrenal and other responses to hypoglycaemia in the young foal. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1987;35:607–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek B., Lischka A., Hörtnagl H., Pollak A. Sympatho-adrenal response to hypoglycaemia in infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Dec;148(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00441414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses. Diabetes. 1971 Dec;20(12):834–838. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.12.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


