Abstract
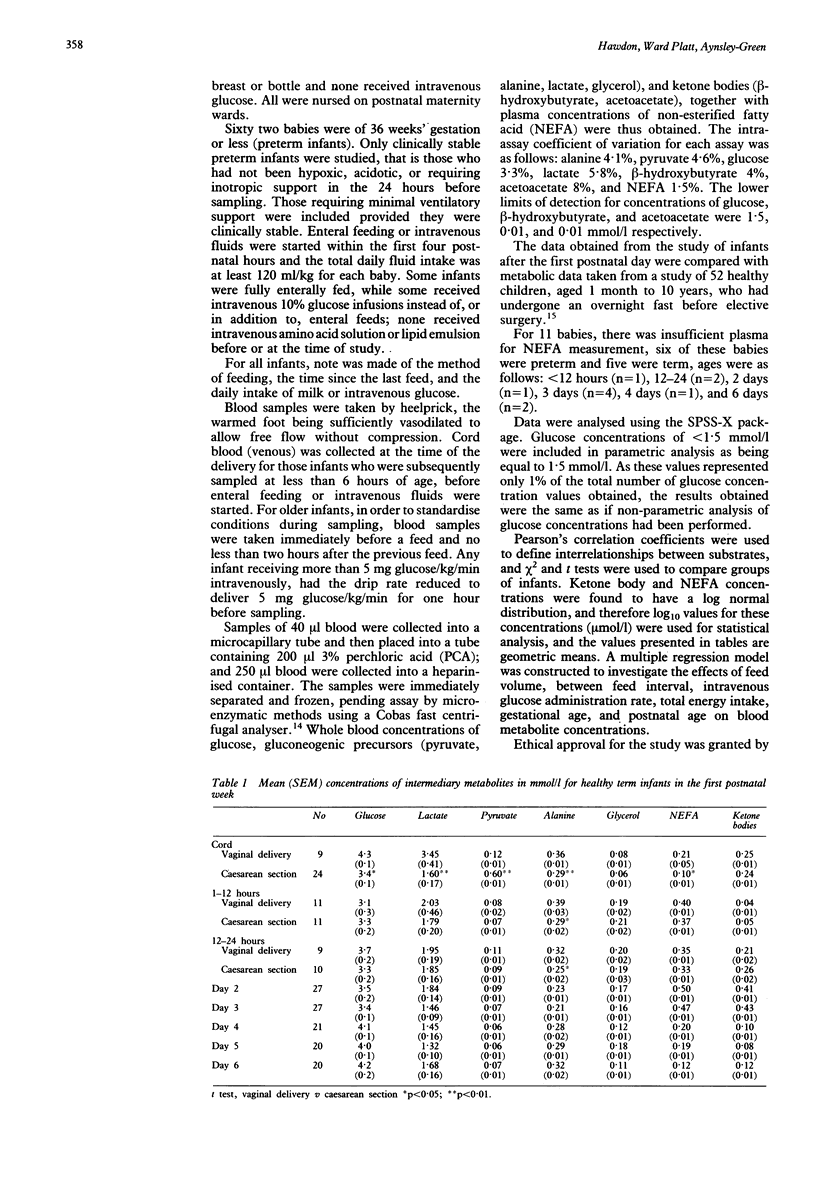
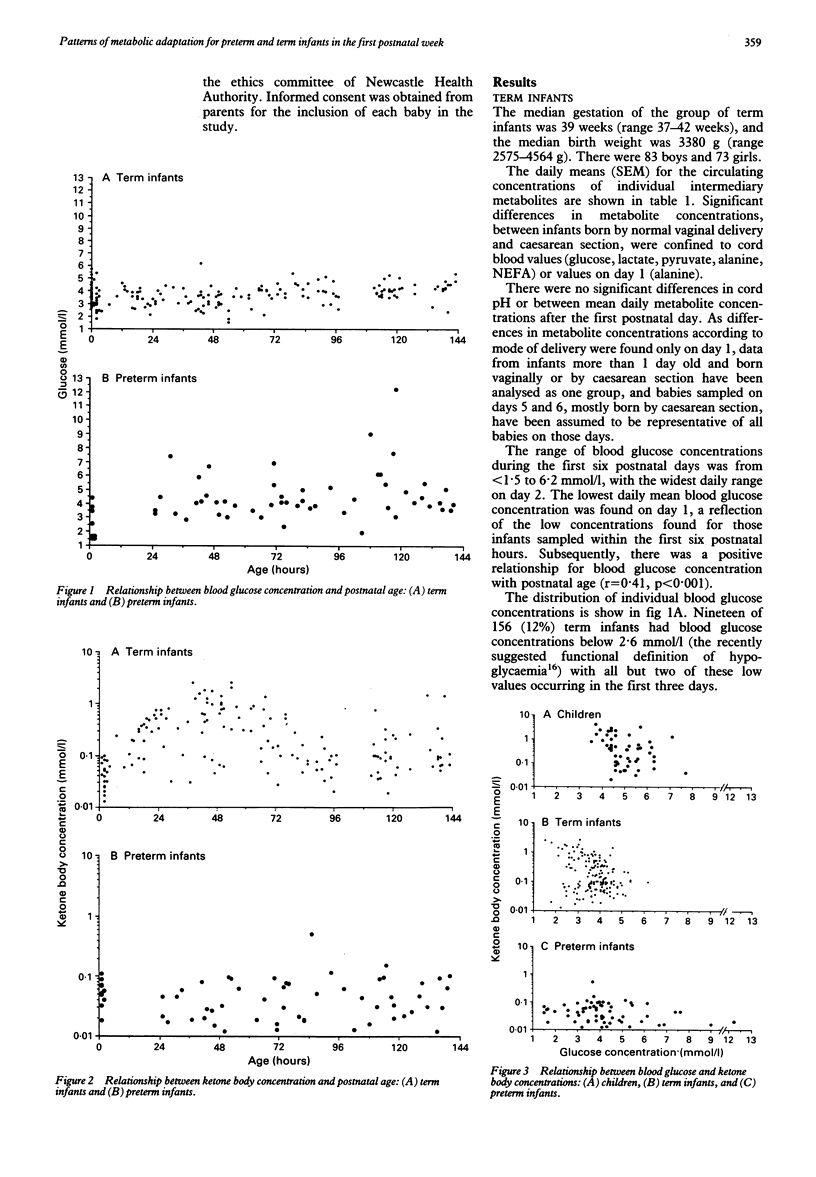
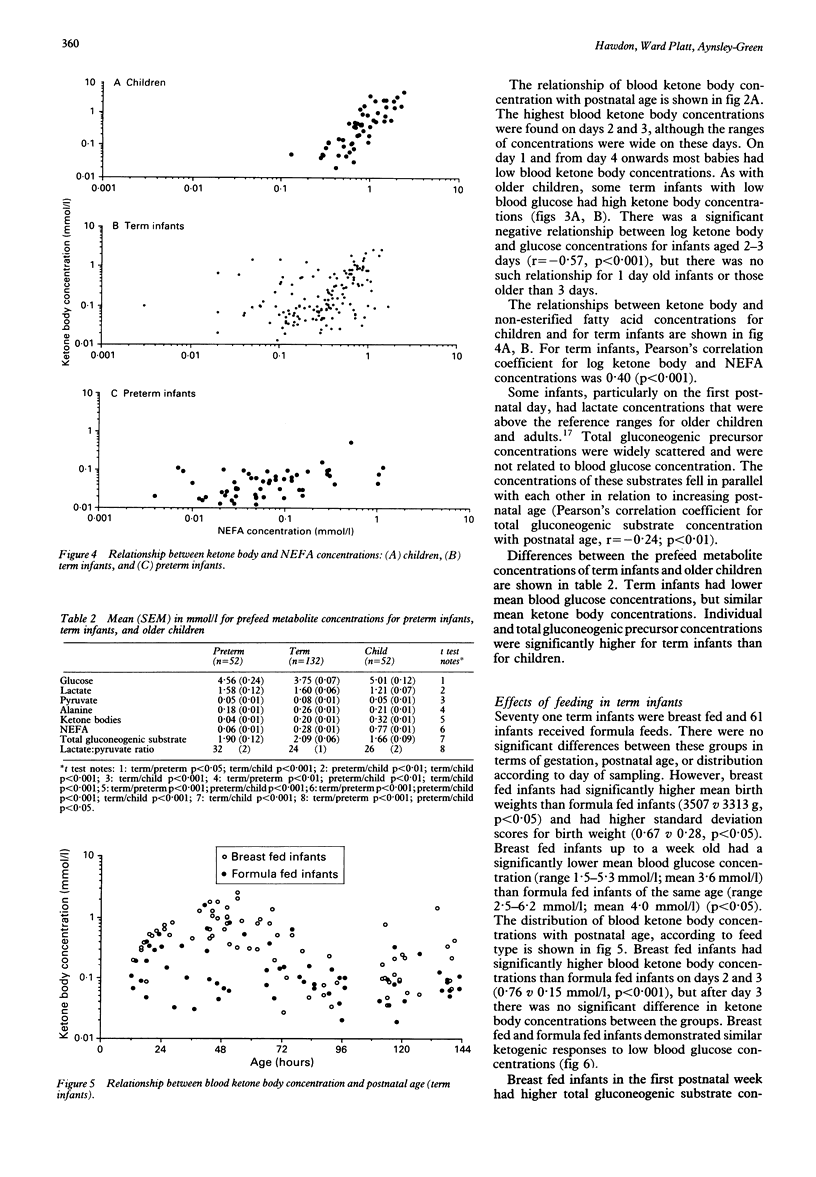
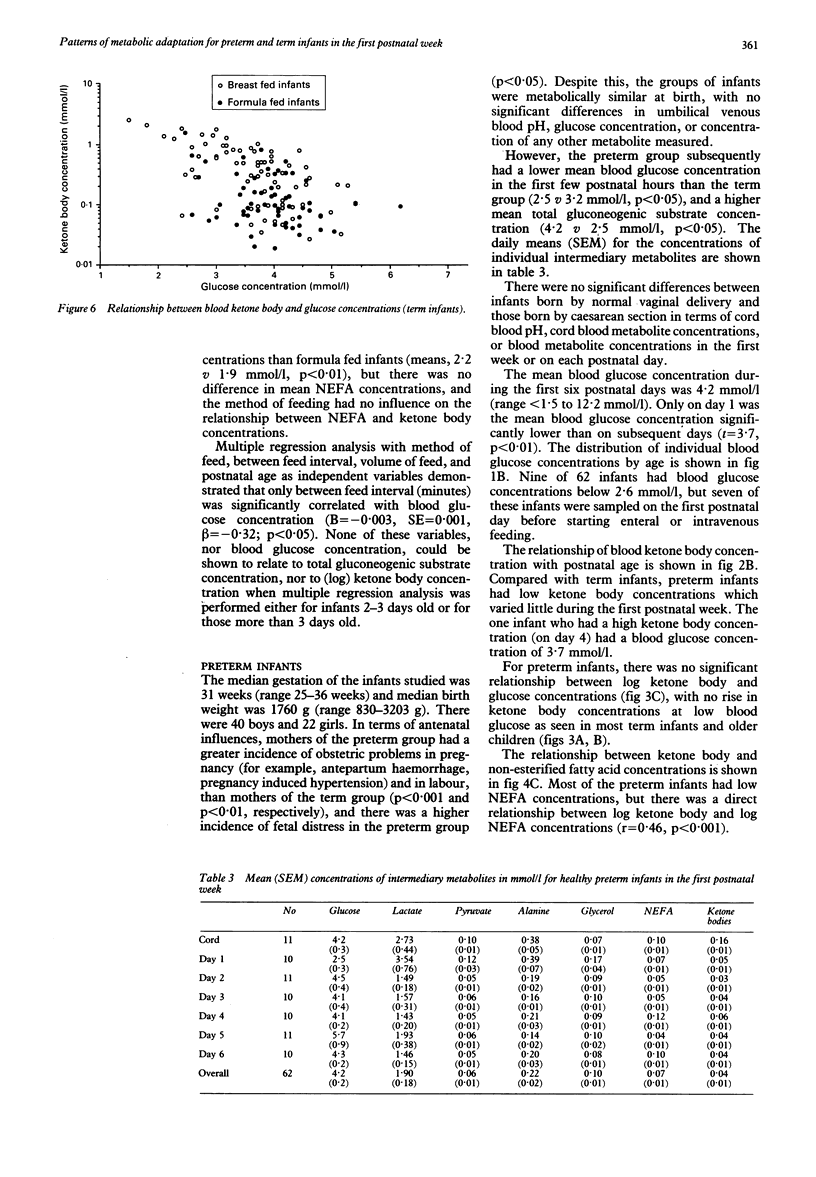
There have been few comprehensive accounts of the relationships between glucose and other metabolic fuels during the first postnatal week, especially in the context of modern feeding practises. A cross sectional study was performed of 156 term infants and 62 preterm infants to establish the normal ranges and interrelationships of blood glucose and intermediary metabolites in the first postnatal week, and to compare these with those of 52 older children. Blood glucose concentrations varied more for preterm than for term infants (1.5-12.2 mmol/l v 1.5-6.2 mmol/l), and preterm infants had low ketone body concentrations, even at low blood glucose concentrations. Breast feeding of term infants and enteral feeding of preterm infants appeared to enhance ketogenic ability. Term infants had lower prefeed blood glucose concentrations than children but, like children, appeared to be capable of producing ketone bodies. This study demonstrates that neonatal blood glucose concentrations should be considered in the context of availability of other metabolic fuels, and that the preterm infant has a limited ability to mobilise alternative fuels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Milner R. D., Strich S. J. Effects of neonatal hypoglycaemia on the nervous system: a pathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Aug;30(4):295–310. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
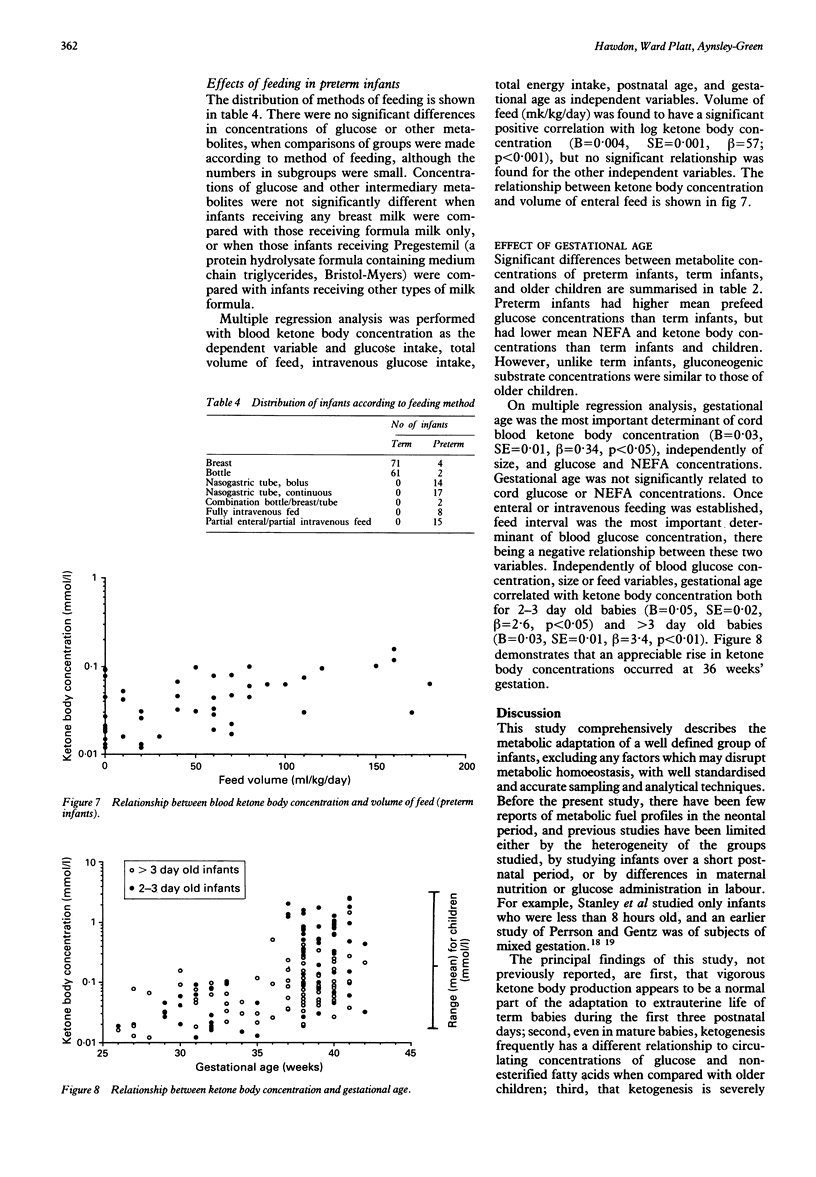
- Anwar M., Vannucci R. C. Autoradiographic determination of regional cerebral blood flow during hypoglycemia in newborn dogs. Pediatr Res. 1988 Jul;24(1):41–45. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198807000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A. Metabolic and endocrine interrelations in the human fetus and neonate. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Feb;41(2 Suppl):399–417. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard A. G., Panos T. C., Marasigan B. V., Eminians J., Kennedy H. F., Lamb J. Perinatal stress and the premature neonate. II. Effect of fluid and calorie deprivation on blood glucose. J Pediatr. 1966 Mar;68(3):329–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bougneres P. F., Lemmel C., Ferré P., Bier D. M. Ketone body transport in the human neonate and infant. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):42–48. doi: 10.1172/JCI112299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance G. W., Bower B. D. Hypoglycaemia and temporary hyperglycaemia in infants of low birth weight for materity. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Jun;41(217):279–285. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.217.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornblath M., Joassin G., Weisskopf B., Swiatek K. R. Hypoglycemia in the newborn. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1966 Aug;13(3):905–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dweck H. S., Cassady G. Glucose intolerance in infants of very low birth weight. I. Incidence of hyperglycemia in infants of birth weights 1,100 grams or less. Pediatrics. 1974 Feb;53(2):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmond J., Auestad N., Robbins R. A., Bergstrom J. D. Ketone body metabolism in the neonate: development and the effect of diet. Fed Proc. 1985 Apr;44(7):2359–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluge G. Clinical aspects of neonatal hypoglycaemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1974 Nov;63(6):826–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1974.tb04871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck L. J., Erenberg A. Serum glucose levels in term neonates during the first 48 hours of life. J Pediatr. 1987 Jan;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetenyi G., Jr, Cowan J. S. Glucoregulation in the newborn. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;58(8):879–888. doi: 10.1139/y80-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh T. H., Aynsley-Green A., Tarbit M., Eyre J. A. Neural dysfunction during hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Nov;63(11):1353–1358. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.11.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh T. H., Eyre J. A., Aynsley-Green A. Neonatal hypoglycaemia--the controversy regarding definition. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Nov;63(11):1386–1388. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.11.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto M., Blanco-Sequeiros M., Krause U. Neonatal symptomatic and asymptomatic hypoglycaemia: a follow-up study of 151 children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1972 Oct;14(5):603–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb02642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers K. J., Doesburg W. H., Gabreëls F. J., Romsom A. C., Renier W. O., Wevers R. A., Lemmens W. A. Reference values of blood components related to fuel metabolism in children after an overnight fast. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jan 15;145(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louik C., Mitchell A. A., Epstein M. F., Shapiro S. Risk factors for neonatal hyperglycemia associated with 10% dextrose infusion. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Aug;139(8):783–786. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140100045025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubchenco L. O., Bard H. Incidence of hypoglycemia in newborn infants classified by birth weight and gestational age. Pediatrics. 1971 May;47(5):831–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Bloom S. R., Aynsley-Green A. Metabolic and endocrine consequences of depriving preterm infants of enteral nutrition. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Mar;72(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Bloom S. R., Green A. A. Gastrointestinal peptides and the adaptation to extrauterine nutrition. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 May;63(5):527–537. doi: 10.1139/y85-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Boyes S., Bloom S. R., Aynsley-Green A. Metabolic and endocrine responses to a milk feed in six-day-old term infants: differences between breast and cow's milk formula feeding. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Mar;70(2):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Morley R., Cole T. J. Adverse neurodevelopmental outcome of moderate neonatal hypoglycaemia. BMJ. 1988 Nov 19;297(6659):1304–1308. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6659.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Johnson C. A., Rajan R., Owen O. E. The metabolism of ketone bodies in developing human brain: development of ketone-body-utilizing enzymes and ketone bodies as precursors for lipid synthesis. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):905–908. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pildes R. S., Pyati S. P. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in tiny infants. Clin Perinatol. 1986 Jun;13(2):351–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryds O., Christensen N. J., Friis-Hansen B. Increased cerebral blood flow and plasma epinephrine in hypoglycemic, preterm neonates. Pediatrics. 1990 Feb;85(2):172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALLPEICE V., DAVIES P. A. IMMEDIATE FEEDING OF PREMATURE INFANTS WITH UNDILUTED BREAST-MILK. Lancet. 1964 Dec 26;2(7374):1349–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexson W. R. Incidence of neonatal hypoglycemia: a matter of definition. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):149–150. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan G., Pildes R. S., Cattamanchi G., Voora S., Lilien L. D. Plasma glucose values in normal neonates: a new look. J Pediatr. 1986 Jul;109(1):114–117. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80588-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A., Anday E. K., Baker L., Delivoria-Papadopolous M. Metabolic fuel and hormone responses to fasting in newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1979 Nov;64(5):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannucci R. C., Nardis E. E., Vannucci S. J., Campbell P. A. Cerebral carbohydrate and energy metabolism during hypoglycemia in newborn dogs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):R192–R199. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.240.3.R192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward Platt M. P., Tarbit M. J., Aynsley-Green A. The effects of anesthesia and surgery on metabolic homeostasis in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr Surg. 1990 May;25(5):472–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(90)90553-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


