Abstract
The bacterial plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae requires a type III protein secretion system (TTSS) to cause disease. The P. syringae TTSS is encoded by the hrp-hrc gene cluster. One of the genes within this cluster, hrpJ, encodes a protein with weak similarity to YopN, a type III secreted protein from the animal pathogenic Yersinia species. Here, we show that HrpJ is secreted in culture and translocated into plant cells by the P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 TTSS. A DC3000 hrpJ mutant, UNL140, was greatly reduced in its ability to cause disease symptoms and multiply in Arabidopsis thaliana. UNL140 exhibited a reduced ability to elicit a hypersensitive response (HR) in nonhost tobacco plants. UNL140 was unable to elicit an AvrRpt2- or AvrB1-dependent HR in A. thaliana but maintained its ability to secrete AvrB1 in culture via the TTSS. Additionally, UNL140 was defective in its ability to translocate the effectors AvrPto1, HopB1, and AvrPtoB. Type III secretion assays showed that UNL140 secreted HrpA1 and AvrPto1 but was unable to secrete HrpZ1, a protein that is normally secreted in culture in relatively large amounts, into culture supernatants. Taken together, our data indicate that HrpJ is a type III secreted protein that is important for pathogenicity and the translocation of effectors into plant cells. Based on the failure of UNL140 to secrete HrpZ1, HrpJ may play a role in controlling type III secretion, and in its absence, specific accessory proteins, like HrpZ1, may not be extracellularly localized, resulting in disabled translocation of effectors into plant cells.
Pseudomonas syringae is a host-specific bacterial plant pathogen that is capable of infecting many different plant species (3, 38). P. syringae causes a variety of diseases on susceptible plants, typically producing symptoms that manifest as necrotic and chlorotic lesions on aerial plant parts. On resistant plants, P. syringae often triggers plant innate immune responses, including the hypersensitive response (HR), a programmed cell death response associated with plant resistance (36).
A central pathogenicity factor for P. syringae is a type III protein secretion system (TTSS) called the Hrp TTSS, which is encoded by the hrp-hrc cluster within the Hrp pathogenicity island (2). The P. syringae Hrp TTSS translocates or injects many type III secreted proteins, known as effectors, into plant cells. P. syringae mutants defective in the Hrp TTSS are severely compromised in pathogenicity and are unable to elicit an HR on nonhost plants (53, 54). This indicates that collectively, these injected effectors are required for pathogenesis and that the nonhost HR is likely due to plant recognition of a subset of injected effectors in resistant plants. This is consistent with the well-documented recognition of bacterial type III effectors historically referred to as avirulence (Avr) proteins by plant resistance (R) proteins (16, 19).
The availability of the complete genomes of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (9), P. syringae pv. syringae B728a (23), and P. syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448a (44) facilitated the identification of many P. syringae type III secreted proteins (12, 17, 30). Recently, a unified naming system for P. syringae type III secreted proteins was established, and these names will be used for the proteins described in this paper (52). Evidence that many of the P. syringae type III effectors injected into plant cells act as suppressors of the plant's innate immune system is accumulating (21, 57, 58). However, the enzymatic activities of the majority of P. syringae effectors and their plant targets remain unknown.
Bacterial TTSSs secrete other helper or accessory proteins that make up the extracellular portion of the type III apparatus and other proteins that function to help the type III apparatus deliver effector proteins into host cells. These include proteins that make up the type III-related needles, sheaths, or pili (depending on the TTSS) needed for the extracellular conduit that transports effectors. In the P. syringae TTSS, the HrpA1 protein has been shown to be the main component of the Hrp pilus (43, 51, 63). Other accessory proteins include translocator proteins that assist effectors in crossing the eukaryotic plasma membrane (10). Another group of proteins, called harpins, which are glycine-rich, heat-stable proteins predicted to modify the plant cell wall and/or act as translocators, have been identified (39, 50, 67). P. syringae has two harpins identified thus far, HrpZ1 and HrpW1. HrpZ1 was the first protein shown to be secreted via the P. syringae Hrp TTSS (34) and has been shown to form pores in artificial membranes, suggesting a role in translocation (50). HrpW1 has an N-terminal harpin domain and a C-terminal pectate lyase domain, suggesting that it acts on the plant cell wall (13). More recently, type III secreted HrpK1 has been shown to be required for pathogenicity and for effector translocation (60). Because of these phenotypes and other circumstantial evidence, HrpK1 appears to be a type III translocator.
The P. syringae type III apparatus is made up of about 20 proteins. Ten of these proteins, the so-called Hrc proteins (for HR and conserved), are conserved in all nonflagellar TTSSs, and nine of the Hrc proteins are conserved in flagellar TTSSs (4, 40). The lone exception is HrcC, which belongs to the secretin family of outer-membrane proteins present in several macromolecule transport systems in gram-negative bacteria (27). The TTSSs of bacterial plant pathogens fall into two different groups based on the degree of conservation of their protein components. Group I includes the model TTSSs of P. syringae and Erwinia amylovora, and group II includes the model TTSSs of Ralstonia solanacearum and Xanthomonas campestris (4, 35). Several P. syringae Hrp proteins encoded by the hrp-hrc cluster are conserved in a subset of nonflagellar TTSSs, several are conserved only in bacterial plant pathogen TTSSs, and others appear to be unique to P. syringae and other group I Hrp TTSSs (4, 35).
One P. syringae protein, HrpJ, appears to be conserved in a subset of nonflagellar TTSSs and possesses clear homologs in plant pathogenic group I TTSSs but is not noticeably similar to any proteins in plant pathogenic group II TTSSs (4, 40). HrpJ is encoded by a gene within a five-gene operon in the P. syringae hrp-hrc cluster, and it has been reported to share similarity with YopN, a protein secreted via the Yersinia sp. Ysc TTSS (4, 40). Yersinia spp. grown in culture secrete Yop proteins via their Ysc TTSS at 37°C in the absence of calcium but not in the presence of calcium (8, 55). Thus, the absence of calcium appears to act as an environmental cue for the contact-dependent injection of Yop proteins by the Ysc TTSS into animal cells (61). Yersinia yopN mutants secrete Yop proteins in the presence or absence of calcium, a phenotype referred to as “calcium blind” (25). Thus, YopN is viewed as a control protein that prevents inappropriate type III secretion.
To address the role that HrpJ has in the DC3000 TTSS, we tested whether HrpJ was secreted in culture and translocated by the TTSS and determined its effect on the secretion and translocation of other P. syringae type III secreted proteins. Here, we report that HrpJ is secreted in culture and translocated into plant cells by the P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 TTSS. A DC3000 hrpJ mutant was greatly reduced in its ability to cause disease and multiply in plant tissue. Moreover, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant was reduced in its ability to elicit the nonhost HR, suggesting that it was less competent in the translocation of type III effectors. This was confirmed by the finding that individual DC3000 effectors were translocated at very low levels, if at all, by the DC3000 hrpJ mutant. Interestingly, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant retained its ability to secrete type III effectors in culture but was unable to secrete the HrpZ1 extracellular accessory protein. These findings allowed us to propose that HrpJ functions as a control protein for the P. syringae TTSS and that its activities are required for the translocation of effectors into plant cells and for the secretion of the HrpZ1 harpin in culture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and media.
Escherichia coli strain DH5α was used for general cloning (Table 1) and was grown in Luria-Bertani broth at 37°C. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 was grown in King's B broth at 30°C or type III-inducing fructose minimal medium at 20°C (41, 46). Antibiotics were used at the following concentrations (μg ml−1): rifampin, 100; ampicillin, 100; gentamicin, 10; kanamycin, 50; chloramphemiol, 20; tetracycline, 20; and spectinomycin, 50.
TABLE 1.
Strains and plasmids
| Designation | Main feature | Characteristics | Reference and/ or source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial strains | |||
| E. coli DH5α | General use | supE44 ΔlacU169(φ80lacZΔM15) hsdR17 recA1 endA1 gyrA96 thi-1 relA1 Nair | 33; Life Technologies |
| P. syringae pv. tomato | |||
| DC3000 | Wild-type strain | spontaneous Rifr | 18 |
| DC3000 hrcC mutant | TTSS defective | DC3000 hrcC mutant, Rifr Cmr | 70 |
| UNL140 | hrpJ mutant | DC3000 nonpolar hrpJ deletion, Rifr Kmr | This work |
| Plasmids | |||
| pAvrRpt2-600 | Broad-host-range construct encoding AvrRpt2 | pDSK600 derivative, Spr/Smr | 62 |
| pBBR1MCS1/5 | Broad-host-range vector | Cmr (MCS1) or Gmr (MCS5) | 47 |
| pBluescript-II KS(−) | Cloning vector | Apr | Stratagene |
| pCPP2308 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HrpL | pML122 derivative, Gmr | Alan Collmer |
| pCPP2318 | Broad-host-range construct encoding mature β-lactamase | pCPP30 derivative carrying blaM lacking signal peptide sequences, Tcr | 14 |
| pCPP2330 | Broad-host-range construct encoding AvrB1-FLAG | pML123 derivative, Gmr | 28 |
| pCPP2988 | Construct carrying nptII | pBluescript II KS(−) vector carrying 1.5-kb HindIII-SalI fragment with nptII lacking transcriptional terminator, Apr Kmr | 1 |
| pCPP3234 | Gateway destination vector for CyaA fusions | Spr Smr | 64 |
| pCPP5040 | Broad-host-range Gateway destination vector for HA fusions | pML123 derivative, Gmr | 42 |
| pENTR/D-TOPO | Gateway entry vector | Kmr | Invitrogen |
| pLN307 | avrPto1 entry construct | Kmr | This work |
| pLN323 | avrPtoB entry construct | Kmr | 42 |
| pLN375 | hrpJ entry construct | Kmr | This work |
| pLN420 | hopB1 entry construct | pENTR/D-TOPO derivative, Kmr | 60 |
| pLN421 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HopB1-CyaA | pCPP3234 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN420, Spr/Smr | 60 |
| pLN426 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HrpJ-CyaA | pML123 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN375, Gmr | This work |
| pLN677 | Broad-host-range Gateway destination vector for HA fusions | pBBR1MCS-5 derivative, Gmr | 60 |
| pLN705 | Broad-host-range Gateway destination vector for HA fusions | pBBR1MCS-1 derivative, Cmr | 31 |
| pLN726 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HrpJ-HA | pLN677 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN375, Gmr | This work |
| pLN736 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HrpJ-HA | pLN705 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN375, Cmr | This work |
| pLN820 | avrB1 entry construct | pENTR/D-TOPO derivative, Kmr | This work |
| pLN918 | Broad-host-range construct encoding AvrB1-CyaA | pCPP3234 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN820, Spr/Smr | This work |
| pLN1979 | Broad-host-range construct encoding AvrPtoB-CyaA | pCPP3234 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN323, Spr/Smr | This work |
| pLN1985 | Broad-host-range construct encoding AvrPto1-CyaA | pCPP3234 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN307, Spr/Smr | This work |
| pLN2043 | Construct carrying cyaA | pBluescript II KS(−) derivative containing cyaA, Apr | This work |
| pLN2179 | Construct carrying DNA upstream of hrpJ adjacent to an nptII cassette | pBluescript II KS(−) derivative, Apr Kmr | This work |
| pLN2180 | Broad-host-range hrpJ deletion construct | pBluescript II KS(−) derivative, Apr Kmr | This work |
| pLN2190 | Construct carrying cyaA with flanking Gateway recombination sites | pBluescript II KS(−) derivative, Apr Cmr | This work |
| pLN2193 | Gateway destination vector for CyaA fusions | pML123 derivative, Gmr Cmr | This work |
| pLN2234 | Broad-host-range construct encoding HrpJ-CyaA | pLN2193 derivative obtained by recombination with pLN375, Gmr | This work |
| pLN2302 | hrpJ deletion construct | pRK415 derivative carrying insert from pLN2180, Tcr | This work |
| pML122/23 | Broad-host-range vector | Gmr | 49 |
| pRK415 | Broad-host-range vector | Tcr | 45 |
General DNA manipulations.
Restriction enzymes, T4 ligase, and DNA polymerase were purchased from New England Biolabs (Beverly, Mass.). The thermostable DNA polymerase used in PCRs was Pfu polymerase (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.). The oligonucleotide primers used for plasmid constructions were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, Iowa), and these primers or information about them will be made available upon request. For cloning using Gateway technology, we amplified desired target genes using PCR and Pfu polymerase and cloned the amplified fragments into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.). The resulting pENTR constructs were recombined with Gateway destination vectors by LR reaction using LR clonase (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions. We used standard cycling conditions for PCRs. Plasmids were introduced into P. syringae strains by electroporation. General DNA sequence analysis was performed with Lasergene software (DNAstar Inc., Madison, Wis.). Database searches were done with the BLASTN, BLASTP, BLASTX, and PSI-BLAST programs at NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/index.shtml) (5).
Construction of plasmids.
hrpJ, avrPto1, and avrB1 were cloned into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) by PCR with primers P759 and P760, P689 and P690, and P1134 and P1135, resulting in constructs pLN375, pLN307, and pLN820, respectively. pLN820, pLN323, and pLN307 were recombined into the CyaA Gateway destination vector pCPP3234, resulting in pLN918, pLN1979, and pLN1985, respectively. The hrpJ entry construct pLN375 was recombined into the destination vectors pCPP5040, pLN705, and pLN677, resulting in constructs pLN426, pLN736, and pLN726, respectively. The adenylate cyclase coding region lacking its start codon was amplified by PCR with primers P1963 and P1710 from pCPP3234 and ligated into pBluescript KS(−) by use of SacI and NotI restriction enzymes, resulting in construct pLN2043. Gateway cassette frame A was digested with EcoRV and ligated into the NotI restriction site of pLN2043, resulting in construct pLN2190. The Gateway CyaA cassette from pLN2190 was isolated and ligated into the HindIII and SacI restriction sites of pML123, resulting in the broad-host-range Gateway destination vector pLN2193. The hrpJ entry construct pLN375 was recombined into pLN2193, resulting in pLN2234.
Construction of the DC3000 hrpJ nonpolar mutant UNL140.
To construct a DC3000 nonpolar hrpJ mutant, DNA upstream of hrpJ was amplified by PCR with primers P801 and P802. This PCR product was ligated into the XbaI and HindIII restriction enzyme sites of pCPP2988, which is a pBluescript derivative that contains an nptII gene lacking a transcriptional terminator, resulting in pLN2179. A DNA region downstream of hrpJ was amplified by PCR with primers P803 and P804 and ligated into the XhoI and KpnI sites of pLN2179, resulting in construct pLN2180. The insert in pLN2180, which contained an nptII gene flanked by the upstream and downstream fragments of hrpJ, was isolated by digestion with restriction enzymes KpnI and XbaI and ligated into pRK415, resulting in construct pLN2302. This construct was electroporated into DC3000. Putative mutants were identified by selection for retention of the antibiotic marker linked to the mutation and loss of the plasmid marker. A colony with this phenotype was confirmed to have the hrpJ gene replaced with nptII by PCR with primer sets P759 and P760 and P988 and P986. This DC3000 mutant was designated UNL140. Additionally, UNL140 was confirmed to carry an hrpJ deletion mutation by Southern analysis by probing with DNA flanking hrpJ.
Type III secretion assays.
P. syringae strains were grown overnight on King's B plates containing appropriate antibiotics. Test strains were inoculated at an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.3 in type III-inducing minimal medium at 20°C (41) (or at 30°C in experiments to test for temperature regulation) and grown for 6 h. Cell and supernatant fractions were separated by centrifugation, and the protein in the supernatant fraction was precipitated with 12.5% trichloroacetic acid. Proteins were separated on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels and transferred to membranes for immunoblotting. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-AvrPto1, anti-HrpZ1, anti-HrpA1, anti-hemagglutinin (HA) (Roche Diagnostics Corp., Indianapolis, Ind.), anti-β-lactamase (Chemicon International, Temecula, Calif.), anti-FLAG (Sigma Chemical Co.), and anti-NptII (Cortex Biochem, San Leandro, Calif.). Primary antibodies were recognized by anti-mouse, anti-rabbit, or anti-rat immunoglobulin G-alkaline phosphatase conjugate secondary antibodies (Sigma Chemical Co.) and visualized on autoradiographs with the Western-Light chemiluminescence system (Tropix, Bedford, Mass.). NptII or β-lactamase was used as an indicator of nonspecific cell lysis in secretion assays.
Pathogenicity and HR assays.
DC3000 strains were assessed for their ability to cause disease symptoms and multiply in planta by dipping of Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Col-0 plants into bacterial suspensions that were adjusted to an OD600 of 0.2 in 10 mM MgCl2 containing 0.02% Silwet L-77 (Lehle Seeds, Round Rock, TX) and enumerated as previously described (22). DC3000 strains were tested for the ability to elicit an HR on Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi by infiltration of plant tissue with strains adjusted to an OD600 of 0.2 along with 10-fold serially diluted samples by use of a needleless syringe. The DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 was complemented with pLN426 for the HR and pathogenicity assay. For AvrB1- and AvrRpt2-dependent HR assays, pCPP2330 (encoding AvrB1-FLAG) and pAvrRpt2-600 (encoding AvrRpt2) were electroporated into DC3000 or the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140. A. thaliana ecotype Col-0 was infiltrated with these strains at an OD600 of 0.1 in 5 mM MES (morpholineethanesulfonic acid). HR production was assessed 12 h after infiltration. The DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 was complemented with pLN736 (in strains expressing AvrB1-FLAG) or pLN726 (in strains expressing AvrRpt2).
Adenylate cyclase (CyaA) translocation assays.
Constructs that encoded CyaA fusions were electroporated into DC3000 for translocation assays. These included constructs pLN2234, pLN421, pLN1985, pLN918, and pLN1979, which express HrpJ-CyaA, HopB1-CyaA, AvrPto1-CyaA, AvrB1-CyaA, and AvrPtoB-CyaA, respectively. Nicotiana benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with test strains at an OD600 of 0.6 in 5 mM MES (pH 5.6). After 10 h, the leaf samples were taken with a 0.8-cm cork borer. Leaf disks were ground in liquid nitrogen and resuspended in 300 μl of 0.1 M HCl. Protein concentrations were measured with Bio-Rad total protein assays. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) was quantified with a direct cAMP corrected enzyme immunoassay kit (Assay Design, Ann Arbor, MI).
RESULTS
HrpJ shares similarity with YopN homologs from animal pathogens and contains secretion signal characteristics of P. syringae TTSS substrates.
The Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hrpJ gene is the first gene of a five-gene operon within the hrp-hrc cluster (2). HrpJ protein was previously reported to share similarity with Yersinia sp. YopN homologs (4, 40). PSI-BLAST searches using DC3000 HrpJ identified HrpJ homologs from Erwinia amylovora and other bacterial plant pathogens that contain similar group I Hrp TTSSs in the first PSI-BLAST iteration. Also identified in iteration 1 were YopN homologs from Bordetella bronchiseptica and other Bordetella species. YopN and YopN homologs from other TTSS-containing bacteria were identified in the second and third iterations of PSI-BLAST. The amino acid sequence identity between HrpJ and the YopN homologs was low (between 18 and 22% identity). The only proteins that were clear homologs of P. syringae HrpJ were the HrpJ homologs in other group I Hrp TTSSs. Interestingly, we were unable to identify any proteins similar to HrpJ in Ralstonia solanacearum and Xanthomonas campestris, two bacterial plant pathogens that have group II Hrp TTSSs (4). Our analyses further support that the DC3000 HrpJ protein is similar to the large family of YopN proteins identified in many bacteria that contain TTSSs.
The DC3000 HrpJ protein also contained several characteristics identified in the N termini of other P. syringae type III secreted substrates (32, 59). For example, the predicted amino acid sequence of HrpJ contains an isoleucine in position 3, 6% serine in the first 50 amino acids, and no aspartate or glutamates in the first 12 residues, consistent with the N-terminal biochemical characteristics of other P. syringae TTSS substrates. In sum, HrpJ appears to be similar to YopN and contains biochemical characteristics in its N terminus, consistent with it being a type III secreted protein.
HrpJ is secreted in culture and translocated into plant cells via the P. syringae TTSS.
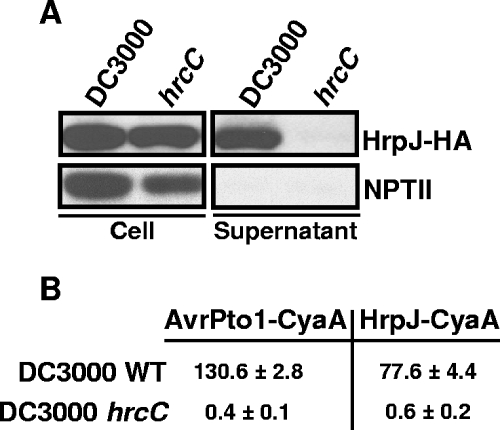
To determine whether HrpJ is secreted in culture by the DC3000 TTSS, we made a plasmid construct, pLN426, which expressed HrpJ fused to an HA epitope. This construct was introduced by electroporation into wild-type DC3000 and a DC3000 hrcC mutant defective in type III secretion. Type III secretion assays were performed with these strains, and HrpJ-HA was localized to supernatant fractions from wild-type DC3000 cultures, indicating that HrpJ is secreted in culture via the P. syringae TTSS (Fig. 1A). HrpJ-HA remained cell bound in cultures from the DC3000 hrcC mutant, confirming that it required a functional TTSS to be extracellularly localized (Fig. 1A).
FIG. 1.
HrpJ is secreted in culture and translocated into plant cells by the DC3000 type III system. (A) DC3000 and the DC3000 hrcC mutant, both carrying pLN426, which encodes HrpJ fused to the hemagglutinin epitope (HrpJ-HA), were grown under conditions that induce type III secretion and separated into cell-bound and supernatant fractions as described in Materials and Methods. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using anti-HA or anti-NPTII antibodies. The NPTII protein is also encoded by pLN426 and is used here as a control for nonspecific cell lysis. HrpJ-HA was detected in supernatant fractions of DC3000 but not in supernatant fractions from the hrcC mutant, indicating that HrpJ is secreted by the DC3000 TTSS. (B) Adenylate cyclase (CyaA) assays with HrpJ-CyaA and AvrPto1-CyaA fusions were carried out by infiltration of Nicotiana benthamiana with DC3000 strains carrying construct pLN2234 or pLN1985, which produced either HrpJ-CyaA or AvrPto1-Cya (a type III effector known to be injected into plant cells), respectively. Plant tissue was harvested 10 h after infiltration, and cAMP levels were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Levels of cAMP are reported in picomoles of cAMP per microgram of protein, with standard errors. WT, wild type.
To determine whether HrpJ is translocated or injected into plant cells, we used the adenylate cyclase (CyaA) translocation assay (11, 65). In this assay, C-terminal CyaA fusions are made to a candidate type III translocated protein. The CyaA fusion is expressed in a TTSS-containing bacterium and exposed to eukaryotic cells. Because CyaA activity is dependent on calmodulin, only fusions that are injected into the eukaryotic cell produce cAMP. Nicotiana benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with DC3000 and the DC3000 hrcC mutant, each carrying construct pLN2234, which encoded HrpJ-CyaA. After 10 h, levels of cAMP were determined with a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit as described in Materials and Methods. Plant tissue infiltrated with wild-type DC3000 expressing HrpJ-CyaA had significantly higher cAMP levels than plant tissue infiltrated with the type III defective mutant expressing HrpJ-CyaA (Fig. 1B). These results clearly indicate that HrpJ-CyaA is injected into plant cells by the DC3000 TTSS.
The DC3000 hrpJ mutant is greatly reduced in disease symptom production, multiplication in planta, and ability to elicit an HR on nonhost plants.
To determine the extent to which HrpJ contributed to plant-microbe interactions, a nonpolar hrpJ mutant was constructed by marker exchange recombination as described in Materials and Methods. Briefly, we PCR amplified DNA fragments 2 kb upstream and 2.2 kb downstream of hrpJ and cloned these in the same orientation on either side of a 1.5-kb neomycin phosphotransferase II (nptII) cassette that lacked a rho-independent transcription terminator. A construct carrying this nptII cassette and hrpJ flanking DNA was introduced into DC3000, and marker exchange was selected for by loss of the plasmid marker and retention of the nptII cassette marker. The resulting mutant would have the hrpJ gene replaced by the nptII cassette except for the first 2 codons and the last 2 codons of the 368-codon hrpJ gene. The hrpJ mutation needed to be nonpolar because hrpJ is the first gene of an apparent five-gene operon. A nonpolar hrpJ mutant designated UNL140 was confirmed to contain an nptII cassette insertion by PCR and Southern analyses. Pathogenicity assays were carried out by dip inoculation of A. thaliana Col-0 plants with wild-type DC3000, the DC3000 hrcC mutant defective in TTSS, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140, and UNL140 carrying pLN426, which encodes HrpJ-HA. UNL140 was greatly reduced in its ability to produce disease symptoms on A. thaliana leaves compared to wild-type DC3000 (Fig. 2A). Indeed, the symptoms produced by UNL140 were similar to those produced by the type III defective hrcC mutant, indicating that HrpJ is required for the bacterium to be pathogenic and benefit from possessing a TTSS. Wild-type levels of symptom production were restored when pLN426, which carries hrpJ, was introduced into UNL140 (Fig. 2A), demonstrating that the defect was due to the absence of hrpJ and that the mutation was nonpolar.
FIG. 2.
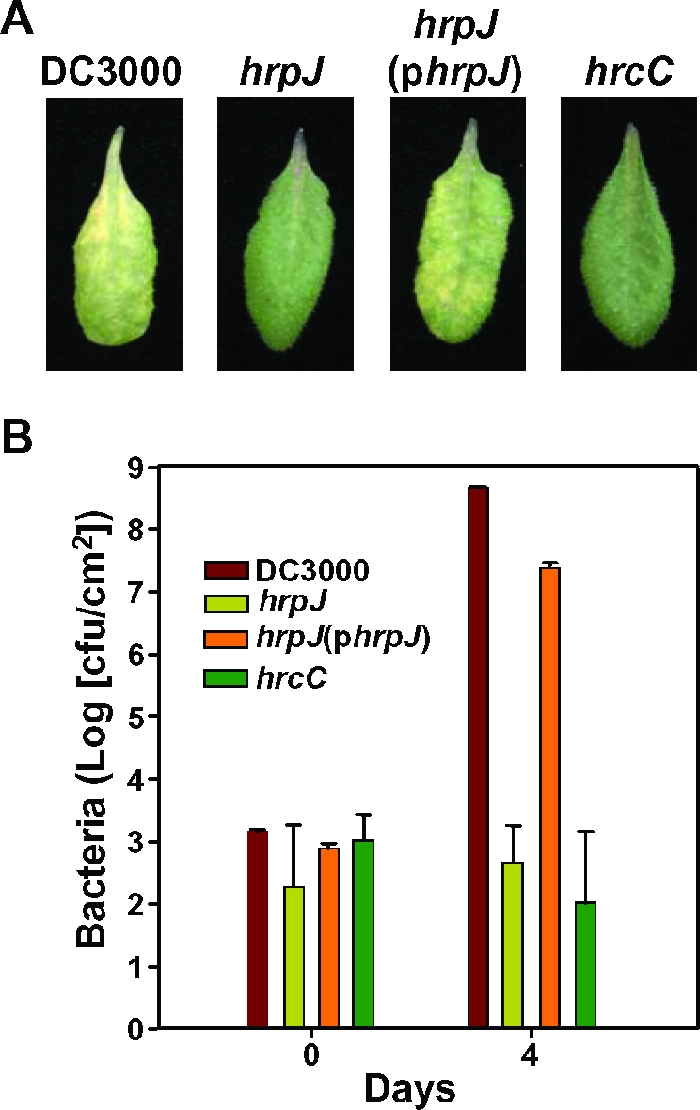
HrpJ is required for symptom production and bacterial growth in Arabidopsis. (A) Leaves from A. thaliana Col-0 plants that were dip inoculated into DC3000 suspensions at a concentration of 1 × 108 cells/ml. The strains used were wild-type DC3000, a DC3000 hrcC mutant, UNL140 (a nonpolar hrpJ mutant), and UNL140 carrying pLN426, a plasmid containing hrpJ-HA. Photographs were taken 4 days after inoculation. (B) Bacterial growth in A. thaliana Col-0 leaves of the strains in panel A was monitored over a 4-day period. Results show that DC3000 hrpJ mutants are greatly reduced in their ability to grow in planta and in disease symptom production, and these phenotypes are complemented when hrpJ is provided in trans.
The DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 was monitored for its ability to multiply in A. thaliana leaves over a 4-day period. UNL140 was greatly reduced in its ability to grow in planta, exhibiting bacterial titers that were similar to those in the DC3000 hrcC mutant (Fig. 2B). Near-wild-type DC3000 growth levels were restored when UNL140 carried hrpJ in trans (Fig. 2B). Taken together, the production of reduced disease symptoms and the reduction of growth in planta indicate that HrpJ plays an important role in the TTSS and plant pathogenicity.
Type III translocation of effectors into plant cells is impaired in the DC3000 hrpJ mutant.
The pathogenicity phenotypes of the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 suggested that HrpJ was required for pathogenicity. Because the central function of the TTSS is to translocate proteins into eukaryotic cells, we sought to determine the extent to which UNL140 was affected in its ability to translocate type III effector proteins into plant cells. One indication that a P. syringae mutant is affected in effector translocation is the reduction or abrogation of its ability to elicit a nonhost HR (60). We infiltrated N. tabacum cv. Xanthi (tobacco) leaves with different titers of wild-type DC3000, UNL140, or UNL140(pLN426), which expressed HrpJ-HA. DC3000 elicited an HR at or above a cell titer of 1 × 107 cells/ml. The DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 was unable to elicit an HR at a titer of 1 × 107 cells/ml (Fig. 3). UNL140 was capable of eliciting an HR at 1 × 108 cells/ml. The reduced HR phenotype displayed by UNL140 was complemented when hrpJ was provided in trans. Since the elicitation of this HR requires translocation of effectors into plant cells, a reduced ability to elicit an HR suggests that UNL140 is impaired in its ability to translocate effectors into plant cells. However, it is important to note that the residual HR-eliciting ability displayed by UNL140 suggests that it is not completely disabled in translocation.
FIG. 3.
DC3000 hrpJ mutant is reduced in its ability to elicit a nonhost HR, suggesting that it is impaired in effector translocation. Tobacco leaves (N. tabacum cv. Xanthi) were infiltrated with DC3000 strains at 1 × 108 cells/ml (top of each panel) or 1 × 107 cells/ml (bottom of each panel). The strains used for infiltration were wild-type DC3000 (left panel), the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 (middle panel), and UNL140 carrying pLN375 (right panel), which contains hrpJ. UNL140 was unable to elicit an HR at 1 × 107 cells/ml, and this phenotype was complemented when pLN375 was introduced into UNL140.
To directly test whether UNL140 is affected in its ability to translocate specific effectors into plant cells, two different assays were used. First, we infiltrated A. thaliana Col-0 with DC3000 and UNL140 expressing the P. syringae type III effector AvrB1 (fused to a FLAG epitope) or AvrRpt2 in trans. AvrB1 and AvrRpt2 are recognized by the resistance proteins RPM1 and RPS2, respectively, of the innate immune system of A. thaliana Col-0 and result in the induction of defense responses, including an HR (6, 29, 56). As shown in Fig. 4A, DC3000 expressing either AvrB1-FLAG or AvrRpt2 elicited an HR in A. thaliana Col-0 plants within 12 h. In contrast, UNL140 expressing AvrB1-FLAG or AvrRpt2 did not elicit an HR in these plants unless hrpJ was also provided in trans (Fig. 4A).
FIG. 4.
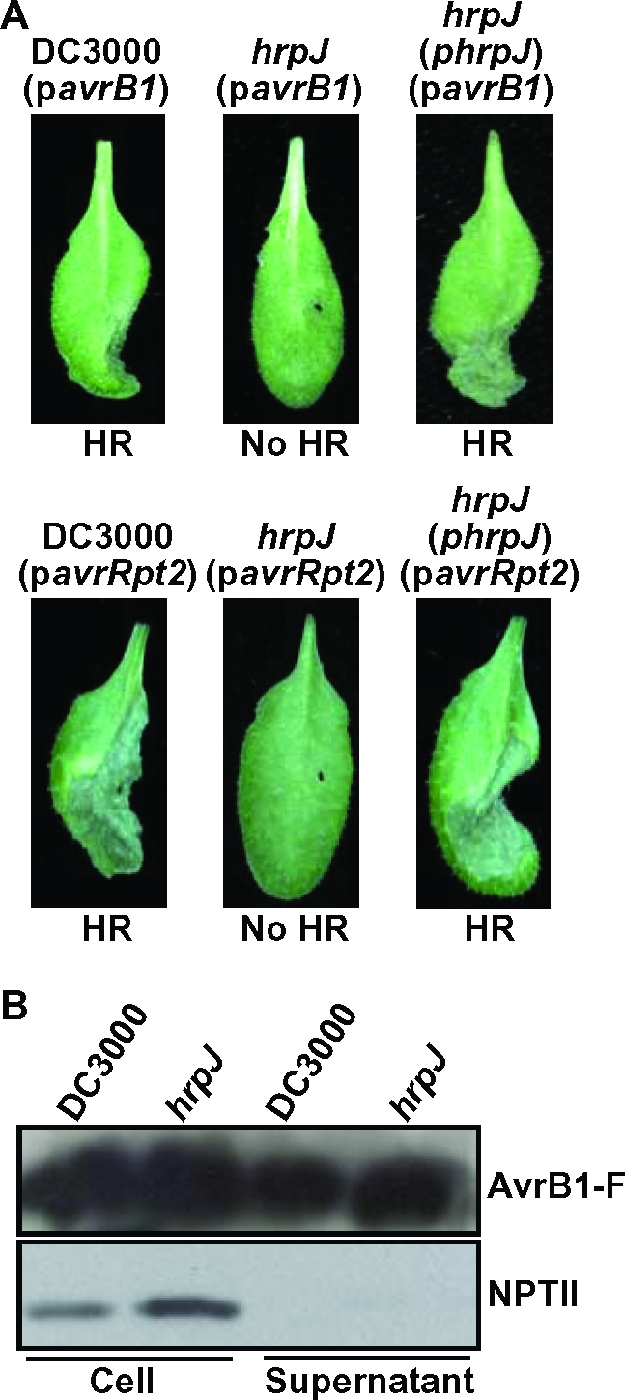
DC3000 hrpJ mutant does not translocate Avr proteins into Arabidopsis but maintains the ability to secrete AvrB1 in culture. (A) The well-characterized type III effector genes avrB1 and avrRpt2, which encode proteins recognized by the innate immune system of A. thaliana Col-0 (i.e., Avr proteins), were introduced into wild-type DC3000 and the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 on plasmids pCPP2330 and pAvrRpt2-600, respectively. A. thaliana Col-0 was infiltrated with these strains separately, and 12 h later, they were assessed for HR production. UNL140 was unable to elicit an AvrB1- or AvrRpt2-specific HR unless plasmid-encoded HrpJ was provided. (B) DC3000(pCPP2330) and UNL140(pCPP2330) were grown in type III-inducing conditions and separated into cell-bound and supernatant fractions. These samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using anti-FLAG or anti-NPTII antibodies, and these immunoblots are shown. NPTII was used as a control for nonspecific cell lysis. The DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 secreted AvrB1-FLAG in culture, indicating that HrpJ was not required for type III secretion of this effector into culture supernatants.
Failure to elicit an Avr protein-dependent HR may be due to the inability to inject the Avr protein (i.e., effector protein) into plant cells, or it may be due to the failure of the Avr protein to be exported from the bacterial cell. To determine whether the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 was competent to secrete AvrB1 via the TTSS, we performed secretion assays with DC3000 and UNL140 expressing AvrB1-FLAG. Immunoblot analysis of culture supernatant fractions confirmed that AvrB1-FLAG was secreted via the TTSS by both DC3000 and UNL140 (Fig. 4B). Collectively, these data indicate that the DC3000 hrpJ mutant cannot translocate AvrB1 or AvrRpt2 in the amounts required to elicit an HR. Because the hrpJ mutant secreted AvrB1 in culture, the translocation defect exhibited by this mutant appears to be at the level of translocation and not in the secretion of these proteins from the bacterial cell.
We used CyaA translocation assays to test whether UNL140 was defective in the translocation of other P. syringae type III effectors that have previously been shown to be translocated into plant cells by P. syringae. Constructs that encoded AvrPto1-CyaA, AvrB1-CyaA, HopB1-CyaA, and AvrPtoB-CyaA were electroporated into wild-type DC3000 and the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140. N. benthamiana was infiltrated with these strains, and cAMP levels in plant tissue were determined at 10 h postinfiltration. In each case, cAMP levels were significantly elevated in tissue infiltrated with DC3000 expressing the effector-CyaA fusions whereas cAMP levels in tissue infiltrated with the corresponding UNL140 strains were extremely low, indicating that UNL140 is defective in translocation (Table 2). It is important to note that even though cAMP levels were low in samples infiltrated with UNL140 expressing AvrB1-CyaA and AvrPtoB-CyaA, they were higher than the levels produced by UNL140 infiltrated with HopB1-CyaA and AvrPto1-CyaA (Table 2). This suggests that the translocation of specific effectors was affected differently by the absence of HrpJ. This is consistent with UNL140 retaining residual nonhost HR-eliciting ability (Fig. 3). It is not clear whether the very low levels of cAMP produced by all of the effector-CyaA fusion strains correspond to biologically relevant translocation. Indeed, the fact that UNL140 expressing AvrB1 did not elicit an HR when infiltrating A. thaliana (Fig. 4A) suggests that the translocation of AvrB1 was not at levels needed for detection by the RPM1-dependent innate immune system. In sum, HrpJ plays an important role in the translocation of specific effectors but is not required for the type III secretion of effectors from the bacterial cell.
TABLE 2.
Adenylate cyclase (CyaA) translocation assays of effector CyaA fusions in wild-type DC3000 and the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140
| Effector-CyaA fusiona | cAMP activity (pmol/μg protein)b for:
|
|
|---|---|---|
| DC3000 | UNL140 | |
| AvrPto1 | 123.3 ± 3.5 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| AvrB1 | 58.2 ± 0.0 | 4.8 ± 0.0 |
| HopB1 | 50.1 ± 5.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| AvrPtoB | 51.0 ± 5.2 | 8.2 ± 1.3 |
Wild-type DC3000 or the hrpJ mutant UNL140 carrying pLN1985 (AvrPto1), pLN918 (AvrB1), pLN421 (HopB1), or pLN1979 (AvrPtoB) was used in CyaA assays.
cAMP was quantified in triplicate for each sample, and the values are means ± standard deviations.
DC3000 hrpJ mutants can secrete the HrpA1 pilus protein and the AvrPto1 effector in culture but cannot secrete the HrpZ1 harpin.
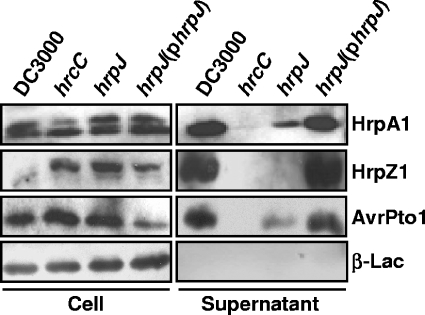
The failure of effectors to be translocated by the DC3000 hrpJ mutant may be related to the failure of the mutant to secrete to the milieu accessory proteins needed for translocation. To investigate more closely the effect that HrpJ has on secretion in culture of other type III substrates, we performed type III secretion assays that monitored the secretion of three different types of type III secreted proteins from the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140: HrpA1, which is the major component of the Hrp pilus (63); HrpZ1, which is an accessory protein belonging to a group of proteins called harpins, which are secreted in high abundance in culture (34); and AvrPto1, which is a member of the effector class and known to be secreted in culture (66). DC3000 and UNL140 were grown in type III-inducing conditions, separated into cell-bound and supernatant fractions, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using antibodies that recognized natively expressed proteins. HrpA1 and AvrPto1 were detected in the supernatant fraction of DC3000 and UNL140, although in somewhat reduced amounts (Fig. 5). Surprisingly, we were unable to detect HrpZ1 in supernatant fractions of UNL140 cultures even though the experiment was repeated several times, indicating that HrpJ plays an important role in the secretion of HrpZ1 that is different from its role in the type III secretion of either HrpA1 or AvrPto1 (Fig. 5).
FIG. 5.
DC3000 hrpJ mutant maintains the ability to secrete HrpA1 and AvrPto1 in culture but cannot secrete detectable amounts of HrpZ1. DC3000 strains were grown in type III-inducing conditions, and secretion assays were performed to determine whether natively expressed TTSS substrates were secreted in culture. The strains used were as follows: wild-type DC3000, a DC3000 hrcC mutant defective in TTSS, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140, and UNL140 carrying pLN726, which contains hrpJ. The cultures were separated into cell-bound and supernatant fractions, and these were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis. HrpA1, HrpZ1, and AvrPto1 were detected with anti-HrpA1, -HrpZ1, and -AvrPto1 antibodies, respectively. Each strain also contained pCPP2318, which encodes β-lactamase (β-Lac) lacking its export sequence and therefore remains cell bound unless significant nonspecific cell lysis occurs. Reduced levels of HrpA1 and AvrPto1 were detected in hrpJ supernatant fractions. In contrast, HrpZ1 was not detected in supernatant fractions of the hrpJ mutant.
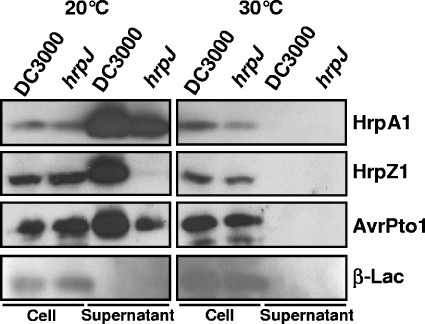
Yersinia mutants defective in YopN constitutively secreted Yop effectors even under conditions that normally inhibit type III secretion (i.e., in the presence of 2.5 mM calcium at 37°C) (25, 69). The addition of calcium to DC3000 cultures did not inhibit type III secretion (data not shown). However, the P. syringae TTSS does secrete TTSS substrates in a temperature- and pH-dependent manner (66). To determine whether the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 displayed a deregulation phenotype analogous to that of Yersinia yopN mutants, we tested whether UNL140 could secrete TTSS substrates in temperature and pH conditions reported to inhibit P. syringae type III secretion (66). We performed type III secretion assays with wild-type DC3000 and the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 at 20°C, a permissive temperature for secretion, and at 30°C, a nonpermissive temperature for type III secretion. At 20°C, we detected HrpA1 and AvrPto1 in the supernatant fractions of both wild-type DC3000 and UNL140, indicating that these proteins were secreted from both strains. However, at 30°C, neither strain secreted detectable amounts of HrpA1 or AvrPto1 to the supernatant fraction. As observed in Fig. 5, HrpZ1 was not detected in the supernatant fractions of UNL140. In analogous experiments with varied pH, secretion assays were performed with a pH of 6.0, which is permissive for type III secretion, and a pH of 7.0, which is nonpermissive. HrpA1 and AvrPto1 were found to be secreted by both strains under the permissive-pH condition but not under the nonpermissive-pH condition (data not shown). To ensure that the TTSS was fully induced, we repeated the temperature and pH experiments with strains constitutively expressing HrpL, which is an alternate sigma factor required for the transcription of P. syringae type III-related genes (68). These experiments produced results identical to those described above with strains that did not express HrpL in trans (data not shown). Thus, UNL140 did not exhibit a detectable deregulation phenotype and maintained a temperature- and pH-dependent TTSS.
DISCUSSION
We have shown here that HrpJ is secreted and translocated by the P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 TTSS (Fig. 1). A DC3000 mutant defective in HrpJ was severely affected in its ability to grow in planta and cause disease symptoms in A. thaliana (Fig. 2). This demonstrates that HrpJ is important for the DC3000 TTSS and plant pathogenesis. Additionally, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant possessed phenotypes that suggested that it was impaired in effector translocation into plant cells (Fig. 3 and 4; Table 2). Interestingly, this defect appeared to be at the level of translocation because the hrpJ mutant secreted AvrPto1 and AvrB1, two type III effectors, in culture (Fig. 4B and 5) but was unable to translocate these and other effectors into plant cells (Fig. 4 and Table 2). The DC3000 hrpJ mutant was also capable of secreting HrpA1 (Fig. 5), the main component of the Hrp type III pilus (63), suggesting that the hrpJ mutant could secrete type III effectors and at least one class of extracellular accessory protein. However, the hrpJ mutant could not secrete the HrpZ1 harpin (Fig. 5), a protein that is a candidate translocator and normally secreted in high abundance by P. syringae in culture (1, 34, 50).
What is the role of HrpJ in the DC3000 TTSS? One important clue is that HrpJ shares weak similarity with YopN from Yersinia spp. as well as other apparent YopN homologs in other TTSS-containing bacteria (4, 40). YopN acts as a control protein for the Ysc TTSS because Yersinia sp. yopN mutants constitutively secrete Yop type III effectors in culture, even under conditions (e.g., in the presence of calcium) that normally prevent Yop secretion (25). The possibility of identifying a DC3000 mutant that constitutively secretes effectors was one of the reasons that we initiated this study. However, as we show here, the DC3000 hrpJ mutant did not secrete type III effectors under temperature and pH conditions known to inhibit type III secretion (Fig. 6). Thus, we failed to detect a constitutive secretion phenotype similar to the phenotype exhibited by Yersinia yopN mutants. It may be that a hrpJ mutant would exhibit such a phenotype under other repressive conditions that as of yet have not been identified.
FIG. 6.
DC3000 hrpJ mutant retains a TTSS that functions in a temperature-dependent manner. DC3000 and the DC3000 hrpJ mutant UNL140 were grown in type III-inducing medium at temperatures that are known to induce wild-type DC3000 type III secretion (20°C) or inhibit it (30°C). These cultures were separated into cell-bound and supernatant fractions and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis. HrpA1, HrpZ1, and AvrPto1 were detected with anti-HrpA1, -HrpZ1, and -AvrPto1 antibodies, respectively. Both strains also carried pCPP2318, which encodes β-lactamase (β-Lac) without its export signal and acted as a control for nonspecific cell lysis. An immunoblot from a representative experiment is shown. UNL140 type III secretion maintained regulation by temperature as previously shown for DC3000 (66).
We found that HrpJ-CyaA was translocated into plant cells (Fig. 1B). Since hrpJ resides in a DNA region that encodes the Hrp type III apparatus and the hrpJ mutant is defective in translocation, we suspect that HrpJ plays a role in controlling the secretion of other type III secreted proteins. It does appear that type III secreted proteins that act outside the plant cell can be found to be translocated. For example, Guttman et al. (32) found that HrpW1 was translocated into plant cells by P. syringae even though its pectate lyase domain suggests that this protein is active on the plant cell wall. The Yersinia YopN protein has been reported to be translocated into animal cells even though no function in host cells has been determined (15, 20, 26). Thus, the translocation of a type III secreted protein inside eukaryotic cells does not necessarily indicate that it acts within eukaryotic cells.
The DC3000 hrpJ mutant was severely reduced in its ability to translocate type III effectors into plant cells (Fig. 4 and Table 2). However, it retained a reduced ability to elicit a nonhost HR on tobacco plants (Fig. 3), and strains expressing AvrB1-CyaA and AvrPtoB-CyaA produced cAMP amounts that, while very small, were still significantly larger than cAMP production by strains expressing AvrPto1-CyaA and HopB1-CyaA. This suggests that the hrpJ mutant retained a weak ability to translocate specific effectors. Because the hrpJ mutant is essentially nonpathogenic (Fig. 2), the very low level of translocation must be insufficient to support pathogenicity. The translocation defect in the DC3000 hrpJ mutant appears more severe than those in Yersinia yopN mutants, which retain the ability to translocate effectors (7, 20). This suggests that these proteins, while sharing similarities, may not have identical roles in their respective TTSSs.
The implications of the failure of the hrpJ mutant to secrete the HrpZ1 harpin in culture deserve additional comment. Unlike the hrpJ mutant, hrpZ1 mutants are not greatly affected in pathogenicity (37). Therefore, it seems likely that the hrpJ phenotype is not due solely to the failure to secrete HrpZ1. The secretion of other extracellular accessory proteins may be blocked in hrpJ mutants. Interestingly, Salmonella enterica InvE, a type III-related protein that has been reported to share similarity with YopN (40), is required for effector translocation and the secretion of wild-type amounts of the translocators SipB, SipC, and SipD (48). As noted above, there is indirect evidence that HrpZ1 acts as a translocator (28, 50), and our results provide additional circumstantial evidence that this is the case. Therefore, an attractive hypothesis is that the P. syringae hrpJ mutant is unable to translocate type III effectors due, at least in part, to its inability to secrete translocators.
The hrpJ mutant phenotype seems more similar to the S. enteric invE mutant phenotype than it does to the phenotype of Yersinia yopN mutants in that yopN mutants can secrete all proteins known to be secreted by their wild-type strains. It should be noted that one important difference between InvE and HrpJ (and YopN) is that InvE remains cell bound and is not a type III secreted protein (48). This leaves open the possibility that YopN and HrpJ exert their function from within the bacterial cell. Indeed, recent models for YopN function suggest that YopN blocks the secretion of other type III secreted proteins by plugging the type III pore from within the bacterial cell (15, 24).
Our current model for HrpJ is that it acts as a control protein that may determine which type III proteins are secreted and the order of their secretion. For example, there may be a requirement for HrpZ1 and other accessory proteins to be secreted prior to the secretion of the effectors and, in the absence of HrpJ, type III effectors are inappropriately released before contact with the plant cell is established, leading to severely reduced translocation. This translocation defect may be further exacerbated by the failure of HrpZ1 to be extracellularly localized. Future experiments will identify the inventory of type III secreted proteins that are not secreted in culture from the hrpJ mutant. Identifying this group of proteins should shed additional light on why the hrpJ mutant is defective in translocation. We will also test whether the hrpJ mutant phenotypes are complemented by a cell-bound HrpJ derivative lacking type III secretion signals. This will allow us to address whether there is a requirement for HrpJ to be secreted before effectors can be translocated or for HrpZ1 to be secreted. Determining the molecular basis for the role of HrpJ in type III secretion will likely lead to a better understanding of how type III protein traffic is deployed during bacterium-plant interactions.
Acknowledgments
We thank Alan Collmer, Martin Romantschuk, and Sheng Yang He for generously providing antibodies that recognize AvrPto1, HrpA1, and HrpZ1, respectively. We thank Zhengxiang Ge for providing construct pLN2043, Tanja Petnicki-Ocwieja for providing constructs pLN820 and pLN918, Vincent Tam for providing construct pLN307, and Fang Tian for providing construct pLN1979. We also thank members of the Alfano laboratory for reviewing the manuscript and for fruitful discussions.
This research was supported by National Science Foundation grants MCB-0317165 and MCB-0544447 and funds from the Plant Science Initiative at the University of Nebraska.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alfano, J. R., D. W. Bauer, T. M. Milos, and A. Collmer. 1996. Analysis of the role of the Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae HrpZ harpin in elicitation of the hypersensitive response in tobacco using functionally nonpolar hrpZ deletion mutants, truncated HrpZ fragments, and hrmA mutations. Mol. Microbiol. 19:715-728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alfano, J. R., A. O. Charkowski, W. Deng, J. L. Badel, T. Petnicki-Ocwieja, K. van Dijk, and A. Collmer. 2000. The Pseudomonas syringae Hrp pathogenicity island has a tripartite mosaic structure composed of a cluster of type III secretions genes bounded by exchangeable effector and conserved effector loci that contribute to parasitic fitness and pathogenicity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:4856-4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alfano, J. R., and A. Collmer. 1996. Bacterial pathogens in plants: life up against the wall. Plant Cell 8:1683-1698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alfano, J. R., and A. Collmer. 1997. The type III (Hrp) secretion pathway of plant pathogenic bacteria: trafficking harpins, Avr proteins, and death. J. Bacteriol. 179:5655-5662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Altschul, S. F., T. L. Madden, A. A. Schäffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller, and D. J. Lipman. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389-3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bent, A. F., B. N. Kunkel, D. Dahlbeck, K. L. Brown, R. Schmidt, J. Giraudat, J. Leung, and B. J. Staskawicz. 1994. RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856-1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boland, A., M.-P. Sory, M. Iriarte, C. Kerbourch, P. Wattiau, and G. R. Cornelis. 1996. Status of YopM and YopN in the Yersinia Yop virulon: YopM of Y. enterocolitica is internalized inside the cytosol of PU5-1.8 macrophages by the YopB, D, N delivery apparatus. EMBO J. 15:5191-5201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brubaker, R. R., and M. J. Surgalla. 1964. The effect of Ca++ and Mg++ on lysis, growth, and productionof virulence antigens by Pasteurella pestis J. Infect. Dis. 114:13-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Buell, C. R., V. Joardar, M. Lindeberg, J. Selengut, I. T. Paulsen, M. L. Gwinn, R. J. Dodson, R. T. Deboy, A. S. Durkin, J. F. Kolonay, R. Madupu, S. Daugherty, L. Brinkac, M. J. Beanan, D. H. Haft, W. C. Nelson, T. Davidsen, N. Zafar, L. Zhou, J. Liu, Q. Yuan, H. Khouri, N. Fedorova, B. Tran, D. Russell, K. Berry, T. Utterback, S. E. Van Aken, T. V. Feldblyum, M. D'Ascenzo, W. L. Deng, A. R. Ramos, J. R. Alfano, S. Cartinhour, A. K. Chatterjee, T. P. Delaney, S. G. Lazarowitz, G. B. Martin, D. J. Schneider, X. Tang, C. L. Bender, O. White, C. M. Fraser, and A. Collmer. 2003. The complete sequence of the Arabidopsis and tomato pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:10181-10186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Buttner, D., and U. Bonas. 2002. Port of entry—the type III secretion translocon. Trends Microbiol. 10:186-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Casper-Lindley, C., D. Dahlbeck, E. T. Clark, and B. J. Staskawicz. 2002. Direct biochemical evidence for type III secretion-dependent translocation of the AvrBs2 effector protein into plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:8336-8341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chang, J. H., J. M. Urbach, T. F. Law, L. W. Arnold, A. Hu, S. Gombar, S. R. Grant, F. M. Ausubel, and J. L. Dangl. 2005. A high-throughput, near-saturating screen for type III effector genes from Pseudomonas syringae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:2549-2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Charkowski, A. O., J. R. Alfano, G. Preston, J. Yuan, S. Y. He, and A. Collmer. 1998. The Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato HrpW protein has domains similar to harpins and pectate lyases and can elicit the plant hypersensitive response and bind to pectate. J. Bacteriol. 180:5211-5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Charkowski, A. O., H.-C. Huang, and A. Collmer. 1997. Altered localization of HrpZ in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae hrp mutants suggests that different components of the type III secretion pathway control protein translocation across the inner and outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 179:3866-3874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cheng, L. W., O. Kay, and O. Schneewind. 2001. Regulated secretion of YopN by the type III machinery of Yersinia enterocolitica J. Bacteriol. 183:5293-5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chisholm, S. T., G. Coaker, B. Day, and B. J. Staskawicz. 2006. Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Collmer, A., M. Lindeberg, T. Petnicki-Ocwieja, D. Schneider, and J. R. Alfano. 2002. Genomic mining type III secretion system effectors in Pseudomonas syringae yields new picks for all TTSS prospectors. Trends Microbiol. 10:462-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cuppels, D. A., and T. Ainsworth. 1995. Molecular and physiological characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola strains that produce the phytotoxin coronatine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61:3530-3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dangl, J. L. 1994. The enigmatic avirulence genes of phytopathogenic bacteria, p. 99-118. In J. L. Dangl (ed.), Current topics in microbiology and immunology: bacterial pathogenesis of plants and animals—molecular and cellular mechanisms, vol. 192. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Day, J. B., F. Ferracci, and G. V. Plano. 2003. Translocation of YopE and YopN into eukaryotic cells by Yersinia pestis yopN, tyeA, sycN, yscB and lcrG deletion mutants measured using a phosphorylatable peptide tag and phosphospecific antibodies. Mol. Microbiol. 47:807-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Espinosa, A., and J. R. Alfano. 2004. Disabling surveillance: bacterial type III secretion system effectors that suppress innate immunity. Cell. Microbiol. 6:1027-1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Espinosa, A., M. Guo, V. C. Tam, Z. Q. Fu, and J. R. Alfano. 2003. The Pseudomonas syringae type III-secreted protein HopPtoD2 possesses protein tyrosine phosphatase activity and suppresses programmed cell death in plants. Mol. Microbiol. 49:377-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Feil, H., W. S. Feil, P. Chain, F. Larimer, G. DiBartolo, A. Copeland, A. Lykidis, S. Trong, M. Nolan, E. Goltsman, J. Thiel, S. Malfatti, J. E. Loper, A. Lapidus, J. C. Detter, M. Land, P. M. Richardson, N. C. Kyrpides, N. Ivanova, and S. E. Lindow. 2005. Comparison of the complete genome sequences of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae B728a and pv. tomato DC3000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:11064-11069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ferracci, F., F. D. Schubot, D. S. Waugh, and G. V. Plano. 2005. Selection and characterization of Yersinia pestis YopN mutants that constitutively block Yop secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 57:970-987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Forsberg, A., A. M. Viitanen, M. Skurnik, and H. Wolf-Watz. 1991. The surface-located YopN protein is involved in calcium signal transduction in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 5:977-986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Francis, M. S., and H. Wolf-Watz. 1998. YopD of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is translocated into the cytosol of HeLa epithelial cells: evidence of a structural domain necessary for translocation. Mol. Microbiol. 29:799-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Genin, S., and C. A. Boucher. 1994. A superfamily of proteins involved in different secretion pathways in gram-negative bacteria: modular structure and specificity of the N-terminal domain. Mol. Gen. Genet. 243:112-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gopalan, S., D. W. Bauer, J. R. Alfano, A. O. Loniello, S. Y. He, and A. Collmer. 1996. Expression of the Pseudomonas syringae avirulence protein AvrB in plant cells alleviates its dependence on the hypersensitive response and pathogenicity (Hrp) secretion system in eliciting genotype-specific hypersensitive cell death. Plant Cell 8:1095-1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Grant, M. R., L. Godlard, E. Straube, T. Ashfield, J. Lewald, A. Sattler, R. W. Innes, and J. L. Dangl. 1995. Structure of the Arabidopsis RPM1 gene enabling dual specificity disease resistance. Science 269:843-846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Greenberg, J. T., and B. A. Vinatzer. 2003. Identifying type III effectors of plant pathogens and analyzing their interaction with plant cells. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6:20-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo, M., S. T. Chancey, F. Tian, Z. Ge, Y. Jamir, and J. R. Alfano. 2005. Pseudomonas syringae type III chaperones ShcO1, ShcS1, and ShcS2 facilitate translocation of their cognate effectors and can substitute for each other in the secretion of HopO1-1. J. Bacteriol. 187:4257-4269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guttman, D. S., B. A. Vinatzer, S. F. Sarkar, M. V. Ranall, G. Kettler, and J. T. Greenberg. 2002. A functional screen for the type III (Hrp) secretome of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae Science 295:1722-1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hanahan, D. 1983. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 166:557-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.He, S. Y., H.-C. Huang, and A. Collmer. 1993. Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae harpinPss: a protein that is secreted via the Hrp pathway and elicits the hypersensitive response in plants. Cell 73:1255-1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.He, S. Y., K. Nomura, and T. S. Whittam. 2004. Type III protein secretion mechanism in mammalian and plant pathogens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1694:181-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Heath, M. C. 2000. Hypersensitive response-related death. Plant Mol. Biol. 44:321-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hirano, S. S., A. O. Charkowski, A. Collmer, D. K. Willis, and C. D. Upper. 1999. Role of the Hrp type III protein secretion system in growth of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae B728a on host plants in the field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:9851-9856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hirano, S. S., and C. D. Upper. 2000. Bacteria in the leaf ecosystem with emphasis on Pseudomonas syringae—a pathogen, ice nucleus, and epiphyte. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64:624-653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hoyos, M. E., C. M. Stanley, S. Y. He, S. Pike, X.-A. Pu, and A. Novacky. 1996. The interaction of harpinPss with plant cell walls. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 9:608-616. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hueck, C. J. 1998. Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62:379-433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huynh, T. V., D. Dahlbeck, and B. J. Staskawicz. 1989. Bacterial blight of soybean: regulation of a pathogen gene determining host cultivar specificity. Science 245:1374-1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jamir, Y., M. Guo, H.-S. Oh, T. Petnicki-Ocwieja, S. Chen, X. Tang, M. B. Dickman, A. Collmer, and J. R. Alfano. 2004. Identification of Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors that suppress programmed cell death in plants and yeast. Plant J. 37:554-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jin, Q., and S.-Y. He. 2001. Role of the Hrp pilus in type III protein secretion in Pseudomonas syringae Science 294:2556-2558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Joardar, V., M. Lindeberg, R. W. Jackson, J. Selengut, R. Dodson, L. M. Brinkac, S. C. Daugherty, R. Deboy, A. S. Durkin, M. G. Giglio, R. Madupu, W. C. Nelson, M. J. Rosovitz, S. Sullivan, J. Crabtree, T. Creasy, T. Davidsen, D. H. Haft, N. Zafar, L. Zhou, R. Halpin, T. Holley, H. Khouri, T. Feldblyum, O. White, C. M. Fraser, A. K. Chatterjee, S. Cartinhour, D. J. Schneider, J. Mansfield, A. Collmer, and C. R. Buell. 2005. Whole-genome sequence analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448A reveals divergence among pathovars in genes involved in virulence and transposition. J. Bacteriol. 187:6488-6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Keen, N. T., S. Tamaski, D. Kobayashi, and D. Trollinger. 1988. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 70:191-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.King, E. O., M. K. Ward, and D. E. Raney. 1954. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J. Lab. Med. 22:301-307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kovach, M. E., P. H. Elzer, D. S. Hill, G. T. Robertson, M. A. Farris, R. M. Roop, and K. M. Peterson. 1995. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kubori, T., and J. E. Galan. 2002. Salmonella type III secretion-associated protein InvE controls translocation of effector proteins into host cells. J. Bacteriol. 184:4699-4708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Labes, M., A. Puhler, and R. Simon. 1990. A new family of RSF1010-derived expression and lac-fusion broad-host-range vectors for gram-negative bacteria. Gene 89:37-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lee, J., B. Klusener, G. Tsiamis, C. Stevens, C. Neyt, A. P. Tampakaki, N. J. Panopoulos, J. Noller, E. W. Weiler, G. R. Cornelis, and J. W. Mansfield. 2001. HrpZPsph from the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola binds to lipid bilayers and forms an ion-conducting pore in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:289-294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li, C. M., I. Brown, J. Mansfield, C. Stevens, T. Boureau, M. Romantschuk, and S. Taira. 2002. The Hrp pilus of Pseudomonas syringae elongates from its tip and acts as a conduit for translocation of the effector protein HrpZ. EMBO J. 21:1909-1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lindeberg, M., J. Stavrinides, J. H. Chang, J. R. Alfano, A. Collmer, J. L. Dangl, J. T. Greenberg, J. W. Mansfield, and D. S. Guttman. 2005. Proposed guidelines for a unified nomenclature and phylogenetic analysis of type III Hop effector proteins in the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 18:275-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lindgren, P. B. 1997. The role of hrp genes during plant-bacterial interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 35:129-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lindgren, P. B., R. C. Peet, and N. J. Panopoulos. 1986. Gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. “phaseolicola” controls pathogenicity of bean plants and hypersensitivity on nonhost plants. J. Bacteriol. 168:512-522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Michiels, T., P. Wattiau, R. Brasseur, J.-M. Ruysschaert, and G. Cornelis. 1990. Secretion of Yop proteins by Yersiniae. Infect. Immun. 58:2840-2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mindrinos, M., F. Katagiri, G.-L. Yu, and F. M. Ausubel. 1994. The A. thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell 78:1089-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mudgett, M. B. 2005. New insights to the function of phytopathogenic bacterial type III effectors in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 56:509-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nomura, K., M. Melotto, and S. Y. He. 2005. Suppression of host defense in compatible plant-Pseudomonas syringae interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8:1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Petnicki-Ocwieja, T., D. J. Schneider, V. C. Tam, S. T. Chancey, L. Shan, Y. Jamir, L. M. Schechter, M. D. Janes, C. R. Buell, X. Tang, A. Collmer, and J. R. Alfano. 2002. Genomewide identification of proteins secreted by the Hrp type III protein secretion system of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:7652-7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Petnicki-Ocwieja, T., K. van Dijk, and J. R. Alfano. 2005. The hrpK operon of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 encodes two proteins secreted by the type III (Hrp) protein secretion system: HopB1 and HrpK, a putative type III translocator. J. Bacteriol. 187:649-663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pettersson, J., R. Nordfelth, E. Dubinina, T. Bergman, M. Gustafsson, K. E. Magnusson, and H. Wolf-Watz. 1996. Modulation of virulence factor expression by pathogen target cell contact. Science 273:1231-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pirhonen, M. U., J. C. Lidell, D. L. Rowley, S. W. Lee, S. Jin, Y. Liang, S. Silverstone, N. T. Keen, and S. W. Hutcheson. 1996. Phenotypic expression of Pseudomonas syringae avr genes in E. coli is linked to the activities of the hrp-encoded secretion system. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 9:252-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Roine, E., W. Wei, J. Yuan, E. L. Nurmiaho-Lassila, N. Kalkkinen, M. Romantschuk, and S. Y. He. 1997. Hrp pilus: an hrp-dependent bacterial surface appendage produced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:3459-3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schechter, L. M., K. A. Roberts, Y. Jamir, J. R. Alfano, and A. Collmer. 2004. Pseudomonas syringae type III secretion system targeting signals and novel effectors studied with a Cya translocation reporter. J. Bacteriol. 186:543-555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sory, M. P., and G. R. Cornelis. 1994. Translocation of ahybrid YopE-adenylate cyclase from Yersinia enterocolitica into HeLa cells. Mol. Microbiol. 14:583-594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.van Dijk, K., D. E. Fouts, A. H. Rehm, A. R. Hill, A. Collmer, and J. R. Alfano. 1999. The Avr (effector) proteins HrmA (HopPsyA) and AvrPto are secreted in culture from Pseudomonas syringae pathovars via the Hrp (type III) protein secretion system in a temperature- and pH-sensitive manner. J. Bacteriol. 181:4790-4797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wei, Z.-M., R. J. Laby, C. H. Zumoff, D. W. Bauer, S. Y. He, A. Collmer, and S. V. Beer. 1992. Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora Science 257:85-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Xiao, Y., and S. W. Hutcheson. 1994. A single promoter sequence recognized by a newly identified alternate sigma factor directs expression of pathogenicity and host range determinants in Pseudomonas syringae J. Bacteriol. 176:3089-3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yother, J., and J. D. Goguen. 1985. Isolation and characterization of Ca2+-blind mutants of Yersinia pestis. J. Bacteriol. 164:704-711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yuan, J., and S. Y. He. 1996. The Pseudomonas syringae Hrp regulation and secretion system controls the production and secretion of multiple extracellular proteins. J. Bacteriol. 178:6399-6402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]