Full text
PDF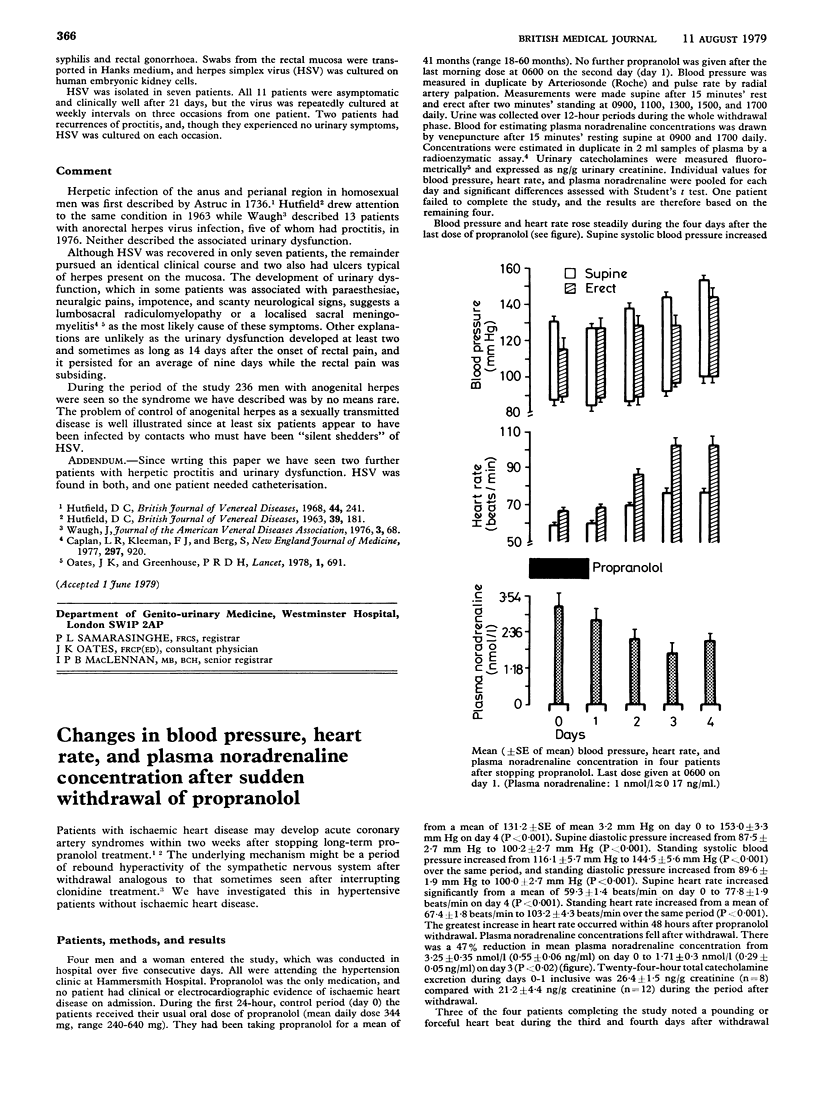

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Henry D. P., Starman B. J., Johnson D. G., Williams R. H. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for norepinephrine in tissues and plasma. Life Sci. 1975 Feb 1;16(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Wing L. M., Dargie H. J., Hamilton C. A., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Clonidine withdrawal in hypertension. Changes in blood-pressure and plasma and urinary noradrenaline. Lancet. 1977 Jun 4;1(8023):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92715-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., LISHAJKO F. Improved technique for the fluorimetric estimation of catecholamines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Apr;51:348–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


