Abstract
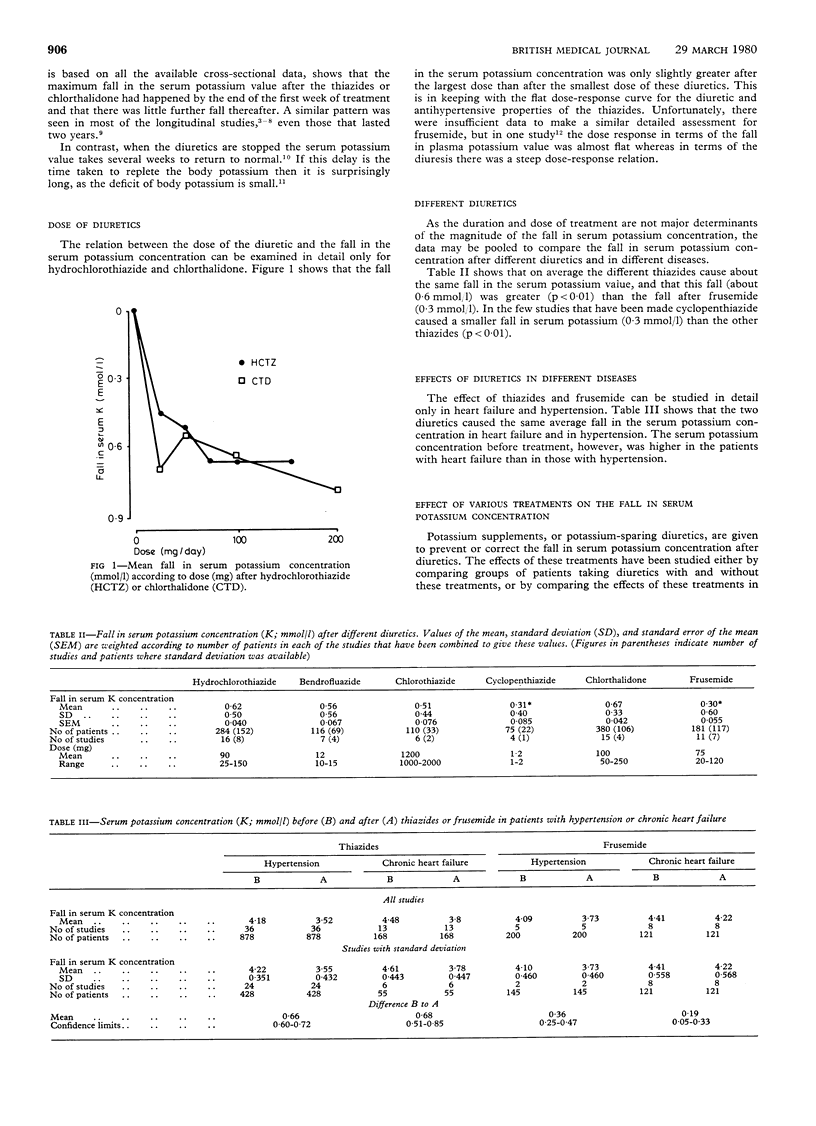
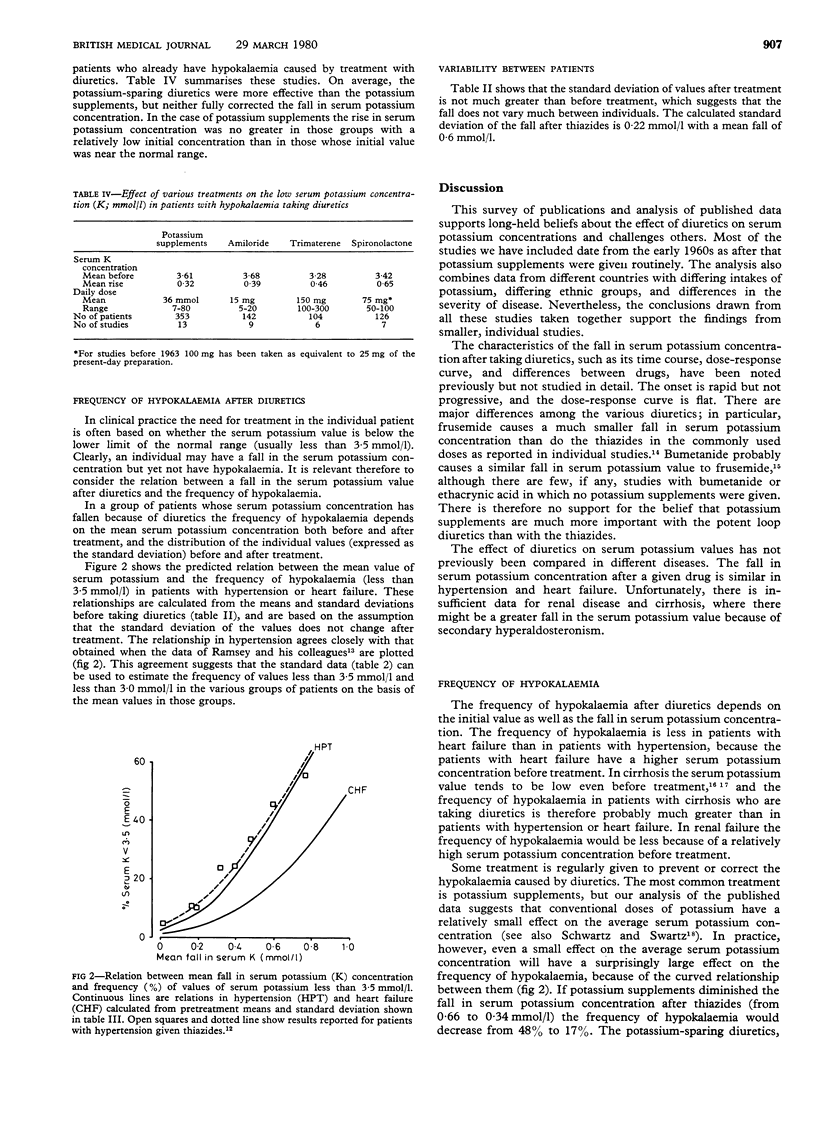
Published data have been used to define the characteristics of the fall in serum potassium concentration after taking diuretics and the efficacy of the various treatments given to prevent or correct it. The average fall is less after the usual doses of frusemide (about 0.3 mmol/l) than after the usual doses of thiazides (about 0.6 mmol/l) and is little influenced by the dose or duration of treatment. The fall with a given drug is the same in heart failure and hypertension, but the initial serum potassium concentration is higher in heart failure, so that the final value is lower in hypertension. In standard doses potassium supplements are less effective than potassium-retaining diuretics in correcting the hypokalaemia. The relation between the average serum potassium value and the frequency of low values (hypokalaemia) is such that very low values after taking diuretics are unusual in patients with hypertension or heart failure. Hypokalaemia would almost disappear as an important complication of diuretic treatment if it was defined as a value less than 3.0 mmol/l rather than as a value less than 3.5 mmol/l.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMATUZIO D. S., STUTZMAN F., SHRIFTER N., NESBITT S. A study of serum electrolytes (Na, K, Ca, P) in patients with severely decompensated portal cirrhosis of the liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Jan;39(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARTMAN E. L., WISE R. A. Hypokalemia in liver cell failure. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J., Godfrey B. E., Hill D. M., Munro-Faure A. D., Sheldon J. A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and of frusemide in the treatment of hypertensive patients. Q J Med. 1971 Oct;40(160):541–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargie H. J., Boddy K., Kennedy A. C., King P. C., Read P. R., Ward D. M. Total body potassium in long-term frusemide therapy: is potassium supplementation necessary? Br Med J. 1974 Nov 9;4(5940):316–319. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5940.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson C., McLachlan M. S., Burkinshaw L., Morgan D. B. Effect of long-term diuretic treatment on body-potassium in heart-disease. Lancet. 1976 Nov 13;2(7994):1044–1047. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90965-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson S., Surawicz B. Ectopic beats and atrioventricular conduction disturbances. In patients with hypopotassemia. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Sep;120(3):280–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSFIELD E., Jr, GILLENWATER J. SIX-MONTH DOUBLE-BLIND STUDY OF BENZOTHIADIAZINE DRUG EFFECTS ON HYPERTENSION AND SELECTED BLOOD CHEMISTRIES. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1965 Apr;7:249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHEON D. E., MEHTA D., ROMANO A. DIURETIC ACTION OF FUROSEMIDE. Arch Intern Med. 1965 May;115:542–546. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1960.03860170024006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haug T. O. Time course of changes in concentration of some plasma components after frusemide. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 11;2(6036):622–622. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6036.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. J., Duffy G. J., Muldowney F. P. A comparison of diuretic induced potassium losses in normal and abnormal subjects. Ir J Med Sci. 1968 Mar;7(3):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02946448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesp R., Wilkinson P. R. Potassium supplementation of thiazide therapy. Lancet. 1976 Nov 20;2(7995):1144–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON L. C., GRIEBLE H. G., SCHOENBERGER J. A., FULLER J. B. TREATMENT OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE WITH DIURETICS. III. CHLORTHALIDONE ALONE AND IN COMBINATION WITH SPIRONOLACTONE. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Feb;247:164–174. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196402000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jättelä A. Clinical efficacy of fixed combinations of saluretic agents and potassium in sustained release form for the treatment of arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;4(3):146–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00561137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P., Harrington J. T. Diuretics and potassium metabolism: a reassessment of the need, effectiveness and safety of potassium therapy. Kidney Int. 1977 Jun;11(6):505–515. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. H. Adverse reactions to potassium chloride. Q J Med. 1974 Jul;43(171):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. H., Boddy K., Gray J. M., Mahaffey M., Mills E. Potassium supplements in patients receiving long-term diuretics for oedema. Q J Med. 1976 Jul;45(179):469–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leemhuis M. P., van Damme K. J., Struyvenberg A. Effects of chlorthalidone on serum and total body potassium in hypertensive patients. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200(1-2):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb08193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall A. J., Barritt D. W., Pocock J., Heaton S. T. Evaluation of beta blockade bendrofluazide, and prazosin in severe hypertension. Lancet. 1977 Feb 5;1(8006):271–274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchison L. E., Bewsher P. D. Lack of effect of bumetanide on body potassium content in hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;2(1):87–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb01691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ A. E., LAIDLAW J., HASLAM R. M., SHERLOCK S. Neuropsychiatric complications following chlorothiazide therapy in patients with hepatic cirrhosis: possible relation to hypokalaemia. Clin Sci. 1959 Aug;18:409–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay L. E., Boyle P., Ramsay M. H. Factors influencing serum potassium in treated hypertension. Q J Med. 1977 Oct;46(184):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. B., Swartz C. D. Dosage of potassium chloride elixir to correct thiazide-induced hypokalemia. JAMA. 1974 Nov 4;230(5):702–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiness E., Olesen K. H. Cardiac arrhythmias induced by hypokalaemia and potassium loss during maintenance digoxin therapy. Br Heart J. 1976 Feb;38(2):167–172. doi: 10.1136/hrt.38.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. R., Issler H., Hesp R., Raftery E. B. Total body and serum potassium during prolonged thiazide therapy for essential hypertension. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):759–762. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92432-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


