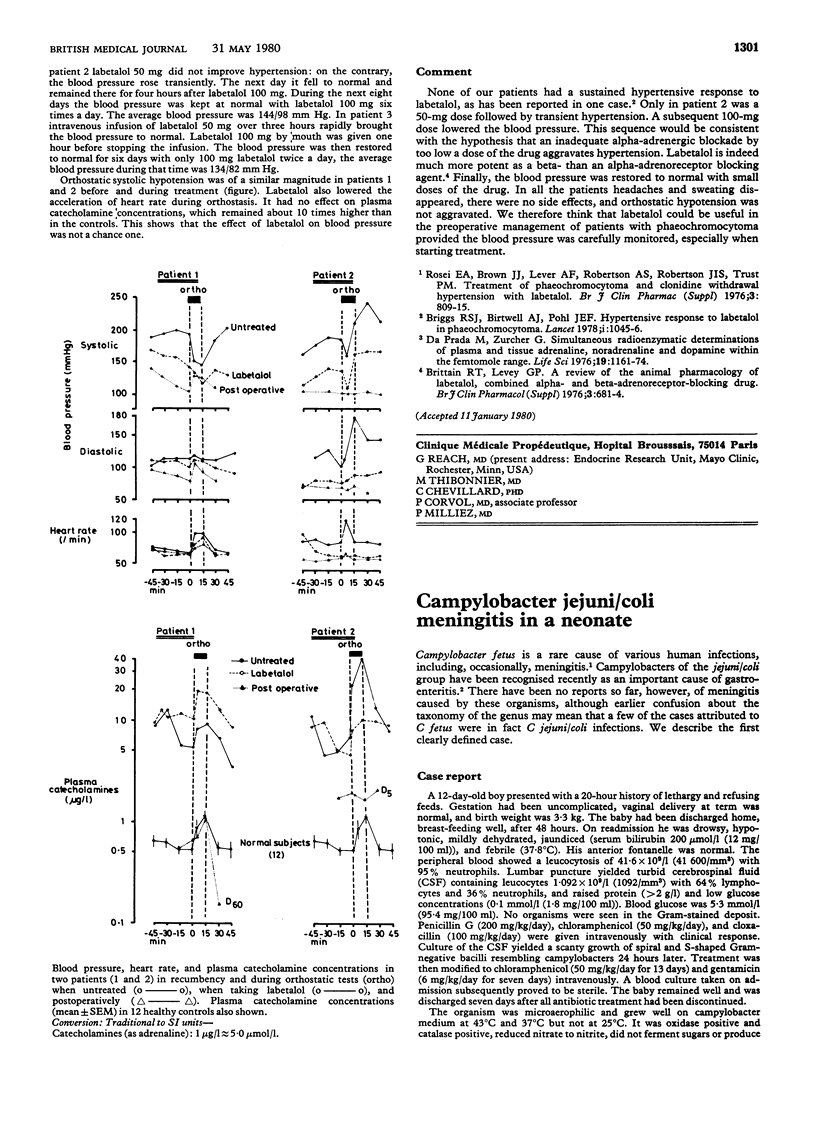
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs R. S., Birtwell A. J., Pohl J. E. Hypertensive response to labetalol in phaeochromocytoma. Lancet. 1978 May 13;1(8072):1045–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90772-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain R. T., Levy G. P. A review of the animal pharmacology of labetalol, a combined alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drug. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosei E. A., Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Robertson A. S., Robertson J. I., Trust P. M. Treatment of phaeochromocytoma and of clonidine withdrawal hypertension with labetalol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;3(4 Suppl 3):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]