Abstract
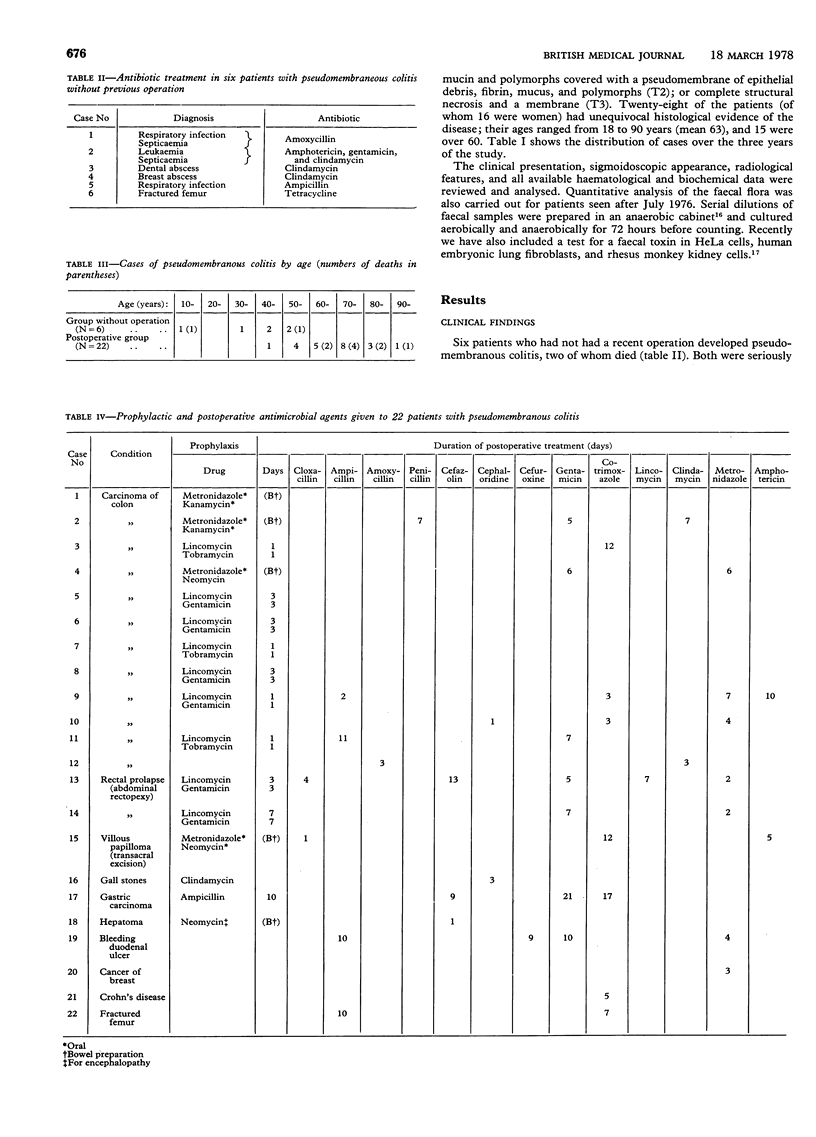
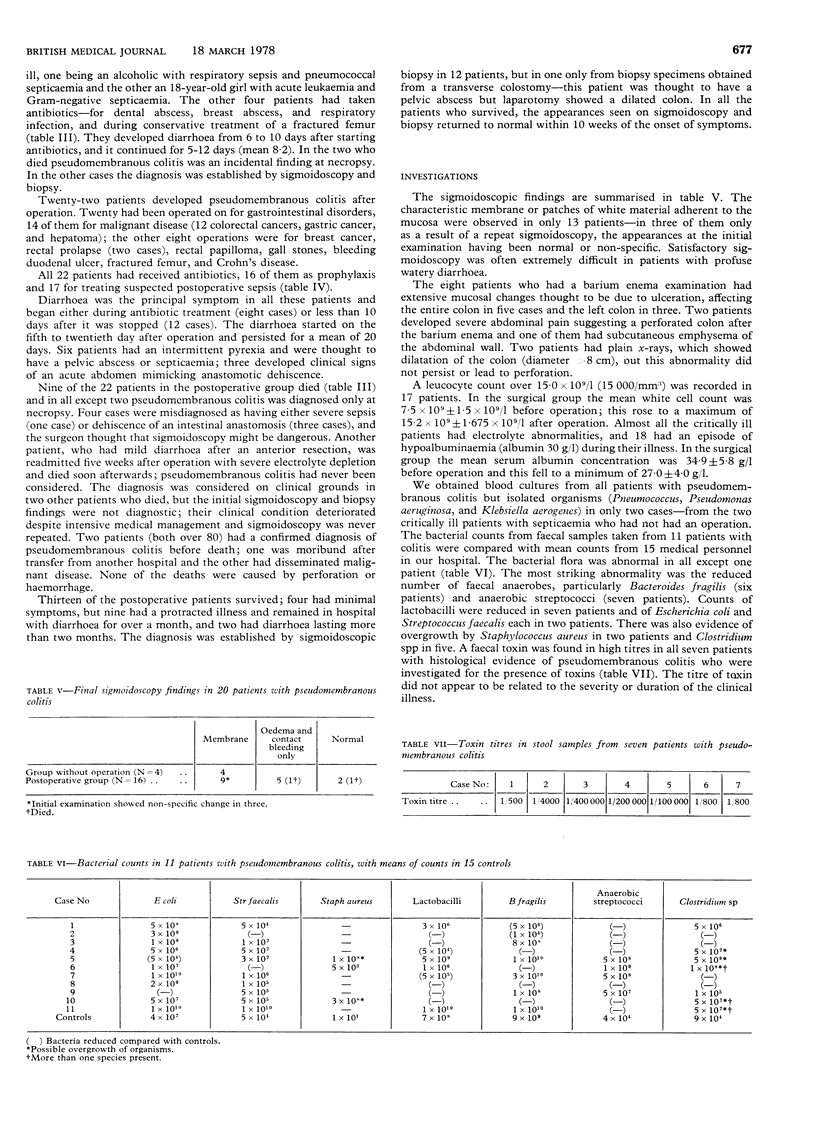
Twenty-eight patients with histologically proved pseudomembranous colitis have been seen in one hospital since July 1975. All patients with the disease had received antibiotics, six for infections not requiring operations; the other 22 cases all occurred after major surgery. All the patients had diarrhoea; six patients also had fever with clinical signs of sepsis, and three had abdominal pain thought to be due to anastomotic dehiscence after colonic resection. Pseudomembranous colitis was associated with white blood counts over 15 000/mm3 in 17 patients and albumin concentrations of less than 30 g/1 in 18. Pseudomembranous colitis was an incidental finding at necropsy in two of six patients who had not had an operation. Of the 22 patients who had had major surgery, nine died from this complication; in all except two of these cases the diagnosis was made only at necropsy. If pseudomembranous colitis is suspected on clinical grounds or if there is an unexplained complication after colorectal surgery repeat sigmoidoscopy and testing for faecal toxins should be carried out to establish the diagnosis so that prompt supportive treatment can be given.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen S. D., Dunn G. D., Page D. L., Wilson F. A. Bacteriological studies in a patient with antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):158–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis J. P., Parsons R. L., Salfield J. Colitis and diarrhoea: a problem with antibiotic therapy. Br J Surg. 1976 Apr;63(4):299–304. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A., Thomas M. Pseudomembranous colitis and co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1977 May 21;1(6072):1321–1321. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6072.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane T. E., King E. G. Fatal pseudomembranous enterocolitis following clindamycin therapy. Br J Surg. 1976 Apr;63(4):305–308. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee H. J., Ament M. E., Holmes E. C. Pseudomembranous colitis associated with cephazolin therapy. Am J Surg. 1977 Feb;133(2):247–248. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(77)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. J., Truelove S. C. Intensive intravenous regimen for membranous colitis. Br Med J. 1976 Aug 7;2(6031):354–354. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6031.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulston S. J., McGovern V. J. Pseudo-membranous colitis. Gut. 1965 Jun;6(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLECKNER M. S., BARGEN J. A., BAGGENSTOSS A. H. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis: clinicopathologic study of fourteen cases in which the disease was not preceded by an operation. Gastroenterology. 1952 Jun;21(2):212–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Parry J. V., Price A. B., Davies D. R., Dolby J., Tyrrell D. A. Undescribed toxin in pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1977 May 14;1(6071):1246–1248. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6071.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Sans M. D., Tedesco F. J. Bacterial studies of Clindamycin-associated colitis. A preliminary report. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):352–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Davies D. R., Morson B. C. Proceedings: The diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis by rectal biopsy. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):346–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin G. D., Fekety F. R., Silva J., Jr Antibiotic-induced colitis implication of a toxin neutralised by Clostridium sordellii antitoxin. Lancet. 1977 Nov 26;2(8048):1103–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90547-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sclafani S. J., Dallemand S. E., Sutton A., Farman J. Radiopathologic correlation in pseudomembranous colitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(8):694–698. doi: 10.1007/BF02604279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. J., Nicholson G. I., Kerr A. R. Lincomycin as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1232–1234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkin P. M., Link R. J. Pseudomembranous colitis: a consideration in the barium enema differential diagnosis of acute generalized ulcerative colitis. Br J Radiol. 1973 Jun;46(546):437–439. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-546-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simila S., Kouvalainen K., Makela P. Letter: Pseudomembranous colitis after amoxycillin. Lancet. 1976 Aug 7;2(7980):317–318. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90773-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer H. W. The pseudomembranous colitis associated with clindamycin therapy--a viral colitis. Gut. 1975 Sep;16(9):695–706. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.9.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F. J., Barton R. W., Alpers D. H. Clindamycin-associated colitis. A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Oct;81(4):429–433. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-4-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodoropoulos G., Seitanidis B., Archimandritis A., Bougas S. Clindamycin-associated colitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(5):435–437. doi: 10.1007/BF02587440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truelove S. C., Jewell D. P. Intensive intravenous regimen for severe attacks of ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1974 Jun 1;1(7866):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90552-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viteri A. L., Howard P. H., Dyck W. P. The spectrum of lincomycin-clindamycin colitis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1137–1144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


