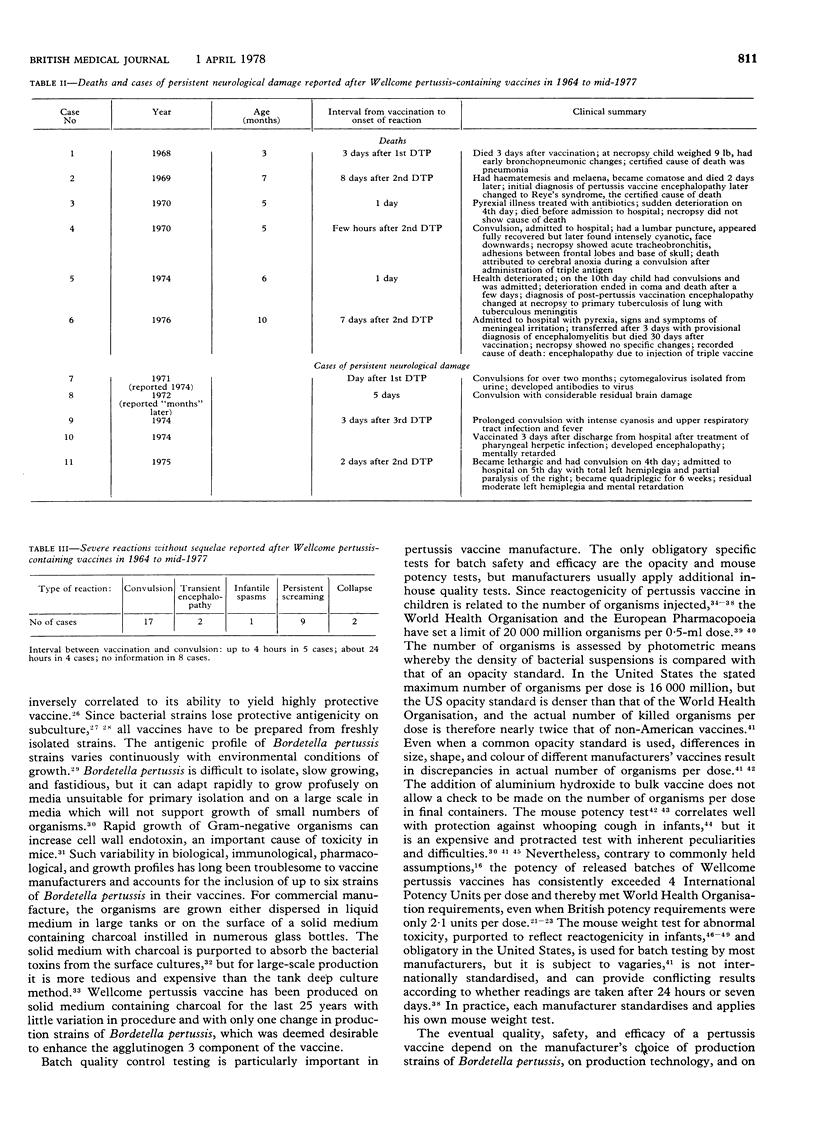
Abstract
Pertussis vaccines vary in quality, safety, and efficacy according to the production strains of Bordetella pertussis, the method of manufacture, and quality control procedures. It is therefore not justifiable to combine information on the incidence, nature, and severity of reactions after all manufacturers' pertussis vaccines as if they were a single product. Attempts were made to collect information on all suspected cases of severe reactions that occurred after administration of about 15 million doses of Wellcome pertussis vaccines in the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland from 1964 to mid-1977. Altogether six deaths, six neurological reactions with sequelae, and 17 convulsions without sequelae were reported, but some were clearly not attributable to the vaccine, while, in other cases, the available information was inadequate for assessing the role of vaccination. Neurological disorders, similar to those reported in a few children after pertussis vaccination, occur unexpectedly in apparently healthy infants at the recommended age for immunisation, so chance association between vaccination and these events can be expected in some children. The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation has made several recommendations aimed at reducing severe reactions after pertussis vaccination. These include replacing plain vaccine with aluminium-adsorbed vaccine, but there is no clear evidence that the aluminium-adsorbed vaccine produces fewer reactions than the plain.
There are difficulties enough in deciding the cause of events that occur after vaccination, since these reactions often occur naturally in children of vaccination age. The task is made even harder by the assumption that various manufacturers' vaccines are the same and the lack of information available to manufacturers about cases in which their vaccine has been implicated. Information on vaccines administered is entered on immunisation records cards; it should be used and referred to if reactions occur.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. R. Problems associated with the development and clinical testing of an improved pertussis vaccine. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1976;20:43–56. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD H. W., 3rd, BOROFSKY L. G. Infantile myoclonic seizures. J Pediatr. 1957 Mar;50(3):332–339. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG J. M. Neurological complications of pertussis immunization. Br Med J. 1958 Jul 5;2(5087):24–27. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5087.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines J. H. Immunization against whooping-cough. Br Med J. 1965 Sep 4;2(5461):592–593. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5461.592-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler N. R., Voyce M. A., Burland W. L., Hilton M. L. Advantages of aluminium hydroxide adsorbed combined diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines for the immunization of infants. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 15;1(5645):663–666. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5645.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. Problems associated with the control testing of pertussis vaccine. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1976;20:57–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. Variation in Bordetella pertussis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):367–374. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P. E. En vurdering af difteri-tetanus-kighoste-vaccinens bivirkninger. Efter 7 års udbredt anvendelse i Danmark. Ugeskr Laeger. 1969 Apr 24;131(17):741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Wheeler M. W. Pertussis Vaccine Prepared with Phase-I Cultures Grown in Fluid Medium. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 Apr;36(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick G. Combined vaccines. Can J Public Health. 1966 Oct;57(10):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick G. Letter: Protection by pertussis vaccine. Lancet. 1976 Jun 5;1(7971):1239–1239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick G. Letter: Whooping-cough vaccine. Br Med J. 1975 Oct 18;4(5989):161–161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5989.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick G. Reactions to routine immunization in childhood. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 May;67(5):371–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doull J. A., Shibley G. S., McClelland J. E. Active Immunization Against Whooping Cough : Interim Report of the Cleveland Experience. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1936 Nov;26(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.2105/ajph.26.11.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSALL G., McCOMB J. A., WETTERLOW L. H., IPSEN J., Jr Significance of the loss of potency in the pertussin component of certain lots of "quadruple antigen". N Engl J Med. 1962 Oct 4;267:687–689. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196210042671403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froggatt P., Lynas M. A., MacKenzie G. Epidemiology of sudden unexpected death in infants ('cot death') in Northern Ireland. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1971 Aug;25(3):119–134. doi: 10.1136/jech.25.3.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama Y., Tomori N., Sugitate M. Critical evaluation of the role of immunization as an etiological factor of infantile spasms. Neuropadiatrie. 1977 Aug;8(3):224–237. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gostling J. V., Payne D. J. Letter: Whooping-cough vaccination. Lancet. 1974 Sep 28;2(7883):773–773. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90959-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith A. H. A fresh look at bacterial vaccines. Public Health. 1972 Nov;87(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(72)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker P. Primary immunisation and febrile convulsions in Oxford 1972-5. Br Med J. 1977 Aug 20;2(6085):490–493. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6085.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDRICK P. L., UPDYKE E. L., ELDERING G. Comparison of pertussis cultures by mouse protection and virulence tests . Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1949 Feb;39(2):179–184. doi: 10.2105/ajph.39.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick P. L., Eldering G., Dixon M. K., Misner J. Mouse Protection Tests in the Study of Pertussis Vaccine: A Comparative Series Using the Intracerebral Route for Challenge. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1947 Jul;37(7):803–810. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulenkampff M., Schwartzman J. S., Wilson J. Neurological complications of pertussis inoculation. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jan;49(1):46–49. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane J. M., Ruben F. L., Neff J. M., Millar J. D. Complications of smallpox vaccination, 1968. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 27;281(22):1201–1208. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911272812201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: Whooping-cough vaccination. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 8;4(5992):347–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMGREN B., VAHLQUIST B., ZETTERSTROM R. Complications of immunization. Br Med J. 1960 Dec 17;2(5215):1800–1801. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5215.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELIN K. A. Pertussis immunization in children with convulsive disorders. J Pediatr. 1953 Dec;43(6):652–654. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(53)80306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER H. G., STANTON J. B. Neurological sequelae of prophylactic inoculation. Q J Med. 1954 Jan;23(89):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manclark C. R. The current status of pertussis vaccine: an overview. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1976;20:1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlan A. M., Topley E., Fisher M. Trial of Whooping-cough Vaccine. Br Med J. 1945 Aug 18;2(4415):205–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4415.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior J. C. Infantile spasmer og vaccinationer. Ugeskr Laeger. 1969 Apr 24;131(17):746–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior J. C. Infantile spasms and early immunization against whooping cough. Danish survey from 1970 to 1975. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Feb;52(2):134–137. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior J. C. Infantile spasms and immunisation in the first year of life. Neuropadiatrie. 1971 Jul;3(1):3–10. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggleton P. W. Vaccines against pertussis. Public Health. 1967 Jul;81(5):252–264. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(67)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. B., Ellenberg J. H. Predictors of epilepsy in children who have experienced febrile seizures. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 4;295(19):1029–1033. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611042951901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noah N. D. Attack rates of notified whooping cough in immunised and unimmunised children. Br Med J. 1976 Jan 17;1(6002):128–129. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6002.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M., COX C. B. PERTUSSIS VACCINE TESTING FOR FREEDOM-FROM-TOXICITY. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:447–456. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.447-456.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M. Instability of pertussis-vaccine component in quadruple antigen vaccine. Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis and poliomyelitis vaccines. JAMA. 1962 Jul 7;181:25–30. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050270027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN M. Variability of the potency of pertussis vaccine in relation to the number of bacteria. J Pediatr. 1954 Jul;45(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(54)80063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON N. W. EFFECTIVENESS OF PERTUSSIS VACCINES. Br Med J. 1965 Jul 3;2(5452):11–13. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5452.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. Role of the genetics and physiology of Bordetella pertussis in the production of vaccine and the study of host-parasite relationships in pertussis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1976;20:27–42. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. D., Ellwood D. C. Growth environment and bacterial toxicity. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):391–393. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins F. T. Vaccination against whooping-cough. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 15;4(5680):429–430. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5680.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. R. Sudden, unexpected death in infants. An epidemiologic study. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Nov;84(3):478–482. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky A. L. Pertussis vaccination. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1974 Aug;16(4):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1974.tb03382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards I. D., McIntosh H. T. Confidential inquiry into 226 consecutive infant deaths. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):697–706. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M. Convulsive disorders in British children. Proc R Soc Med. 1973 Jul;66(7):703–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUER L. W., TUCKER W. H. Immune responses to diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, aluminum phosphate adsorbed. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1954 Jun;44(6):784–788. doi: 10.2105/ajph.44.6.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOULD the child with convulsive disorders be immunized against pertussis? J Pediatr. 1953 Dec;43(6):746–750. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(53)80323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANDFAST A. F. B. The phase I of Haemophilus pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):531–545. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. T. Vaccination against whooping-cough. Efficacy versus risks. Lancet. 1977 Jan 29;1(8005):234–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccination against whooping-cough. Lancet. 1977 Feb 19;1(8008):419–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Berg B. J., Yerushalmy J. Studies on convulsive disorders in young children. I. Incidence of febrile and nonfebrile convulsions by age and other factors. Pediatr Res. 1969 Jul;3(4):298–304. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196907000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


