Abstract
The agglutination test of Nicholls was found to be ineffective in diagnosing active tuberculosis. A positive result (titre of 1/125 or more) was found in the serum of 74 (70%) out of 105 patients with newly diagnosed, smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis; 61 (62%) out of 98 healthy family contacts; and 19 (63%) out of 30 patients with non-tuberculous conditions. These findings were not due to faulty technique since the results obtained at Hammersmith were similar to those obtained by Nicholls's laboratory in the same serum samples. Twenty-seven of the tuberculous patients who had a negative result before treatment were retested two months after the start of chemotherapy but showed no evidence of a rising titre.
Full text
PDF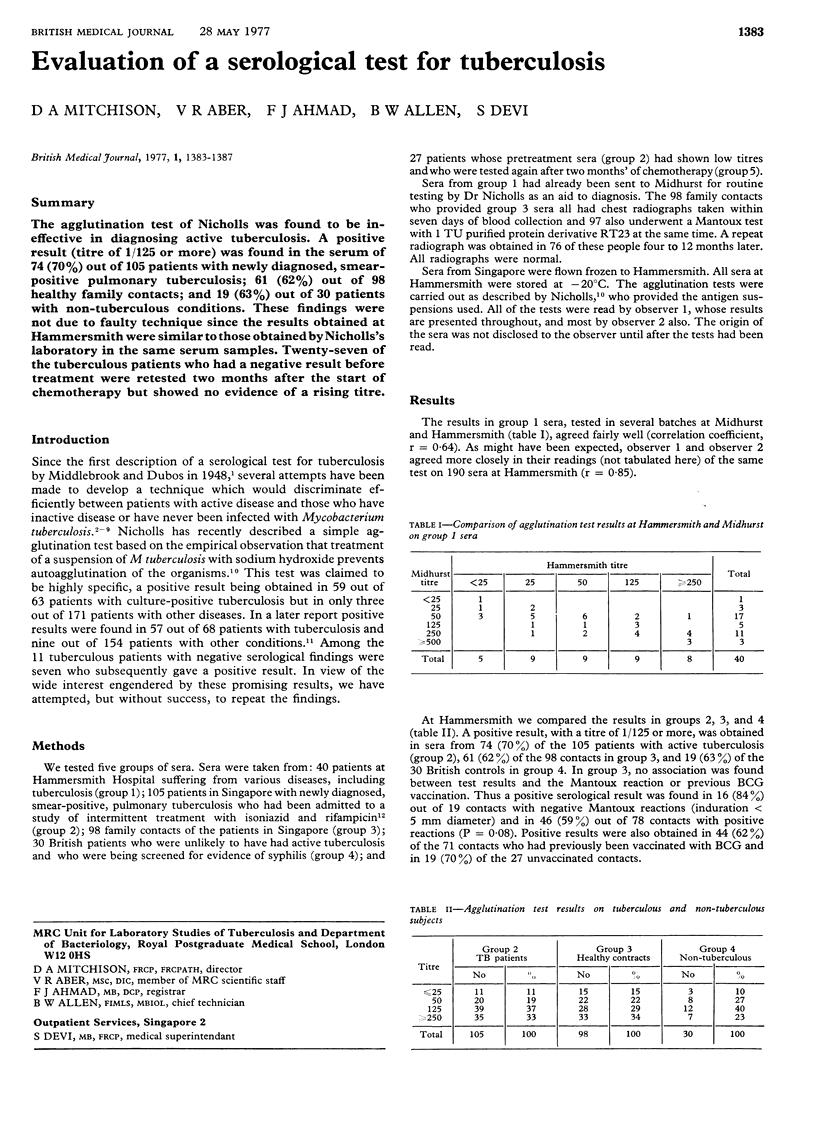

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affronti L. F., Fife E. H., Grow L. Serodiagnostic test for tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 May;107(5):822–825. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. V., Lazarus A. W., Hedrick H. G. Development and evaluation of a simple latex agglutination test for diagnosis of tuberculosis. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):525–534. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.525-534.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassau E., Parsons E. R., Johnson G. D. Detection of antibodies to mycobacterium tuberculosis by solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Horsfield K. Serological diagnosis of tuberculosis: a report of 12 months' clinical experience. Thorax. 1976 Jun;31(3):289–293. doi: 10.1136/thx.31.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARLETT R. C., YOUMANS G. P. An evaluation of the specificty and sensitivity of a gel double-diffusion test for tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Aug;80:153–166. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggiardo Z., Middlebrook G. Serologically active glycolipid families from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. II. Serologic studies on human sera. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Dec;100(6):477–486. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI Y. Specific serum agglutination of kaolin particles sensitized with tubercle phosphatide and its clinical evaluation as a serodiagnostic test for tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 May;85:708–719. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.85.5.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


