Abstract
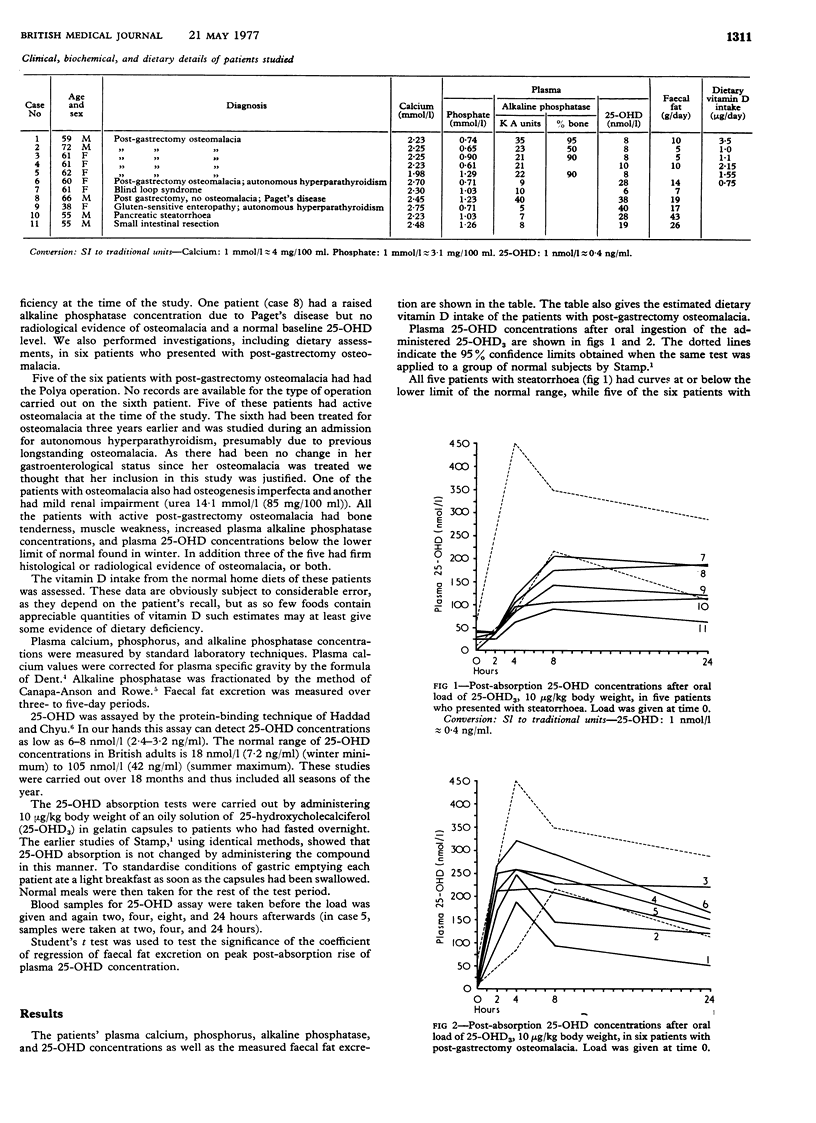
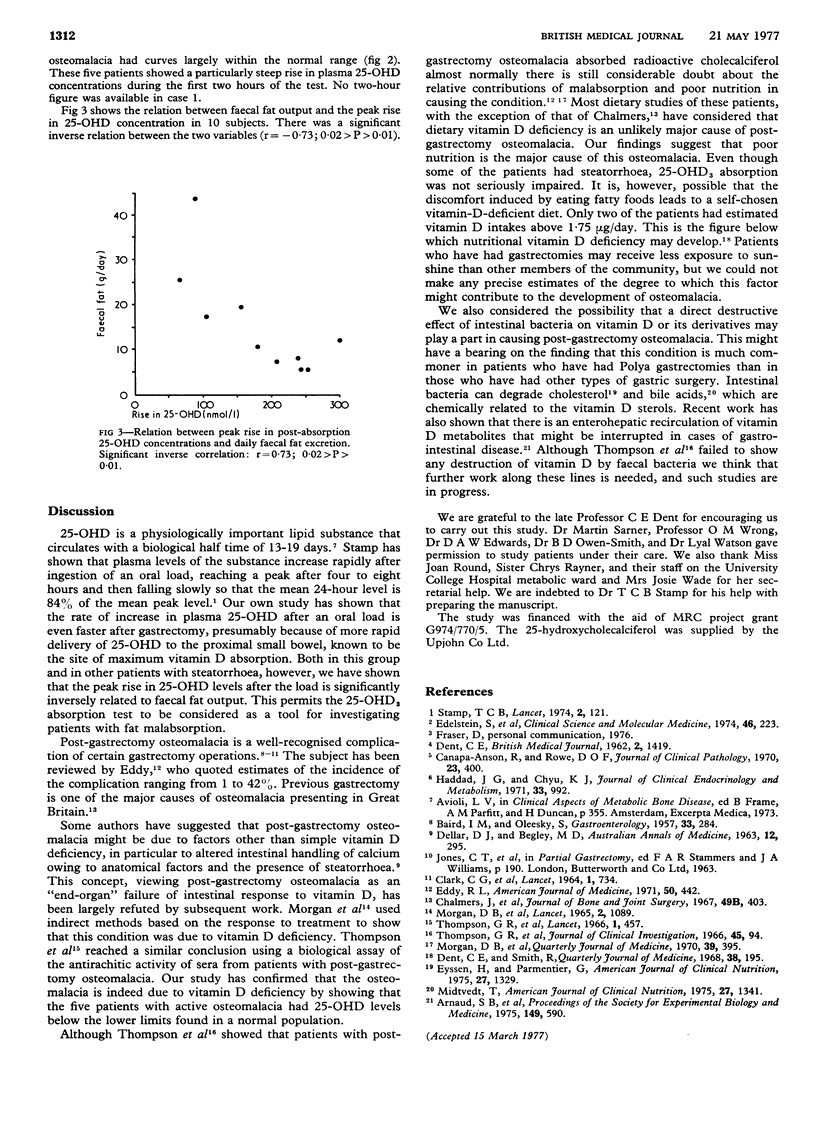
Post-absorption levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25-OHD) after oral administration of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (25-OHD3) were measured in 11 subjects. Five had presented with steatorrhoea of various causes while six had post-gastrectomy osteomalacia. Post-absorption levels of 25-OHD were low in four of the patients with steatorrhoea but normal in five of those with post-gastrectomy osteomalacia. There was a significant inverse correlation between peak post-absorption 25-OHD levels and faecal fat excretion. All patients with active post-gastrectomy osteomalacia had subnormal baseline plasma 25-OHD levels, which indicates that the condition is due to a deficiency of vitamin D. Only two of the patients with osteomalacia had estimated dietary vitamin D intakes ofer 1-75 microng/day. These findings suggest that an oral 25-OHD absorption test may be a valuable measure of small intestinal function and that poor dietary vitamin D intake rather than impaired absorption of the vitamin may be the major cause of post-gastrectomy osteomalacia.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIRD I. M., OLEESKY S. Osteomalacia following gastric surgery. Gastroenterology. 1957 Aug;33(2):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Peters D. K. Metabolism of the third component of complement (C3) in normal human subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Feb;46(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/cs0460223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. E., Smith R. Nutritional osteomalacia. Q J Med. 1969 Apr;38(150):195–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy R. L. Metabolic bone disease after gastrectomy. Am J Med. 1971 Apr;50(4):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyssen H., Parmentier G. Biohydrogenation of sterols and fatty acids by the intestinal microflora. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1329–1340. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Chyu K. J. Competitive protein-binding radioassay for 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):992–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T. Microbial bile acid transformation. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1341–1347. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. B., Hunt G., Paterson C. R. The osteomalacia syndrome after stomach operations. Q J Med. 1970 Jul;39(155):395–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. B., Paterson C. R., Woods C. G., Pulvertaft C. N., Fourman P. Osteomalacia after gastrectomy. A response to very small doses of vitamin D. Lancet. 1965 Nov 27;2(7422):1089–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp T. C. Intestinal absorption of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. Lancet. 1974 Jul 20;2(7873):121–123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Lewis B., Booth C. C. Absorption of vitamin D3-3H in control subjects and patients with intestinal malabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):94–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI105327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


