Abstract
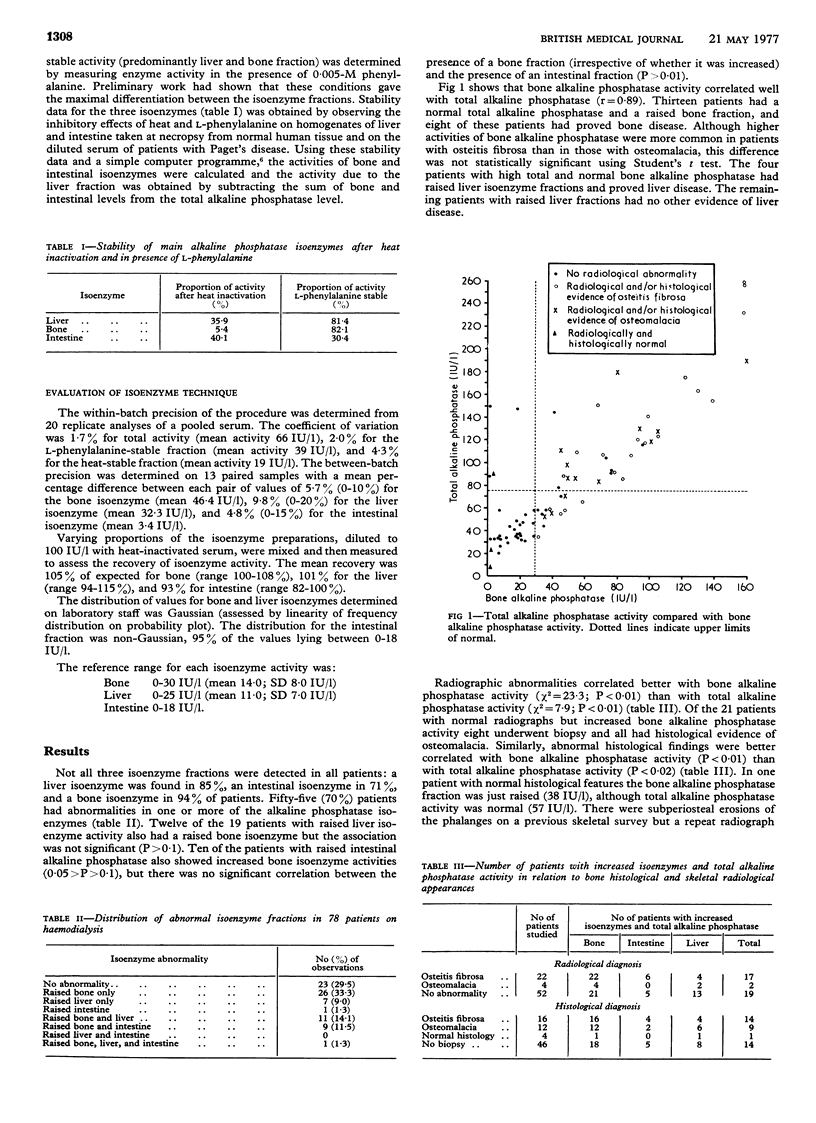
Liver, intestinal, and bone alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes were measured using heat stability and L-phenylalanine inhibition techniques in 78 patients on intermittent haemodialysis. Fifty-five patients had abnormalities in one or more of the isoenzymes. Changes in bone and intestinal alkaline phosphatase activities seemed to be related and raised liver isoenzyme activity was associated with the development of liver disease. Abnormal histological and radiological findings were better correlated with bone alkaline phosphatase levels than with total alkaline phosphatase, and serial estimations of bone isoenzyme activity were useful in assessing the response of renal osteodystrophy to treatment with a vitamin D analogue. Serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme measurement provides another useful and non-invasive index for monitoring metabolic bone disease in patients with chronic renal failure.
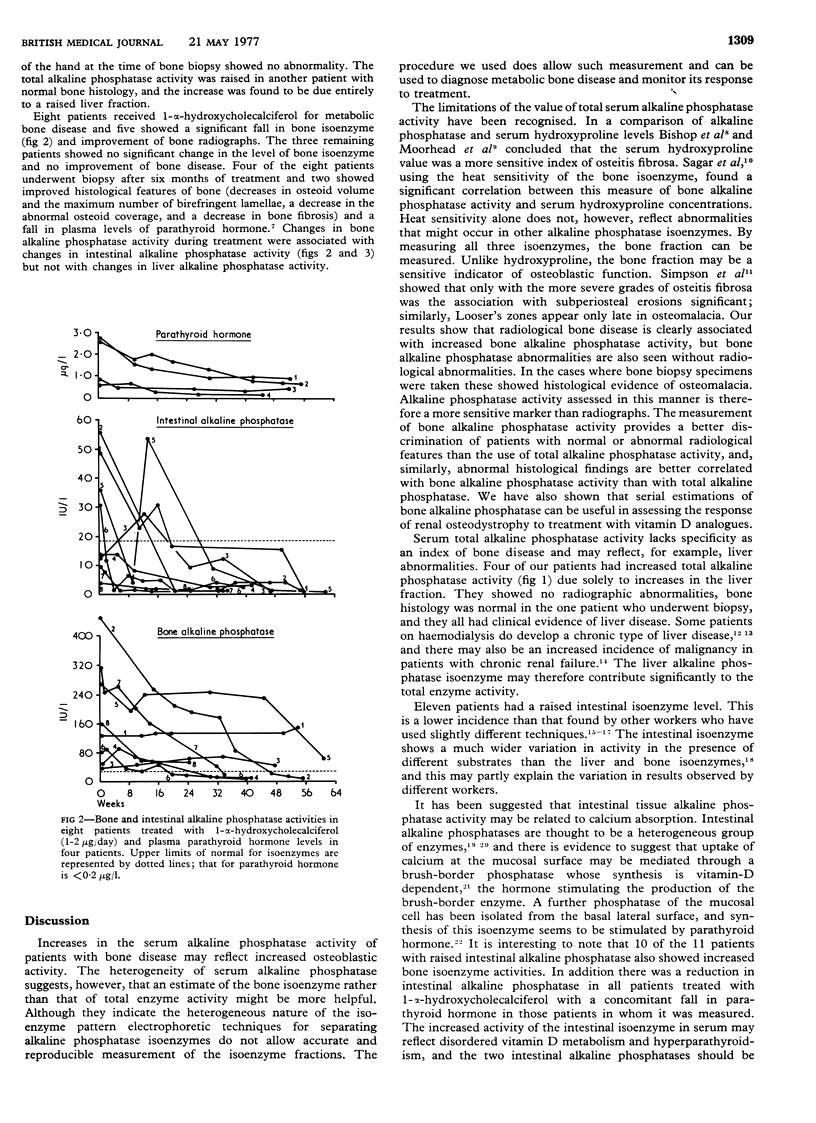
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birge S. J., Gilbert H. R. Indentification of an intestinal sodium and calcium-dependent phosphatase stimulated by parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):710–717. doi: 10.1172/JCI107809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Moog F. Alkaline phosphatases of the chicken duodenum. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of duodenal phosphatase in pre- and post-hatching stages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):154–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90975-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Broe M. E., Bosteels V., Wieme R. J. Letter: Increased intestinal alkaline phosphatase in serum of patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):753–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92980-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle F. H. Radiological patterns of bone disease associated with renal glomerular failure in adults. Br Med Bull. 1972 Sep;28(3):220–224. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey K. J., Clifton J. A. Liver disease in patients treated with chronic hemodialysis. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. B., Jr, Ellingboe K., Gibbs P. A study of various electrophoretic and inhibition techniques for separating serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Clin Chem. 1972 Feb;18(2):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowarski S., Schachter D. Vitamin D and adenosine triphosphatase dependent on divalent cations in rat intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2765–2773. doi: 10.1172/JCI107472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matas A. J., Simmons R. L., Kjellstrand C. M., Buselmeier T. J., Najarian J. S. Increased incidence of malignancy during chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):883–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91684-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead J. F., Varghese Z., Tatler G. L., Baillod R. A., Wills M. R. Comparison of biochemical with radiological findings in renal osteodystrophy. Ann Clin Biochem. 1975 May;12(3):126–131. doi: 10.1177/000456327501200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen V., Clausen E., Ranek L. Liver impairment during chronic hemodialysis and after renal transplantation. Acta Med Scand. 1975 Mar;197(3):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1975.tb04907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. P., Sammons H. G. The nature of the serum alkaline phosphatases in liver diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1974 May;27(5):392–398. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.5.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar S., Borra S., Kaye M. Thermolability of alkaline phosphatase in the evaluation of renal osteodystrophy. Nephron. 1971;8(3):270–277. doi: 10.1159/000179928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saini P. K., Done J. The diversity of alkaline phosphatase from rat intestine. Isolation and purification of the enzyme (s). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90974-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W., Ellis H. A., Kerr D. N., McElroy M., McNay R. A., Ppeart K. N. Bone disease in long-term haemodialysis: the association of radiological with histological abnormalities. Br J Radiol. 1976 Feb;49(578):105–110. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-49-578-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statland B. E., Nishi H. H., Young D. S. Serum alkaline phosphatase: total activity and isoenzyme determinations made by use of the centrifugal fast analyzer. Clin Chem. 1972 Dec;18(12):1468–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepán J., Pilarová T., Votrubová O., Melicharová D. Sérové alkalické fosfatázy jako ukazatel jaterního a kostního postizeni u chronicky dialyzovaných nemocných. Cas Lek Cesk. 1974 Aug 2;113(31):952–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J., Thomas F. Alkaline phosphatase: reaction rate analysis at 340 nm. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:541–543. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Dinwoodie A., Morgan H. G. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes activity using five standard methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Apr;24(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


