Abstract
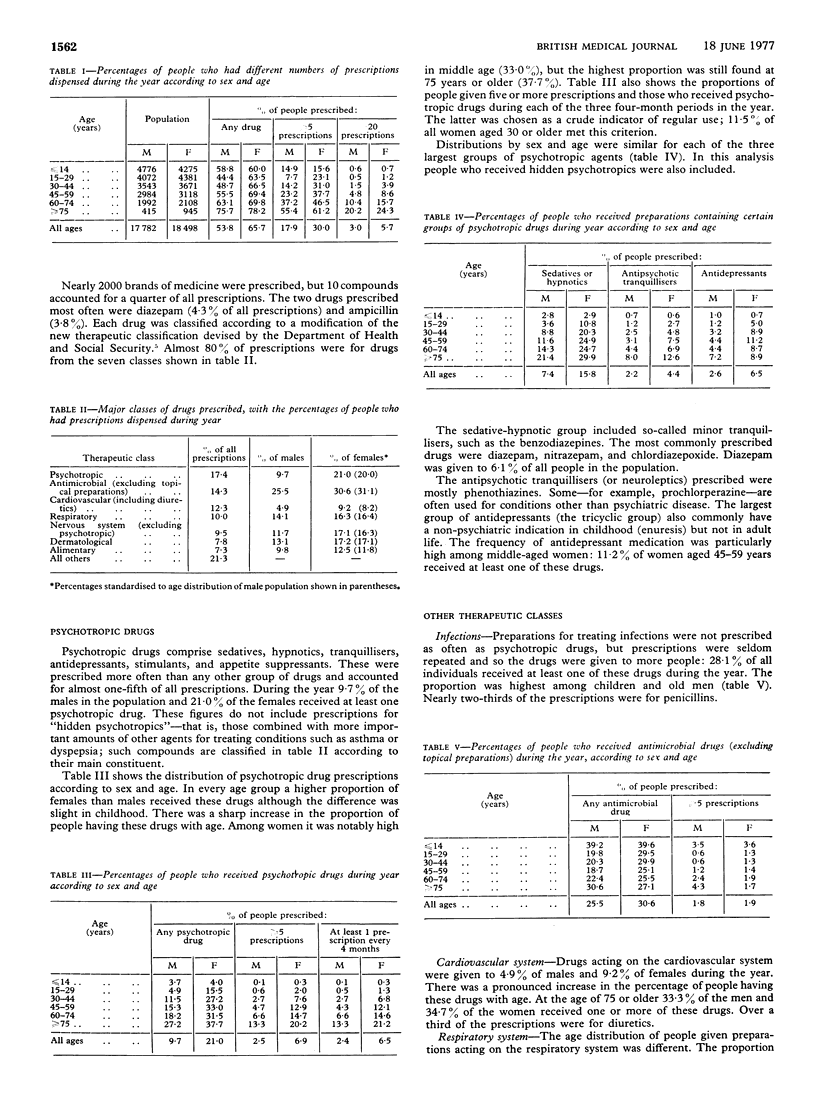
The prescriptions issued by general practitioners to a population of about 40 000 people were studied. During one year 53-8% of all males and 65-7% of all females had at least one drug dispensed. The proportion receiving medicines increased with age and was higher among females at all ages. Psychotropic drugs were prescribed more often than any other group and accounted for almost one-fifth of all prescriptions. Altogether 9-7% of the males in the population and 21-0% of the females received at least one psychotropic drug during the year. Among women aged 45-59 33-0% received a psychotropic drug, and 11-2% were given an antidepressant. Althoug antimicrobial drugs were prescribed less often than psychotropic drugs, they were given to more people.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain D. J., Haines A. J. A year's study of drug prescribing in general practice using computer-assisted records. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1975 Jan;25(150):41–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balter M. B., Levine J., Manheimer D. I. Cross-national study of the extent of anti-anxiety-sedative drug use. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts T. A., Clayton A. B., Mackay G. M. Effects of four commonly-used tranquillizers on low-speed driving performance tests. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 9;4(5840):580–584. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5840.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. J. General-practitioner prescribing. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1977 Feb;27(175):79–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


