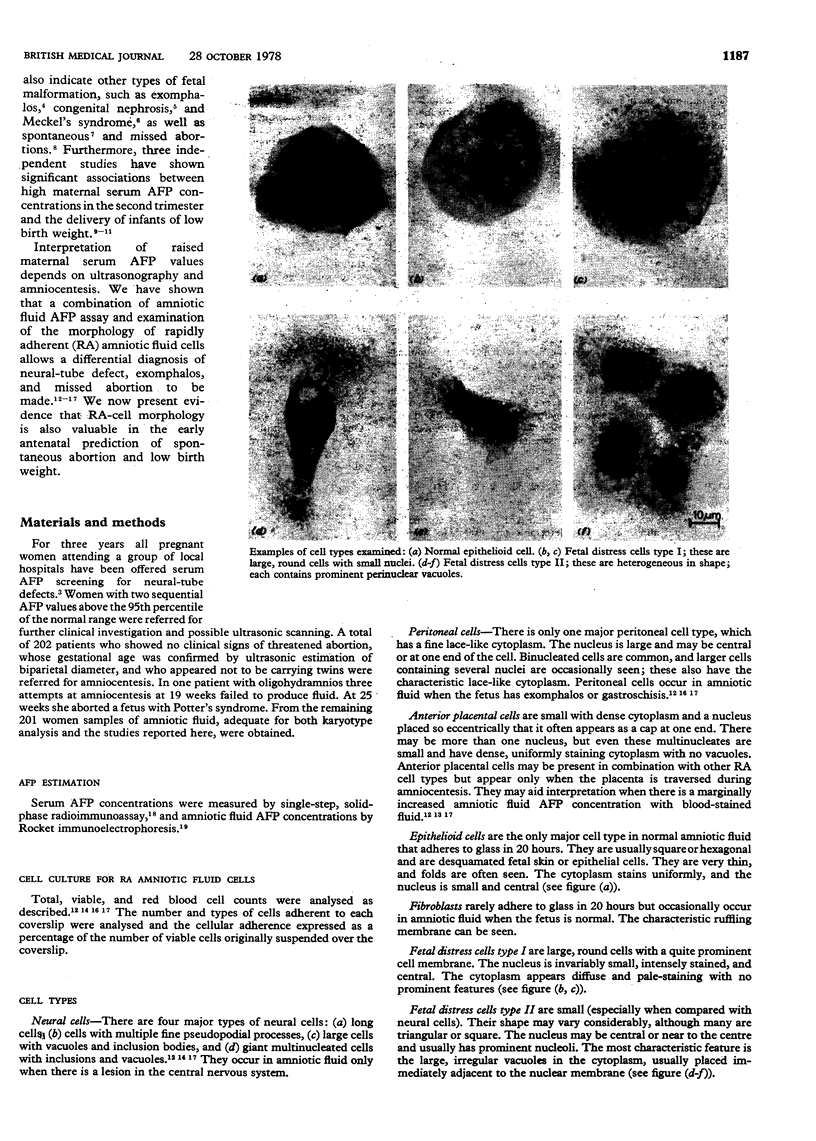
Abstract
The morphology of rapidly adherent (RA) amniotic fluid cells was examined in 201 pregnant women referred for amniocentesis because of two sequential high serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) concentrations. Out of 43 amniotic fluid samples containing increased amounts of AFP, 42 had neural or peritoneal cells predominating among the RA cells, the outcome being an infant with a neural-tube defect or exomphalos. In the other case with a raised amniotic fluid AFP concentration but only anterior placental cells the infant was normal. In 25 amniotic fluid samples containing normal amounts of AFP distinctive new patterns of RA cells were observed, termed fetal distress cells. These pregnancies resulted in five spontaneous abortions and 20 infants with birth weights under 2500 g. Fetal distress cells were not detected in any of the remaining 133 samples. One pregnancy was terminated because of a chromosomal abnormality, and there were seven twin pairs not recognised on ultrasonography before amniocentesis. The remaining 125 pregnancies went to term, resulting in infants with birth weights exceeding 2500 g. The results suggest that RA-cell morphology will prove to be of value in the early antenatal prediction of spontaneous abortion and low birth weight.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock D. J., Barron L., Jelen P., Watt M., Scrimgeour J. B. Maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein measurements as an early indicator of low birth-weight. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):267–268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90952-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Gosden C. Are second-trimester amniotic fluids being properly examined? Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1168–1169. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Gosden C. Early antenatal diagnosis of small open spina bifida lesions. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 8;2(6092):934–934. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6092.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Scrimgeour J. B., Nelson M. M. Amniotic fluid alphafetoprotein measurements in the early prenatal diagnosis of central nervous system disorders. Clin Genet. 1975 Feb;7(2):163–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden C. M., Brock D. J. Morphology of rapidly adhering amniotic-fluid cells as an aid to the diagnosis of neural-tube defects. Lancet. 1977 Apr 30;1(8018):919–922. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden C., Brock D. J. Combined use of alphafetoprotein and amniotic fluid cell morphology in early prenatal diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. J Med Genet. 1978 Aug;15(4):262–270. doi: 10.1136/jmg.15.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden C., Brock D. J., Eason P. The origin of the rapidly adhering cells found in amniotic fluids from foetuses with neural tube defects. Clin Genet. 1977 Oct;12(4):193–2U1. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Gosden C., Lawrie S., Mitchell A. R. The fate of DNA satellites I, II, III and ribosomal DNA in a familial dicentric chromosome 13:14. Hum Genet. 1978 Mar 17;41(2):131–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00273095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjessler B., Johansson S. G., Sherman M., Gustavson K. H., Hultquist G. Alpha-fetoprotein in antenatal diagnosis of congenital nephrosis. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):432–433. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri J. N., Weiss R. R., Libster B., Cagan M. A. Maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein and low birth-weight. Lancet. 1978 Mar 25;1(8065):660–660. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä M. Immunologic detection of alpha fetoprotein as a marker of fetal pathology. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Sep;20(3):737–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä M., Karjalainen O., Rapola J., Lindgren J. Letter: Maternal alpha-fetoprotein and fetal exomphalos. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):303–304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä M., Ruoslahti E. Alpha-fetoprotein in abortion. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 30;4(5843):769–771. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5843.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N., Cuckle H., Stirrat G. M., Bennett M. J., Turnbull A. C. Maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein and low birth-weight. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):268–270. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90953-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]