Abstract
The size and composition of the bile-salt pools in a group of diabetics with neuropathy but no diarrhoea and a group with "diabetic diarrhoea" were compared with those in a group of stable, uncomplicated diabetics. The diabetics with neuropathy had significantly more dihydroxy bile salts, a larger bile-salt pool, and a higher faecal excretion of bile than the controls. The diabetics with diarrhoea had significantly more dihydroxy bile salts, a higher glycine to taurine ratio, a smaller bile-salt pool, and increased excretions of 14C-tracer and total bile salts. We conclude that considerable alterations occur in the bile of diabetics with neuropathy or diarrhoea, and we suggest that in some cases at least these abnormalities may indicate a mechanism for diabetic diarrhoea.
Full text
PDF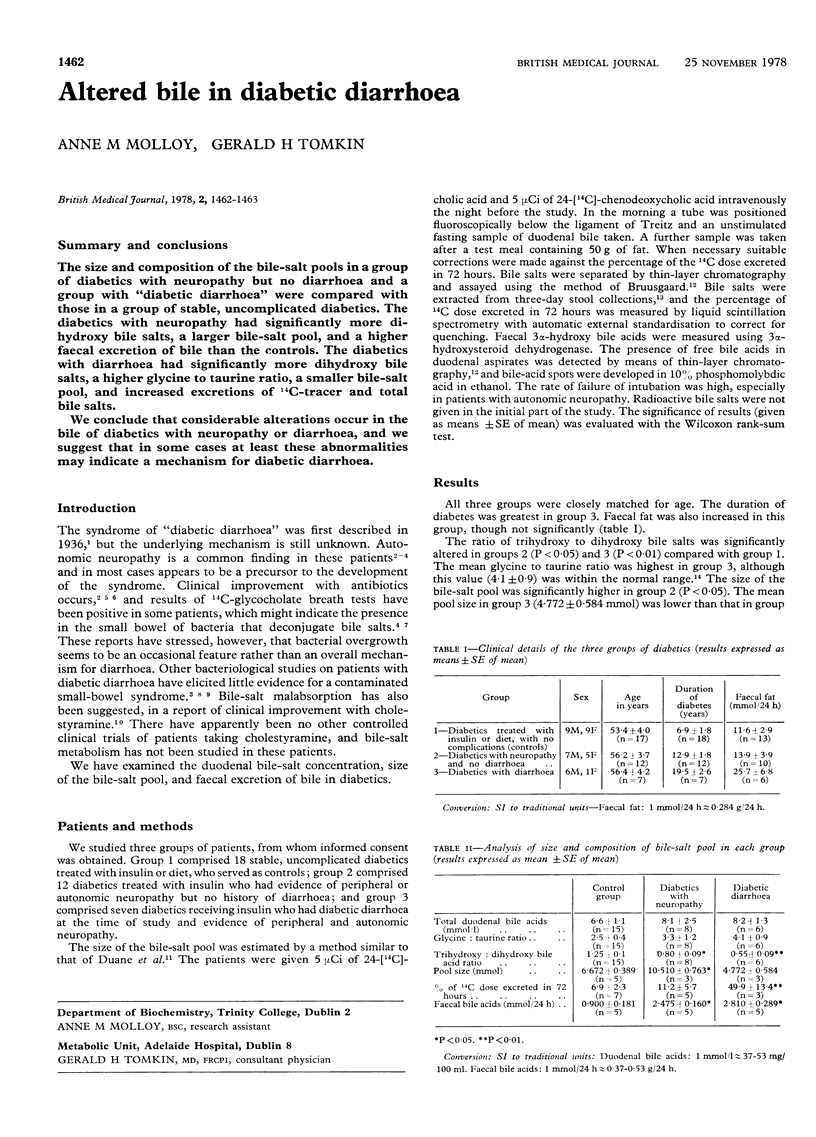

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abaurre R., Gordon S. G., Mann J. G., Kern F., Jr Fasting bile salt pool size and composition after ileal resection. Gastroenterology. 1969 Dec;57(6):679–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. G., Gerskowitch V. P., Russell R. I. The role of bile acids in the pathogenesis of postvagotomy diarrhoea. Br J Surg. 1974 Jul;61(7):516–518. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800610704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Grundy S. M. Effects of diabetes mellitus on cholesterol metabolism in man. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 16;296(24):1365–1371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706162962401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruusgaard A. Quantitative determination of the major 3-hydroxy bile acids in biological material after thin-layer chromatographic separation. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Jun;28(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruusgaard A., Thaysen E. H. Increased ratio of glycine-taurine conjugated bile acids in the early diagnosis of terminal ileopathy. Preliminary report. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Dec;188(6):547–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe V. M., Bolin T. D., Davis A. E. Double-blind trial of cholestyramine in post-vagotomy diarrhoea. Gut. 1977 Jul;18(7):531–535. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.7.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITELSON S., SCHWARTZ A., FRAENKEL M., CHOWERS I. GALL-BLADDER DYSFUNCTION IN DIABETES MELLITUS: THE DIABETIC NEUROGENIC GALL BLADDER. Diabetes. 1963 Jul-Aug;12:308–312. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.4.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F., Wirts C. W., Kowlessar O. D. Diabetic diarrhea and steatorrhea. Microbiologic and clinical observations. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Feb;72(2):215–218. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. A., Berge K. G., Sprague R. G. Control of diabetic diarrhea with antibiotic therapy. Diabetes. 1968 Jun;17(6):385–387. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.6.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzki M., Mazurkiewicz-Rozynska E., Czyzyk A. Diabetic cholecystopathy. Diabetologia. 1968 Dec;4(6):345–348. doi: 10.1007/BF01211770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joliot A. Y., Descos L., Minaire Y., Paffoy J. C. Diarrhée des diabétiques: rôle de la pullulation microbienne entérique. Nouv Presse Med. 1978 Mar 18;7(11):941–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Pomare E. W., Read A. E. The effect of coeliac disease upon bile salts. Gut. 1973 Mar;14(3):204–208. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALINS J. M., FRENCH J. M. Diabetic diarrhoea. Q J Med. 1957 Oct;26(104):467–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malins J. M., Mayne N. Diabetic diarrhea. A study of thirteen patients with jejunal biopsy. Diabetes. 1969 Dec;18(12):858–866. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.12.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory A., Kern F., Jr, Smith J., Savage D. Patterns of bile acids and microflora in the human small intestine. I. Bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok H. Y., Von Bergmann K., Grundy S. M. Regulation of pool size of bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):684–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMI S. M., FINLAY J. M. On the pathogenesis of diabetic steatorrhea. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Dec;55:994–997. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-6-994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpello J. H., Greaves M., Sladen G. E. Small intestinal transit in diabetics. Br Med J. 1976 Nov 20;2(6046):1225–1226. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6046.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpello J. H., Hague R. V., Cullen D. R., Sladen G. E. The 14C-glycocholate test in diabetic diarrhoea. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 18;2(6037):673–675. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6037.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINNIK I. E., KERN F., Jr, STRUTHERS J. E., Jr Malabsorption and the diarrhea of diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology. 1962 Nov;43:507–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen G. E., Soergel K. H., Geenen J. E. Diabetic diarrhea. A clinical and pathophysiological study. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1021–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury J. F., Kern F., Jr Fecal excretion of bile acids: a new technique for studying bile acid kinetics in patients with ileal resection. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2531–2540. doi: 10.1172/JCI106753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


