Abstract
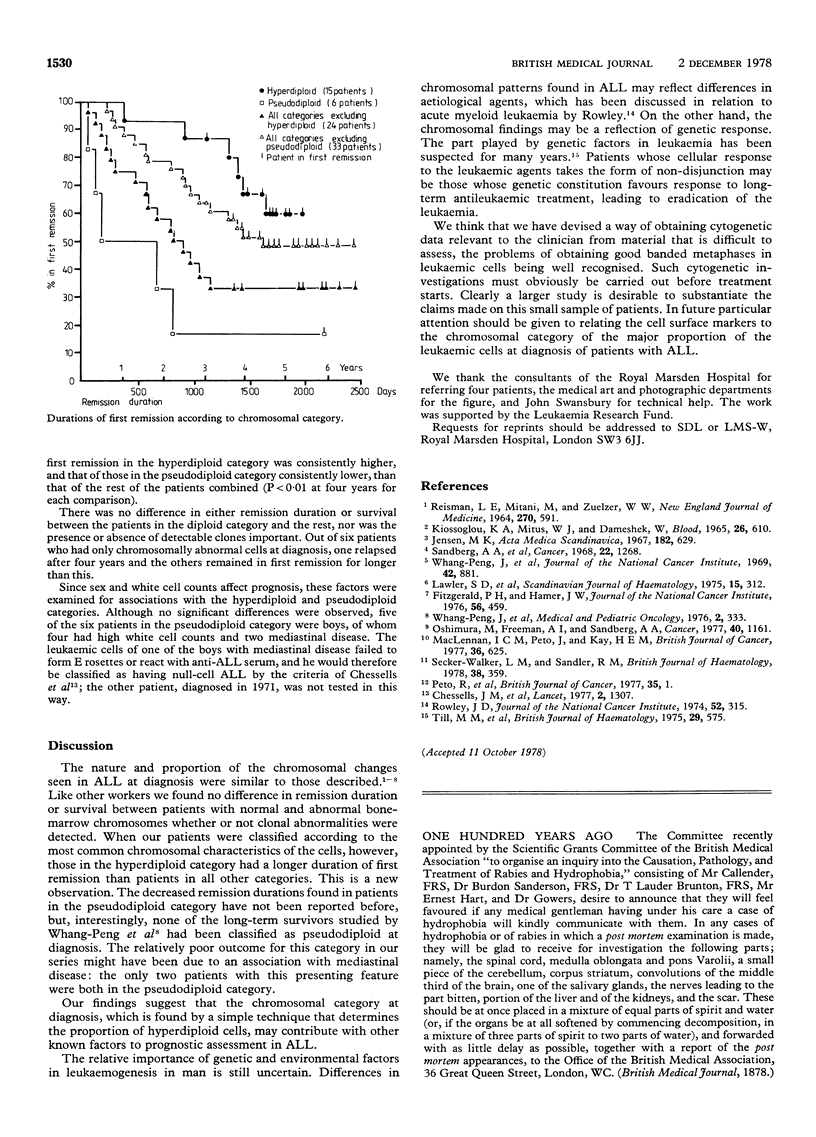
Chromosomes were studied on diagnostic bone-marrow samples from 39 children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). The patients were classified, according to the chromosomal characteristics of the major proportion of their leukaemia cells, into five categories; hyperdiploid, pseudodiploid, diploid, hypodiploid, and mixed. Patients in the hyperdiploid category had significantly longer first remissions than those in all other categories, and those in the pseudodiploid category had the shortest. Neither the absence of any normal cells nor the presence of detectable clones appeared to be an adverse feature. We suggest that the proportion of hyperdiploid cells, determined by conventional chromosomal staining techniques, may be used as an additional prognostic feature in childhood ALL.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chessells J. M., Hardisty R. M., Rapson N. T., Greaves M. F. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children: Classification and prognosis. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1307–1309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90361-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. H., Hamer J. W. Karyotope and survival in human acute leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):459–462. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. K. Chromosome studies in acute leukaemia. 3. Chromosome constitution of bone marrow cells in 30 cases. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Nov;182(5):629–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiossoglou K. A., Mitus W. J., Dameshek W. Chromosomal aberrations in acute leukemia. Blood. 1965 Nov;26(5):610–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Peto J., Kay H. E. Analysis of treatment of childhood leukaemia. V. Advantage of reduced chemotherapy during and immediately after cranial irradiation. Br J Cancer. 1977 Nov;36(5):625–633. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshimura M., Freeman A. I., Sandberg A. A. Chromosomes and causation of human cancer and leukemia. XXVI. Binding studies in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Cancer. 1977 Sep;40(3):1161–1172. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197709)40:3<1161::aid-cncr2820400327>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISMAN L. E., MITANI M., ZUELZER W. W. CHROMOSOME STUDIES IN LEUKEMIA. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC STEM LINES FROM ANEUPLOID MUTANTS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Mar 19;270:591–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196403192701201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. A., Takagi N., Sofuni T., Crosswhite L. H. Chromosomes and causation of human cancer and leukemia. V. Karyotypic aspects of acute leukemia. Cancer. 1968 Dec;22(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196811)22:6<1268::aid-cncr2820220626>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till M. M., Jones L. H., Pentycross C. R., Hardisty R. M., Lawler S. D., Harvey B. A., Soothill J. F. Leukaemia in children and their grandparents: studies of immune function in six families. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):575–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. M., Sandler R. M. Acute myeloid leukaemia with monosomy-7 follows acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1978 Mar;38(3):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Freireich E. J., Oppenheim J. J., Frei E., 3rd, Tjio J. H. Cytogenetic studies in 45 patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Jun;42(6):881–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Ziegler J., Leventhal B. Cytogenetic studies in acute lymphocytic leukemia: special emphasis in long-term survival. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1976;2(3):333–351. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950020315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



