Abstract
Nematode mitochondria possess extremely truncated tRNAs. Of 22 tRNAs, 20 lack the entire T-arm. The T-arm is necessary for the binding of canonical tRNAs and EF (elongation factor)-Tu (thermo-unstable). The nematode mitochondrial translation system employs two different EF-Tu factors named EF-Tu1 and EF-Tu2. Our previous study showed that nematode Caenorhabditis elegans EF-Tu1 binds specifically to T-armless tRNA. C. elegans EF-Tu1 has a 57-amino acid C-terminal extension that is absent from canonical EF-Tu, and the T-arm-binding residues of canonical EF-Tu are not conserved. In this study, the recognition mechanism of T-armless tRNA by EF-Tu1 was investigated. Both modification interference assays and primer extension analysis of cross-linked ternary complexes revealed that EF-Tu1 interacts not only with the tRNA acceptor stem but also with the D-arm. This is the first example of an EF-Tu recognizing the D-arm of a tRNA. The binding activity of EF-Tu1 was impaired by deletion of only 14 residues from the C-terminus, indicating that the C-terminus of EF-Tu1 is required for its binding to T-armless tRNA. These results suggest that C. elegans EF-Tu1 recognizes the D-arm instead of the T-arm by a mechanism involving its C-terminal region. This study sheds light on the co-evolution of RNA and RNA-binding proteins in nematode mitochondria.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans, elongation factor-Tu (EF-Tu1), mitochondrion, nematode, translation, tRNA
Abbreviations: aa-tRNA, aminoacyl tRNA; DTT, dithiothreitol; EF, elongation factor; ENU, N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea; EST, expressed sequence tag; mt, mitochondrial; RACE, rapid amplification of cDNA ends; T-armless tRNA, tRNA lacking a T-arm; Tu, thermo-unstable
INTRODUCTION
In the elongation cycle of translation in bacteria and in eukaryotic organelles, EF (elongation factor)-Tu (thermo-unstable) binds GTP and aa-tRNA (aminoacyl-tRNA) to form a ternary complex that subsequently binds the ribosome [1]. The crystal structure [2,3] and substantial biochemical data [4] have shown that bacterial EF-Tu is composed of three domains and interacts with two regions of tRNAs, the acceptor stem and the T-stem. Domains 1 and 2 bind to the acceptor stem, and domain 3 interacts with the T-stem, the length of which influences ternary complex formation [5].
The cloverleaf secondary structure and the L-shaped tertiary structure [6,7] are common to most tRNAs. However, a variety of exceptional tRNAs exist in metazoan mitochondria. The characteristic feature of the metazoan mt (mitochondrial) translation system is the reduced number of RNA components (tRNA and rRNA) encoded by the mt DNA and the increased number of protein components encoded by the nuclear genome. In nematode mitochondria, this bias is clearly seen in the ternary complex containing tRNA and EF-Tu [8] and in the altered ratio of RNA to protein in ribosomes [9]. Nematode mitochondria possess extremely truncated tRNAs that lack either the T-arm or the D-arm. Out of 22 tRNAs, 20 tRNAs lack the T-arm and two tRNAsSer lack the D-arm. Such a set of bizarre tRNAs has been found in at least seven chromadorean nematodes: Caenorhabditis elegans [10], Ascaris suum [11], Onchocerca volvulus [12], Ancylostoma duodenale [13], Necator americanus [13], Dirofilaria immitis [14] and Cooperia oncophora [15]. These unusual tRNA structures raise the question of how nematode mt EF-Tu can recognize tRNAs lacking the T-arm (T-armless tRNA), which is essential for the binding of canonical EF-Tu.
The nematode mt translation system employs two variants of EF-Tu, EF-Tu1 which specifically recognizes the T-armless tRNAs [16] and EF-Tu2 (tufm-2 gene product) which specifically recognizes the D-armless tRNAs [8]. We have previously reported that the nematode C. elegans EF-Tu1 (encoded by the Y71H2AM.23 gene, here renamed tufm-1) has a 57-amino acid C-terminal extension named domain 3′, which is not seen in canonical EF-Tu molecules. The C-terminal region including the extension is important for the unique tRNA-specificity [16]. However, the details of the tRNA-recognition mechanism of EF-Tu1 remain unknown. Thus, we investigated the mechanism of recognition of T-armless tRNA by EF-Tu.
EXPERIMENTAL
Preparation of A. suum mt tRNAMet and Val-tRNAMet
A synthetic A. suum mt tRNAMet containing m1A9 as the sole modified nucleoside has nearly the same biological activity as native tRNAMet, whereas the unmodified synthetic tRNAMet is much less active than the native tRNAMet [17]. Since isolation of large amounts of native A. suum mt tRNAMet is difficult, we used the synthetic A. suum mt tRNAMet containing m1A9 for the modification interference assay and cross-linking experiments below. The synthetic A. suum mt tRNAMet containing m1A9 as the sole modified base was constructed as previously described [17]. Chemical aminoacylation [18] of the tRNAMet with valine was performed as follows. The tRNAMet without a 3′-CA dinucleotide unit [tRNAMet(-CA)] was ligated to N-(4-pentenoyl)valyl pdCpA (pdCpA-Val) at 10 °C for 1 h in a mixture consisting of 0.01 A260 unit/μl tRNAMet(-CA), 90 μM pdCpA-Val, 50 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.5), 15 mM MgCl2, 3.5 mM DTT (dithiothreitol), 15 μg/ml BSA, 5% PEG [poly(ethylene glycol)] 6000, 10% DMSO, 500 μM ATP and 800 units/ml T4 RNA ligase (Takara). Deprotection of the ligated product was performed at room temperature (25 °C) for 25 min in 200 μl solution containing 1 A260 unit of protected Val-tRNA and 16 μl of 200 mM I2 dissolved in tetrahydrofuran. After deprotection, Val-tRNAMet was purified by phenol extraction, ethanol precipitation and gel filtration on a NAP 5 gel filtration column (GE Healthcare). The Val-tRNAMet was used in the following experiments [ENU (N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea)-modification interference assay and cross-linking analysis] because the deacylation rate of Val-tRNA is lower than that of other aa-tRNAs.
Preparation of the ternary complex and separation of the complex on native PAGE
The ternary complex of EF-Tu1, GTP and Val-tRNAMet was prepared as follows. To prepare the solution including the appropriate concentration of EF-Tu1 as described below, the EF-Tu1–EF-Ts complex was used because it is much more soluble than EF-Tu1 alone. The complex of C. elegans EF-Tu1 and EF-Ts was prepared as described previously [19]. EF-Tu1–EF-Ts (300 pmol) was incubated with 900 pmol of GTP in 15 μl for 40 min at 15 °C, and then 1 μl of 30 μM Val-tRNAMet (60 pmol) and 4 μl of ternary complex buffer containing 250 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.6), 325 mM ammonium acetate and 50 mM magnesium acetate were added, and the mixture was incubated at 0 °C for 10 min. Electrophoresis of the samples was carried out on 5% PAGE at 4 °C in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris/HCl (pH 6.8), 65 mM ammonium acetate, 10 mM magnesium acetate and 1 mM EDTA.
ENU-modification interference assay
An ENU-modification interference assay was performed as described previously [20]. In brief, the assay was carried out as follows. The Val-tRNAMet was 5′-32P-labelled, purified, and resuspended in 40 μl of solution containing 150 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2 and 2 μg of Escherichia coli tRNA. Freshly prepared saturated ENU solution (5 μl) in ethanol was added to the mixture, and the mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. The ternary complex of EF-Tu1, GTP and Val-tRNAMet was prepared and separated by 5% PAGE as described above. Elution of Val-tRNAMet (complexed or free) from gels was performed at 15 °C for 30 min in 100 μl elution buffer containing 0.3 M NaOAc (pH 5.0), 0.1% SDS and 2 mM EDTA. This elution step was repeated three times. The eluate was purified by phenol extraction and ethanol precipitation, and further purified to remove deacyl tRNAs by 7.5% denaturing PAGE containing 0.1 M sodium acetate (pH 5.0). Each tRNA was cleaved at its ethylated position at 50 °C for 6 min in a reaction buffer containing 100 mM Tris/HCl (pH 9.0). The RNA fragments were recovered by ethanol precipitation and then analysed by 12% denaturing PAGE.
Primer extension analysis of the cross-linked ternary complex
Cross-linking of the Val-tRNAMet and EF-Tu1–GTP was carried out basically as described previously [21,22]. The ternary complex was prepared as described above except that Tris/HCl in this procedure was replaced with Hepes/KOH because 2-iminothiolane (Pierce) reacts with primary amines. A 50-fold molar excess of 2-iminothiolane over EF-Tu1 was added to the ternary complex and incubated at 0 °C for 60 min. The complex was then irradiated by UV (254 nm, UVP, model UVS-28) at 0 °C for 4 min. To dissociate non-cross-linked ternary complexes, GDP was added in a 10-fold molar excess over GTP. After the separation and purification of cross-linked complex by 5% native PAGE as described above, primer extension was performed to identify the cross-linked site(s) on the tRNA [23]. The 5′-32P-labelled primer (0.2 pmol) was incubated with the cross-linked complex containing 0.00002 A260 units of tRNAMet in a 10 μl solution containing 10 mM Tris/HCl (pH 8.0) and 1 mM EDTA at 80 °C for 2 min, and then cooled slowly to room temperature for 1 h. Subsequently, 1.5 μl of double-distilled water, 4 μl of 5× Reaction Buffer for reverse transcription (Toyobo), 0.5 μl of 1.5 mM dNTP, 3 μl of 25 mM MgCl2 and 1 μl of M-MLV (Moloney murine leukaemia virus) reverse transcriptase (40 units/μl, Toyobo) were added, and the mixture was incubated at 42 °C for 1 h. The reaction mixture was separated by 15% PAGE containing 7 M urea. The synthetic DNA primers used to probe tRNAMet were: 5′-TATGTTCCTCACAGAC-3′ (Primer 1) to probe the region from A21 to G10, 5′-AGAGGGTATGTTCCTC-3′ (Primer 2) to probe the region from U27 to A20, 5′-ACACCAAGAGGGTATG-3′ (Primer 3) to probe the region from U33 to C24, 5′-AGAAAAACACCAAGAG-3′ (Primer 4) to probe the region from C38 to G31, and 5′-CAATAAGAGAAAAAC-3′ (Primer 5) to probe the region from U(L4) to A37.
Nematode EF-Tu1 cDNA sequencing
The poly(A)+ (polyadenylated) RNA from A. suum adult female body wall muscle was a gift from Dr Kiyoshi Kita (Department of Biomedical Chemistry, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan). Reverse transcription was carried out with ReverTra Ace (Toyobo) and random hexamers. The partial cDNA fragment of the putative EF-Tu was obtained by PCR using the degenerate primers P-748 (5′-ACKATWGGNCAYRTNGAYCA-3′)/P-750 (5′-TCKGMRTGNCCNGGRCARTC-3′) and P-749 (5′-CAYRTKGAYCAYGGNAARAC-3′)/P-750. The putative cDNA fragments were purified by agarose gel electrophoresis and then cloned using the TOPO TA cloning kit (Invitrogen). Positive clones were screened by colony PCR using the vector-specific primers 5′-GTGCTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTGG-3′ and 5′-TCCGGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGGA-3′, and sequenced using a DYEnamic ET terminator Sequencing Kit (GE Healthcare) and a 310 genetic analyser (Applied Biosystems). The full-length cDNA (GenBank® accession number AB211994) was reconstructed from RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) clones prepared with the GeneRacer kit (Invitrogen) and specific primers fully complementary to the partial cDNA sequence obtained above (5′ RACE: 5′-TCCTCTGGCTTTCTCTTCAGGTGCATTG-3′ for the first PCR and 5′-CGCCCCTTTTCGAGCAGCGAGCACTTTA-3′ for the second PCR; 3′ RACE: 5′-CGGAAAGACTACGCTCACTTCTGCAATC-3′ for the first PCR and 5′-TGCTCGCTGCTCGAAAAGGGGCGAAGTT-3′ for the second PCR respectively) together with adopter-specific primers supplied with the GeneRacer Kit (5′ RACE: 5′-CGACTGGAGCACGAGGACACTGA-3′ for the first PCR and 5′-GGACACTGACATGGACTGAAGGAGTA-3′ for the second PCR; 3′ RACE: 5′-GCTGTCAACGATACGCTACGTAACG-3′ for the first PCR and 5′-CGCTACGTAACGGCATGACAGTG-3′ for the second PCR respectively). A tBLASTn search [24] against nematode ESTs (expressed sequence tags) in the public database using C. elegans EF-Tu1 as the query was conducted, and the ESTs encoding putative EF-Tu sequences were identified. The EST clones potentially encoding the full-length cDNAs of Strongyloides ratti and Globodera rostochiensis (GenBank® accession numbers of their partial sequences were BM879408 and BI773024 respectively) were obtained from the Washington University Nematode EST project, and the entire cDNAs were sequenced as described above (S. ratti, AB211996; G. rostochiensis, AB211995).
Preparation of C-terminal deletion mutants of EF-Tu1 and measurement of tRNA binding activity
The expression vectors of C-terminal deletion mutants were prepared using the QuikChange® site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). The primer sets used for mutagenesis were 5′-GTTTGAAACCAGATTTTTCCAATTCTTAACAAAGCCCGAAAGGAAG-3′ and 5′-CTTCCTTTCGGGCTTTGTTAAGAATTGGAAAAATCTGGTTTCAAAC-3′ for the 14 amino acid deletion (d1), 5′-GCTGAAATGGAACGATTGGGATTCAAT-TAACAAAGCCCGAAAGGAAG-3′ and 5′-CTTCCTTTCGGGCTTTGTTAATTGAATCCCAATCGTTCCATTTCAGC-3′ for the 31 amino acid deletion (d12), 5′-TAACCAACGACGAAAAGGACTAACAAAGCCCGAAAGGAAG-3′ and 5′-CTTCCTTTCGGGCTTTGTTAGTCCTTTTCGTCGTTGGTTA-3′ for the 49 amino acid deletion (d123), and 5′-TTCACCGACGTTCTTCCATAACAAAGCCCGAAAGGAAG-3′ and 5′-CTTCCTTTCGGGCTTTGTTATGGAAGAACGTCGGTGAA-3′ for the 57 amino acid (entire domain 3′) deletion (d1234). The mutations in the primers that create premature stop codons are underlined. Recombinant proteins of C. elegans EF-Tu1 and its deletion mutants were expressed in E. coli and purified as described previously [19]. C. elegans mt EF-Ts were added to form mutant EFTu1–EF-Ts complexes after purification by Ni2+-affinity columns. Formation of the mutant EF-Tu1–EF-Ts complexes was confirmed by native gel electrophoresis [19]. Separation of the mutant EF-Tu1 and EF-Ts was performed using 9% native PAGE containing 8 mM Tricine/NaOH (pH 8.2), 1 mM EDTA and 5% glycerol. The buffer for electrophoresis contained 8 mM Tricine/NaOH (pH 8.2) and 1 mM EDTA. The binding activities of these mutants to A. suum mt Met-tRNAMet prepared by aminoacylation with an A. suum mitochondrial extract [17] were measured by a deacylation protection assay [16,17,25].
RESULTS
EF-Tu1-binding sites on T-armless tRNA detected by ENU-modification interference assay
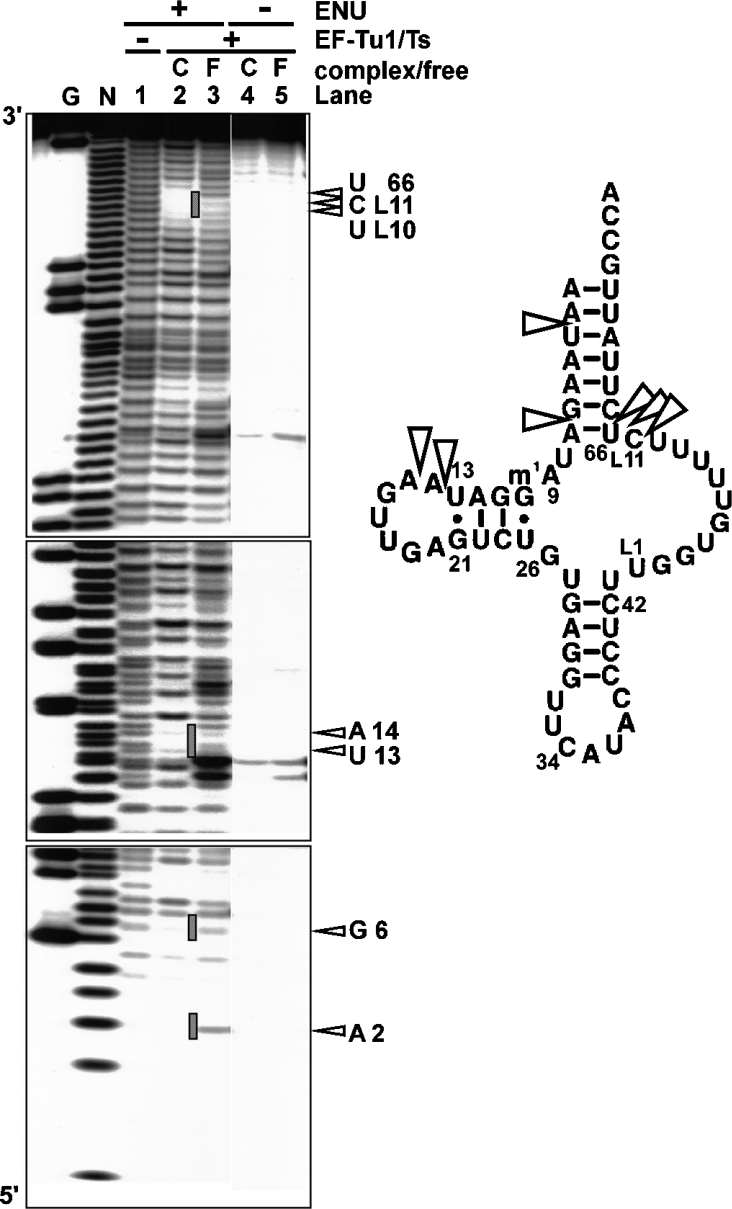
The modification interference assay was performed to investigate where EF-Tu1 binds the T-armless aa-tRNA (Figure 1). RNA modification interference of RNA–protein interactions identifies the protein-binding sites on the RNA [26–29]. In the present study, ENU was used as the modification agent. ENU is a mild alkylating agent that modifies backbone phosphates under mild conditions without base selectivity by forming phosphodiester groups that can be cleaved by mild base treatment [27,28]. EF-Tu cannot bind to Val-tRNA if the tRNA contains ethyl modifications of the phosphodiester bonds at site(s) necessary for EF-Tu binding. In Figure 1, comparison of the ethylated positions of ValtRNA bound to EF-Tu (Figure 1, lane 2) with those of free Val-tRNA (Figure 1, lane 3) shows that ethylation of the phosphates at positions 3, 7, 14, 15, L11, 66 and 67 on the tRNA interfered with EF-Tu1-binding. For nematode mt T-armless tRNAs, the nucleoside positions in the TV-replacement loop are numbered from L1 to L11 as described [10]. These positions are mapped in Figure 1 (right-hand side). The phosphates at positions 3, 7, 66 and 67 are in the acceptor stem, and the phosphate at position L11 is in the TV-replacement loop region. The phosphates at positions 14 and 15, which are in the D-arm region and with which normal EF-Tu cannot interact [2,3], were involved in EF-Tu1 binding. These results indicate that C. elegans mt EF-Tu1 possesses a unique aa-tRNA recognition mechanism that differs from those of canonical EF-Tu molecules.
Figure 1. Identification of the EF-Tu-binding sites on A. suum mt tRNAMet by the ENU-modification interference assay.
Left-hand side, autoradiographs of the ENU-modification interference assay using C. elegans mt EF-Tu1. Lanes: G, RNase T1 ladder; N, alkaline ladder; lanes 1–3, ENU-modified Val-tRNA; lanes 4 and 5, Val-tRNA without ENU modification; lanes 2, 3, 4 and 5, the Val-tRNA incubated with EF-Tu1–EF-Ts; lanes 2 and 4, the Val-tRNA in the ternary complex; lanes 3 and 5, the Val-tRNA free from EF-Tu. The open triangles and hatched lines show the ENU-modification interference of the complex formation. Right-hand side, the EF-Tu1-binding sites on the tRNAMet. The open triangles indicate phosphates interacting with the EF-Tu1. The base numbering is according to [10].
T-armless tRNA sites interacting with EF-Tu1, as determined by cross-linking
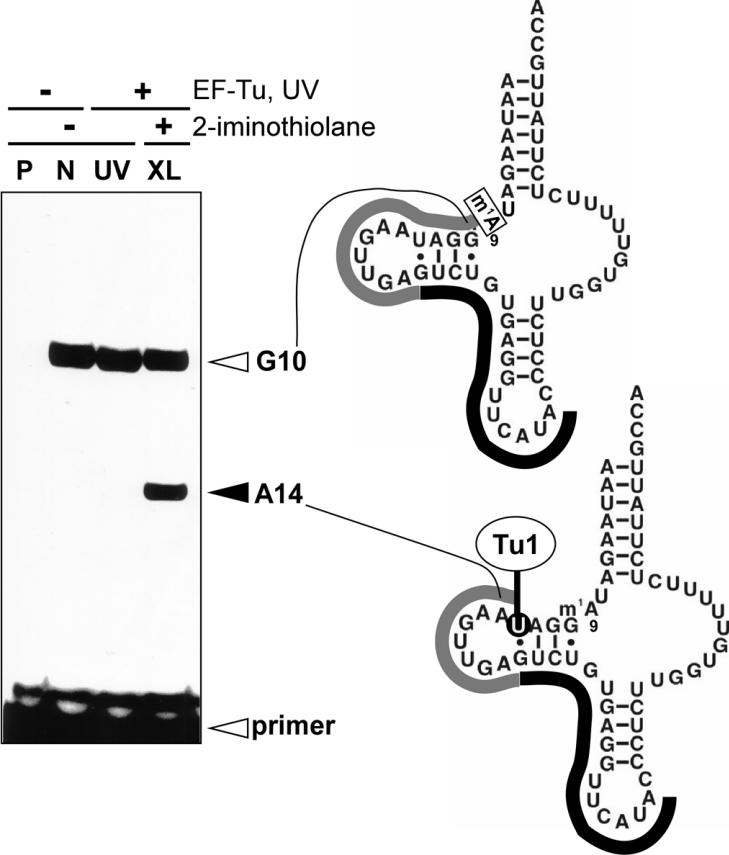
The cross-linking experiment using 2-iminothiolane was performed to identify the EF-Tu1-binding sites on A. suum mt Val-tRNAMet. 2-Iminothiolane reacts with primary amines, primarily lysine, in proteins and becomes coupled to uridine in RNAs after UV irradiation [21]. For example, the interactions detected by the cross-linking between 23 S rRNA and ribosomal proteins in E. coli 50 S ribosomal subunit [30] are consistent with those in the crystal structure of the ribosome [31]. The cross-linked site on the tRNAMet was determined by primer extension. Primers that started every six to nine nucleotides on the tRNA were used to probe all residues of the tRNA except for the 5′- and 3′-end regions. The region from the 3′-end to G(L5) was undetectable because a primer-binding region is necessary. The region from the 5′-end to m1A9 was undetectable because the methyl group at m1A9 inhibits primer extension. Figure 2 shows the results of primer extension using Primer 1, which identifies the cross-linked position on the tRNA. In the control experiment without UV cross-linking (Figure 2, lane N), Primer 1 extended to G10 on the tRNAMet because m1A9 blocks extension (Figure 2, right-hand side). UV irradiation without 2-iminothiolane (Figure 2, lane UV) did not cause cross-linking of the tRNA in the region from A21 to G10. Primer extension after UV irradiation using 2-iminothiolane (Figure 2, lane XL) stopped at A14, indicating that U13 was cross-linked to EF-Tu1. No other cross-linked sites were detected by Primers 2–5 (see Supplementary Figure 1 at http://www.BiochemJ.org/bj/399/bj3990249.add.htm). Thus, in the region from G10 to U(L4) of the tRNA, only U13 in the D-arm was cross-linked to EF-Tu1.
Figure 2. Primer extension analysis of cross-linked ternary complexes using a 5′-32P-labelled DNA primer (Primer 1).
Left-hand side, A. suum mt Val-tRNAMet (m1A9; lane N), the ternary complex irradiated by UV (lane UV) and the ternary complex irradiated by UV in the presence of 2-iminothiolane (lane XL) were analysed by primer extension on 15% denaturing PAGE. Lane P, primer only; lanes N, UV and XL, Val-tRNAMet was used. Right-hand side, diagrams of the primer extension results. Black and grey lines show Primer 1 complementarity to G21–A37 of the tRNA, and the extension of the primer respectively. The primer extensions were stopped at G10 in lanes N, UV and XL because of inhibition by the 1-methyl group at A9.
Binding activity of EF-Tu1 C-terminal deletion mutants
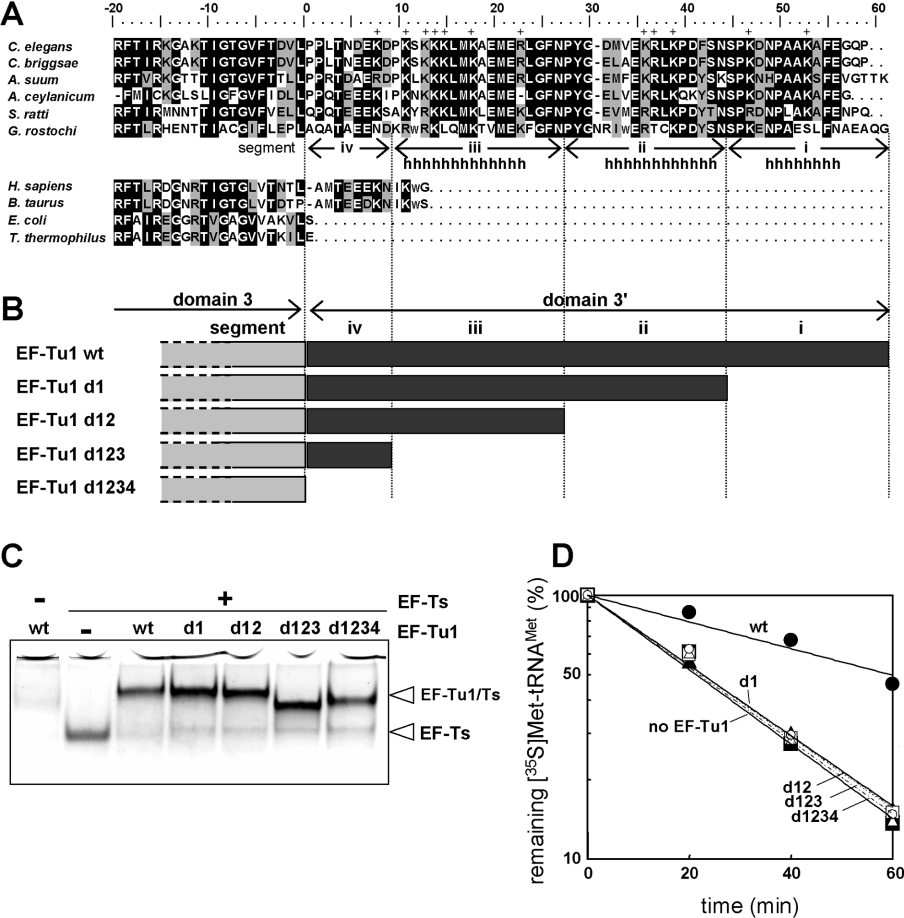
Our previous studies of chimeric proteins made from bovine mt EF-Tu and C. elegans mt EF-Tu1 suggested that the C-terminal extension (domain 3′) of C. elegans EF-Tu1 made a significant contribution to its ability to bind T-armless tRNAs [16]. All of the completely sequenced mt genomes from chromadorean nematodes encode 20 T-armless tRNAs and two D-armless tRNAs, but no cloverleaf-type tRNAs (see Introduction). To evaluate the evolutionary importance of the C-terminal extension of EF-Tu1, we determined full-length cDNA sequences of EF-Tu1 from three additional chromadorean nematodes A. suum (accession number AB211994), S. ratti (accession number AB211996) and G. rostochiensis (accession number AB211995). Protein sequence alignment revealed conservation in sequence and length of the domain 3′ among nematode EF-Tu1 proteins (Figure 3A). A secondary structure prediction of the domain 3′ of C. elegans mt EF-Tu1, using the PredictProtein software [32], suggested three α-helices in this region (Figures 3A and 3B). These three helical regions are represented by segments i, ii and iii and the rest of the domain 3′ is represented by segment iv in Figures 3(A) and 3(B). To determine the importance of these segments in binding T-armless tRNA, we prepared a series of mutants of C. elegans EF-Tu1 using nested deletions from the C-terminus (Figure 3B). First, we investigated complex formation of these mutants with C. elegans mt EF-Ts (encoded by the F55C5.5 gene, here renamed tsfm-1) by the gel mobility-shift assay [19]. The mutants and wild-type EF-Tu1 protein bound to similar extents to EF-Ts (Figure 3C), suggesting that the overall conformation and folding of domains 1 and 3 in these mutants were adequate for EF-Ts binding. Domains 1 and 3 of EF-Tu were shown previously to interact with bacterial and mitochondrial EF-Ts [33,34]. EF-Tu1 stayed in the wells of the gel (Figure 3C), probably because it aggregates in the absence of EF-Ts under these buffer conditions (with EDTA, but without Mg2+ and GDP), which are optimal for EF-Tu–EF-Ts binding. EF-Tu is unstable in the absence of a guanine nucleotide and EF-Ts. Our previous gel-filtration analysis showed that EF-Tu1 aggregates in buffer lacking Mg2+ and GDP, but containing EDTA [19]. Next, the binding activity of the mutants to Met-tRNAMet was measured by hydrolysis protection assay [17] (Figure 3D). Contrary to the results in the EF-Ts binding, the binding activity to the T-armless tRNA was lost when only 14 residues were deleted from the C-terminus. These results suggest that the entire C-terminal extension of the nematode EF-Tu1 is essential for binding to T-armless tRNAs.
Figure 3. C-terminal deletion mutants of C. elegans EF-Tu1.
(A) Amino acid alignment of EF-Tu1 homologues. EF-Tu1 sequences of C. elegans (accession number D38471), and its homologues in other nematodes, Caenorhabditis briggsae (CAE57516), A. suum (AB211994, the present study), Ancylostoma ceylanicum (CA341502, EST data), S. ratti (AB211996, the present study), and G. rostochiensis (AB211995, the present study). EF-Tu sequences of Homo sapiens (X84694), Bos taurus (L38996), E. coli (P02990) and T. thermophilus (SP07157) were also aligned. The alignment was carried out using Clustal X [51] followed by manual modifications. Black and gray areas indicate identical and similar amino acid sequences respectively. The positively charged amino acids in domain 3′ of C. elegans EF-Tu1 are indicated by ‘+’. The probable α-helix region of C. elegans mt EF-Tu1 predicted by a secondary structure prediction program is indicated by ‘h’ [32]. The predicted three helical regions are represented as segments i, ii and iii and the rest of domain 3′ is represented as segment iv. (B) Schematic representations of C-terminal deletion mutants of C. elegans EF-Tu1. (C) Native 9% PAGE analysis of complexes of EF-Tu1 deletion mutants and C. elegans mt EF-Ts. (D) The aa-tRNA-binding activities of the EF-Tu1 deletion mutants. A deacylation protection assay of the aminoacyl ester bond against hydrolysis of A. suum mt [35S]Met-tRNAMet (initial concentration 50 nM) was performed in the absence of EF-Tu (filled triangles and solid line) and in the presence of 5 μM C. elegans EF-Tu1–EF-Ts complex (filled circles and solid line) or mutant EF-Tu1–EF-Ts complex (d1, filled squares and solid line; d12, open circles and dotted line; d123, open squares and dotted line; d1234, open triangles and dotted line).
DISCUSSION
Recognition of T-armless tRNA by C. elegans EF-Tu1
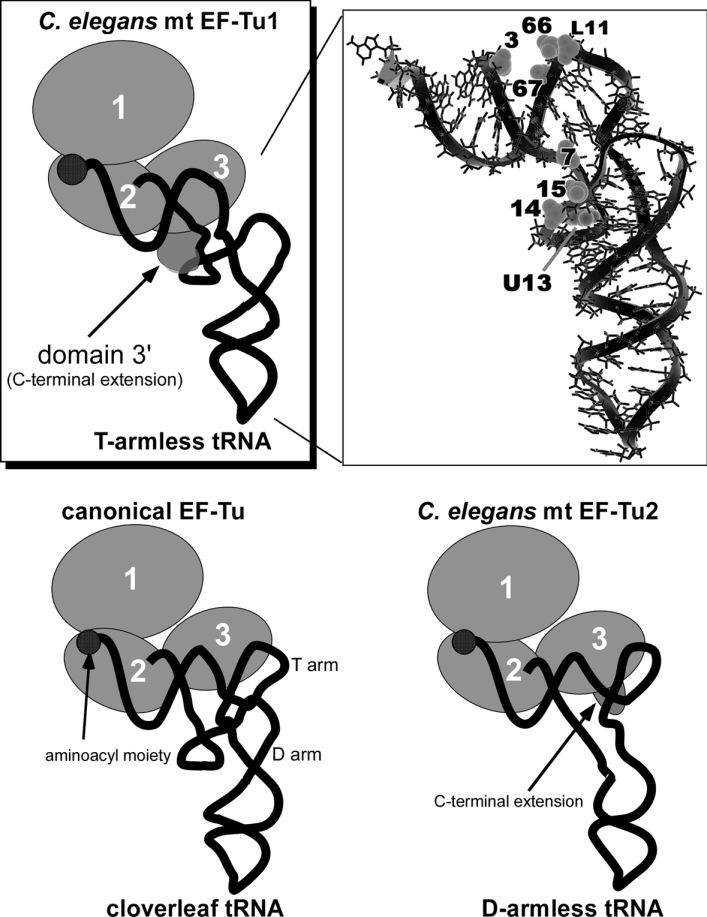
In a previous study, we found that C. elegans mt EF-Tu1 specifically binds to tRNAs lacking the T-stem [16] which is necessary for canonical EF-Tu to bind to tRNAs [2]. In this study, we investigated the mechanism by which EF-Tu1 binds to tRNAs in the absence of the T-stem. Our data demonstrate that the lack of interaction with the T-stem was compensated for in EF-Tu1 by a unique interaction with the D-arm. Figure 4 shows a model of EF-Tu1 binding to T-armless tRNA. Numerous binding experiments [4] and crystallographic analyses [2,3] have shown that bacterial EF-Tu recognizes the acceptor stem through its domains 1 and 2, and the T-arm through its domain 3 as shown in Figure 4 (bottom left). In contrast, the EF-Tu1-binding sites on tRNA identified by the above experiments indicate that EF-Tu1 recognized not only the acceptor stem but also the D-arm. The EF-Tu1-binding sites were the phosphate groups at positions 3, 7, 14, 15, L11, 66, 67 and the uridine base of U13 on the tRNAMet, as shown in Figure 4 (top right). The position L11 in the T-armless tRNAMet is similar to position 65 in the T-stem of standard tRNAs. Canonical EF-Tu interacts with phosphates at positions 3, 65, 66 and 67 in the tRNA, but not with those at positions 7, 14 and 15 [2,3]. Interaction of the D-arm (i.e. phosphates 14 and 15) with EF-Tu1 is rather unexpected, but was observed by two different experiments (ENU-modification interference and cross-linking analyses). It is very likely that the unique region of EF-Tu1 (i.e. domain 3′) interacts with phosphates 7, 14 and 15, as shown in Figure 4 (top).
Figure 4. Models of the ternary complexes.
EF-Tu is shown as a set of circles, each of which corresponds to the domain numbers. The tRNAs are portrayed as simplified backbones with the aminoacyl moiety at the 3′-terminus depicted by filled circles. GTP is not shown. The ternary complex including nematode mt EF-Tu1 and the T-armless tRNA (top left). The hatched domain shows the predicted location of the EF-Tu1 domain 3′. A. suum mt tRNAMet lacking the T-arm is presented by the structural model (top right) [52]. The phosphates important for EF-Tu1-binding, detected by modification interference (3, 7, 14, 15, L11, 66 and 67), and the base cross-linked with EF-Tu1 (U13) are shown in the space-filled representation. The tRNA chemical structure is shown with thin lines and its backbone with the bold line. The bacterial ternary complex is shown bottom left [2]. The ternary complex including nematode mt EF-Tu2 and D-armless Ser-tRNA is shown bottom right [20].
Recognition of the D-arm by domain 3′ is indicated by the following evidence. The chimaeric EF-Tu having domains 1 and 2 of canonical EF-Tu and domains 3 and 3′ of EF-Tu1 has the same tRNA-specificity as EF-Tu1 [16], indicating that domains 1 and 2 do not contribute to D-arm recognition. Domain 3 of EF-Tu1 is 34% homologous with Thermus thermophilus EF-Tu, suggesting that domain 3 of EF-Tu1 is similar to the canonical one. Thus domains 1, 2 and 3 of EF-Tu1 seem not to interact with the D-arm. Domain 3′ has a high content (21%) of positively charged amino acids: ten lysine and two arginine residues (Figure 3A). In contrast, 13% of amino acids in domains 1–3 are positively charged. The positively charged regions of the protein seem to interact with RNA that has negatively charged phosphate groups. ENU-modification of phosphates 14 and 15 interfered the EF-Tu1-binding to the tRNA (Figure 1), suggesting that these phosphate groups in the D-arm interact with EF-Tu1. Interaction of domain 3′ with the tRNA is also supported by the finding that deletion of only 14 C-terminal residues abolished the tRNA-binding activity of EF-Tu1 (Figure 3D). Thus, our data suggest that domain 3′ interacts with the D-arm of the T-armless tRNA.
EF-Tu1 does not bind aa-tRNAs with the canonical cloverleaf structure [16]. This may indicate that EF-Tu1 recognizes structures specific to T-armless tRNA. This study indicated that EF-Tu1 recognized the TV-replacement loop [i.e. U(L10) and C(L11) in A. suum mt tRNAMet] and the D-arm (U13 and A14), which is difficult for EF-Tu to access in canonical tRNA.
Among the 120 T-armless mt tRNAs encoded by C. elegans [10], A. suum [11], O. volvulus [12], Ancylostoma duodenale [13], N. americanus [13] and D. immitis [14], A14 is completely conserved (120/120) and U13 is almost completely conserved (116/120). A2, G6, U(L10), C(L11) and U66 are not conserved among these tRNAs. The extremely high conservation of U13 and A14 suggests that EF-Tu1 may recognize these positions in a sequence-specific manner.
Physiological significance of nematode mt EF-Tu1
RNA interference of the C. elegans tufm-1 gene showed that C. elegans could not survive when expression of EF-Tu1 was suppressed [35]. Many nematodes are parasites of plants and animals, including humans [36]. Bacterial EF-Tu can be a target of antibiotics such as kirromycin and pulvomycin [37]. Since the structure and properties of nematode mt EF-Tu1 differ from those of animal and plant mt EF-Tu and the cytoplasmic counterpart EF-1α, analysis of the structure and function of nematode EF-Tu1 may contribute to the development of new highly selective drugs against parasitic nematodes.
Co-evolution of mitochondrial EF-Tus and tRNAs
The present RNA–DNA–protein world is considered to have originated from an RNA world in which RNA was responsible for both catalysis and information storage (reviewed in [38–40]). According to the RNA world hypothesis, many of the present day biological systems that use both RNA and proteins, such as the translation apparatus, had ancestors that used RNA only. One tenet of this hypothesis is that as RNA components in biological systems were replaced by proteins, the RNA component underwent a reduction in size and function that was compensated by an increase in size and function of the associated protein. In the present study, the co-evolutionary process is shown by the distinct differences that exist between bacterial and mitochondrial ternary complexes.
C. elegans mt EF-Tu1 is the first example of an EF-Tu that can recognize the D-arm of tRNA. This finding provides an example of the co-evolution of RNA and protein that was necessary to maintain RNA–protein interactions. Since canonical EF-Tu cannot bind to T-armless tRNAs [16], EF-Tu1 compensates for the tRNA truncation. Nematode mt EF-Tu1 compensates for the tRNA truncation through an elongation of its C-terminus, which contains the new tRNA-recognition site. The recognition mechanism of the C-terminal extension was also observed for nematode mt EF-Tu2 in our previous work, but the sites recognized by the C-terminus of EF-Tu2 are different from those recognized by EF-Tu1 [20] (Figure 4, bottom right). The common feature of EF-Tu1 and EF-Tu2 is that they have acquired a C-terminal extension which forms novel contacts near the hinge region to compensate for the T- or D-arm truncations. From an evolutionary point of view, one might ask why the D-arm and/or T-arm are shortened in animal mt tRNAs. One of the answers may be that EF-Tu co-evolved to support such truncated tRNAs. In nematode mitochondria, the genomic DNA might have been subjected to severe size reductions, as indicated by its present day extremely small size. Given this reductive pressure and the encoding of EF-Tu1 by the nuclear genome, it may have been possible to shorten the T in most nematode mt tRNAs.
To date, many animal mt genome sequences have been determined. The sequenced mt genomes of all metazoa except for demospongiae and cnidaria have D-armless tRNA genes. Furthermore, there are mt DNAs which encode both T-armless tRNAs and D-armless tRNAs in some animals other than nematodes, for example, the brachiopods Terebratulina retusa [41], Laqueus rubellus [42] and Terebratalia transversa [43], the molluscs Cepaea nemoralis, Albinaria coerulea [44], Pupa strigosa [45] and Euhadra herklotsi [46], the acanthocephalans Leptorhynchoides thecatus [47], and the arthropods Habronattus oregonensis [48], Heptathela hangzhouensis, Ornithoctonus huwena [49] and Leptotrombidium pallidum [50]. Intriguingly, although many arthropod mt genomes, such as Drosophila, have D-armless and cloverleaf tRNAs instead of T-armless tRNA, these arthropods have two EF-Tus resembling nematode EF-Tu1 and EF-Tu2 (A. Sato, Y. Watanabe, K. Watanabe and T. Ohtsuki, unpublished work). These results suggest that gene duplication of mt EF-Tu occurred before the birth of T-armless mt tRNA and that it might have encouraged the birth of T-armless tRNAs. Although the tRNA-specificity of EF-Tu proteins from animals other than nematodes and mammals has not been verified yet, their analysis may serve to further illuminate RNA–protein co-evolution.
Online data
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor K. Kita (University of Tokyo) for A. suum, and Dr T. Suzuki and Dr S. Chimnaronk (Department of Integrated Biosciences, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan) for pdCpA-Val. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan to Y.W., K.W. and T.O., and by the Kurata Memorial Hitachi Science and Technology Foundation to T.O.
References
- 1.Sprinzl M. Elongation factor Tu: a regulatory GTPase with an integrated effector. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994;19:245–250. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nissen P., Kjeldgaard M., Thirup S., Polekhina G., Reshetnikova L., Clark B. F., Nyborg J. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science. 1995;270:1464–1472. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nissen P., Thirup S., Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of Cys-tRNACys-EF-Tu-GDPNP reveals general and specific features in the ternary complex and in tRNA. Structure. 1999;7:143–156. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Clark B. F. C., Kjeldgaard M., Barciszewski J., Sprinzl M. Recognition of aminoacyl-tRNAs by protein elongation factors. tRNA: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Function. In: Soll D., RajBhandary U. L., editors. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 423–442. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rudinger J., Blechschmidt B., Ribeiro S., Sprinzl M. Minimalist aminoacylated RNAs as efficient substrates for elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1994;33:5682–5688. doi: 10.1021/bi00185a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dirheimer G., Keith G., Dumas P., Westhof E. Primary, secondary and tertiary structures of tRNAs. tRNA: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Function. In: Soll D., RajBhandary U. L., editors. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 93–126. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sprinzl M., Horn C., Brown M., Ioudovitch A., Steinberg S. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:148–153. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ohtsuki T., Sato A., Watanabe Y., Watanabe K. A unique serine-specific elongation factor Tu found in nematode mitochondria. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002;9:669–673. doi: 10.1038/nsb826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhao F., Ohtsuki T., Yamada K., Yoshinari S., Kita K., Watanabe Y., Watanabe K. Isolation and physiochemical properties of protein-rich nematode mitochondrial ribosomes. Biochemistry. 2005;44:9232–9237. doi: 10.1021/bi047833c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wolstenholme D. R., Macfarlane J. L., Okimoto R., Clary D. O., Wahleithner J. A. Bizarre tRNAs inferred from DNA sequences of mitochondrial genomes of nematode worms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1987;84:1324–1328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Okimoto R., Macfarlane J. L., Clary D. O., Wolstenholme D. R. The mitochondrial genomes of two nematodes, Caenorhabditis elegans and Ascaris suum. Genetics. 1992;130:471–498. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Keddie E. M., Higazi T., Unnasch T. R. The mitochondrial genome of Onchocerca volvulus: sequence, structure and phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998;95:111–127. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(98)00102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hu M., Chilton N. B., Gasser R. B. The mitochondrial genomes of the human hookworms, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus (Nematoda: Secernentea) Int. J. Parasitol. 2002;32:145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hu M., Gasser R. B., Abs El-Osta Y. G., Chilton N. B. Structure and organization of the mitochondrial genome of the canine heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis. Parasitology. 2003;127:37–51. doi: 10.1017/s0031182003003275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Van der Veer M., de Vries E. A single nucleotide polymorphism map of the mitochondrial genome of the parasitic nematode Cooperia oncophora. Parasitology. 2004;128:421–431. doi: 10.1017/s0031182003004633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ohtsuki T., Watanabe Y., Takemoto C., Kawai G., Ueda T., Kita K., Kojima S., Kaziro Y., Nyborg J., Watanabe K. An “elongated” translation elongation factor Tu for truncated tRNAs in nematode mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:21571–21577. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011118200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sakurai M., Ohtsuki T., Watanabe K. Modification at position 9 with 1-methyladenosine is crucial for structure and function of nematode mitochondrial tRNAs lacking the entire T-arm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:1653–1661. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zuilhof H., Lodder G., Koch H. F. Carbon-oxygen hydrogen bonding in dehydrohalogenation reactions: PM3 calculations on polyhalogenated phenylethane derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 1997;62:7457–7463. doi: 10.1021/jo962154w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ohtsuki T., Sakurai M., Sato A., Watanabe K. Characterization of the interaction between the nucleotide exchange factor EF-Ts from nematode mitochondria and elongation factor Tu. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:5444–5451. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Suematsu T., Sato A., Sakurai M., Watanabe K., Ohtsuki T. A unique tRNA recognition mechanism of Caenorhabditis elegans mitochondrial EF-Tu2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:4683–4691. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wower I., Wower J., Meinke M., Brimacombe R. The use of 2-iminothiolane as an RNA-protein cross-linking agent in Escherichia coli ribosomes, and the localisation on 23S RNA of sites cross-linked to proteins L4, L6, L21, L23, L27 and L29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981;9:4285–4302. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Urlaub H., Kruft V., Bischof O., Muller E. C., Wittmann-Liebold B. Protein-rRNA binding features and their structural and functional implications in ribosomes as determined by cross-linking studies. EMBO J. 1995;14:4578–4588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kirino Y., Goto Y., Campos Y., Arenas J., Suzuki T. Specific correlation between the wobble modification deficiency in mutant tRNAs and the clinical features of a human mitochondrial disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:7127–7132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500563102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Altschul S. F., Madden T. L., Schaffer A. A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D. J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pingoud A., Urbanke C., Krauss G., Peters F., Maass G. Ternary complex formation between elongation factor Tu, GTP and aminoacyl-tRNA: an equilibrium study. Eur. J. Biochem. 1977;78:403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Haynes S. R. Totowa, N.J.: Humana Press; 1999. RNA–Protein Interaction Protocols. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vlassov V. V., Giege R., Ebel J. P. Tertiary structure of tRNAs in solution monitored by phosphodiester modification with ethylnitrosourea. Eur. J. Biochem. 1981;119:51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vlassov V. V., Kern D., Romby P., Giege R., Ebel J. P. Interaction of tRNAPhe and tRNAVal with aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. A chemical modification study. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983;132:537–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mayer C., RajBhandary U. L. Conformational change of Escherichia coli initiator methionyl-tRNA(fMet) upon binding to methionyl-tRNA formyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:2844–2850. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gulle H., Hoppe E., Osswald M., Greuer B., Brimacombe R., Stoffler G. RNA-protein cross-linking in Escherichia coli 50S ribosomal subunits; determination of sites on 23S RNA that are cross-linked to proteins L2, L4, L24 and L27 by treatment with 2-iminothiolane. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:815–832. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schuwirth B. S., Borovinskaya M. A., Hau C. W., Zhang W., Vila-Sanjurjo A., Holton J. M., Cate J. H. Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 Å resolution. Science. 2005;310:827–834. doi: 10.1126/science.1117230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rost B., Sander C., Schneider R. PHD: an automatic mail server for protein secondary structure prediction. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1994;10:53–60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kawashima T., Berthet-Colominas C., Wulff M., Cusack S., Leberman R. The structure of the Escherichia coli EF-Tu.EF-Ts complex at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature. 1996;379:511–518. doi: 10.1038/379511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jeppesen M. G., Navratil T., Spremulli L. L., Nyborg J. Crystal structure of the bovine mitochondrial elongation factor Tu.Ts complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:5071–5081. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411782200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kamath R. S., Fraser A. G., Dong Y., Poulin G., Durbin R., Gotta M., Kanapin A., Le Bot N., Moreno S., Sohrmann M., Welchman D. P., Zipperlen P., Ahringer J. Systematic functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature. 2003;421:231–237. doi: 10.1038/nature01278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blaxter M. L., De Ley P., Garey J. R., Liu L. X., Scheldeman P., Vierstraete A., Vanfleteren J. R., Mackey L. Y., Dorris M., Frisse L. M., Vida J. T., Thomas W. K. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature. 1998;392:71–75. doi: 10.1038/32160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hogg T., Mesters J. R., Hilgenfeld R. Inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2002;3:121–131. doi: 10.2174/1389203023380855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Joyce G. F. The antiquity of RNA-based evolution. Nature. 2002;418:214–221. doi: 10.1038/418214a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yarus M. Boundaries for an RNA world. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999;3:260–267. doi: 10.1016/S1367-5931(99)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Spirin A. S. Omnipotent RNA. FEBS Lett. 2002;530:4–8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stechmann A., Schlegel M. Analysis of the complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the brachiopod Terebratulina retusa places Brachiopoda within the protostomes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1999;266:2043–2052. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1999.0885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Noguchi Y., Endo K., Tajima F., Ueshima R. The mitochondrial genome of the brachiopod Laqueus rubellus. Genetics. 2000;155:245–259. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Helfenbein K. G., Brown W. M., Boore J. L. The complete mitochondrial genome of the articulate brachiopod Terebratalia transversa. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001;18:1734–1744. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yamazaki N., Ueshima R., Terrett J. A., Yokobori S., Kaifu M., Segawa R., Kobayashi T., Numachi K., Ueda T., Nishikawa K., Watanabe K., Thomas R. H. Evolution of pulmonate gastropod mitochondrial genomes: comparisons of gene organizations of Euhadra, Cepaea and Albinaria and implications of unusual tRNA secondary structures. Genetics. 1997;145:749–758. doi: 10.1093/genetics/145.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kurabayashi A., Ueshima R. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial DNA of the primitive opisthobranch gastropod Pupa strigosa: systematic implication of the genome organization. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000;17:266–277. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ueshima R., Asami T. Evolution: single-gene speciation by left-right reversal. Nature. 2003;425:679. doi: 10.1038/425679a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Steinauer M. L., Nickol B. B., Broughton R., Orti G. First sequenced mitochondrial genome from the phylum Acanthocephala (Leptorhynchoides thecatus) and its phylogenetic position within Metazoa. J. Mol. Evol. 2005;60:706–715. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Masta S. E., Boore J. L. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the spider Habronattus oregonensis reveals rearranged and extremely truncated tRNAs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004;21:893–902. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Qiu Y., Song D., Zhou K., Sun H. The mitochondrial sequences of Heptathela hangzhouensis and Ornithoctonus huwena reveal unique gene arrangements and atypical tRNAs. J. Mol. Evol. 2005;60:57–71. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shao R., Mitani H., Barker S. C., Takahashi M., Fukunaga M. Novel mitochondrial gene content and gene arrangement indicate illegitimate inter-mtDNA recombination in the chigger mite, Leptotrombidium pallidum. J. Mol. Evol. 2005;60:764–773. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., Plewniak F., Jeanmougin F., Higgins D. G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4876–4882. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ohtsuki T., Kawai G., Watanabe K. Stable isotope-edited NMR analysis of Ascaris suum mitochondrial tRNAMet having a TV-replacement loop. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1998;124:28–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.