Abstract
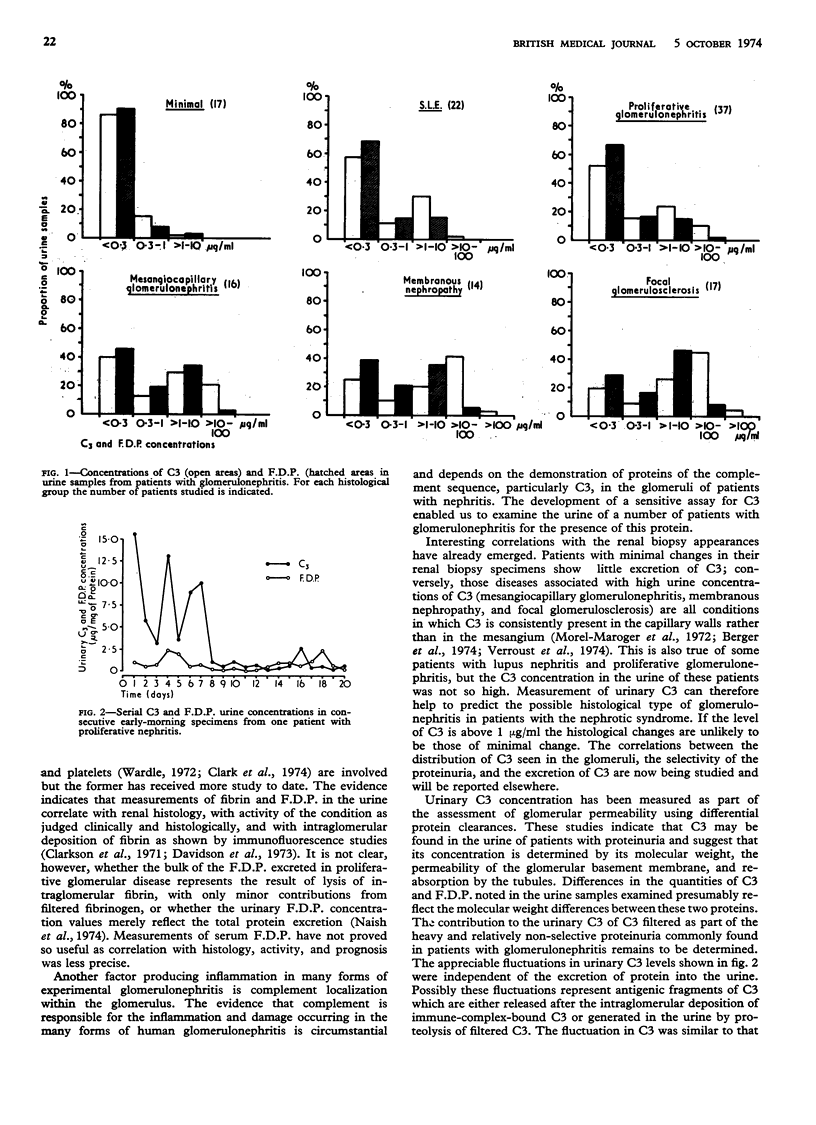
C3 and fibrin degradation products (F.D.P.) have been measured in early morning urine samples from 38 normal people and 123 patients with glomerulonephritis. Normal urine contained less than 0·3 μg of either antigen per ml. C3 and F.D.P. were both detected in the urine of many patients with glomerulonephritis. Levels above 1 μg/ml were exceptional in patients with “minimal change,” and the highest excretion of both antigens occurred in mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, membranous nephropathy, and focal glomerulosclerosis.
Both C3 and F.D.P. excretion showed considerable variation with time, with parellel fluctuations in the two antigens. These fluctuations did not depend on the total protein leakage and suggest that the complement and clotting sequence are closely related in these glomerular disorders.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Churg J., Habib R., White R. H. Pathology of the nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet. 1970 Jun 20;760(1):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. M., Thomson D., Macdonald M. K., Rae J. K., Uttley W. S., Clarkson A. R. Identification of intrarenal fibrin deposition. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Feb;26(2):102–112. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoq M. S., Anderton J. L., Cunningham M., Cash J. D. Urinary excretion of fibrinogen-related materials, complement, and immunoglobulins in proliferative glomerulonephritis and after renal transplantation. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 8;2(5918):535–538. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5918.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humair L., Potter E. V., Kwaan H. C. The role of fibrinogen in renal disease. I. Production of experimental lesions in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):60–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., WENK E. J. Complement components in the sera and urines of patients with severe proteinurias. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Oct;228(4):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrue G., Brécy H., Hartmann L. La complémenturie dans les glomérulopathies humaines. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1969 Apr;14(4):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Maroger L., Leathem A., Richet G. Glomerular abnormalities in nonsystemic diseases. Relationship between findings by light microscopy and immunofluorescence in 433 renal biopsy specimens. Am J Med. 1972 Aug;53(2):170–184. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P., Evans D. J., Peters D. K. Urinary fibrinogen derivative excretion and intraglomerular fibrin deposition in glomerulonephritis. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 23;1(5907):544–546. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5907.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T. The pathogenetic role of the coagulation process in glomerular diseases of immunologic origin. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1971;1:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verroust P. J., Wilson C. B., Cooper N. R., Edgington T. S., Dixon F. J. Glomerular complement components in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):77–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI107562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. The role of platelets in glomerulonephritis and transplantation. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1972 Oct;7(1):5–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]