Abstract
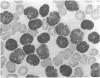
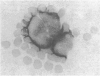
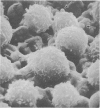
Two cases of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (A.L.L.) of T-cell type are reported. Clinically they were characterized by very high peripheral blood blast cell counts at presentation, the early development of meningeal leukaemia, and relative resistance to treatment with combination chemotherapy. Leukaemic cells from both patients lacked all the B-cell markers investigated, but 60-65% of their cells formed rosettes with sheep red cells. Cytochemical and surface structure studies helped to define additional features of these cells and confirmed their T-cell nature.
It seems that this variant of A.L.L. may not be uncommon and that it can be distinguished on clinical and immunological grounds from the usual type of A.L.L. which runs a less aggressive course and lacks B- or T-cell markers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borella L., Sen L. T cell surface markers on lymphoblasts from acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1257–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B., Stavem P. Immunological characterization of lymphocytes in lymphoproliferative diseases. Restriction of classes, subclasses, and Gm allotypes of membrane-bound Ig. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG A. F., BARKA T. Acid phosphatase activity in human blood cells. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:297–297. doi: 10.1038/195297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman J. U., Rossen R. D., Butler W. T., McCredie K. B., Bodey G. P., Sr, Freireich E. J., Hersh E. M. Immunoglobulin on tumor cells and tumor-induced lymphocyte blastogenesis in human acute leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 25;288(4):169–175. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301252880401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Chera N., Peled A. Thymus and bone marrow derived lymphatic leukaemia in mice. Nature. 1973 Feb 9;241(5389):396–398. doi: 10.1038/241396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Chera N., Peled A. Thymus and bone marrow derived lymphatic leukaemia in mice. Nature. 1973 Feb 9;241(5389):396–398. doi: 10.1038/241396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey J. H., Sabad A., Gajl-Peczalska K., Hallgren H. M., Yunis E. J., Nesbit M. E. Acute lymphoblastic leukemic cells with T (thymus-derived) lymphocyte markers. Science. 1973 Dec 28;182(4119):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4119.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. S., Cooper A. G., Wortis H. H. Scanning electron microscopy of human T-cell and B-cell rosettes. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 13;289(11):548–551. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309132891102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Brown J. C., Holborow E. J. Immunoglobulins on the surface of human lymphocytes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 16;2(7729):850–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovsky S., Eppinger-Helft M., Sackmann Muriel F. Factors that influence the appearance of central nervous system leukemia. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):935–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polliack A., Lampen N., Clarkson B. D., De Harven E., Bentwich Z., Siegal F. P., Kunkel H. G. Identification of human B and T lymphocytes by scanning electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Herberman R., Frank M. M., Green I. Receptors for complement and immunoglobulin on human leukemic cells and human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1933–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI106999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiers A. S. Cure as the aim in therapy for the acute leukaemias. Lancet. 1972 Sep 2;2(7775):473–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91866-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Nossal G. J. Identification of human T and B lymphocytes in normal peripheral blood and in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1971 Oct 9;2(7728):788–791. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92741-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Chantler S., Fudenberg H. H. Isolation of normal T cells in chronic lymphatic leukaemia. Lancet. 1973 Jan 20;1(7795):126–129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]