Abstract
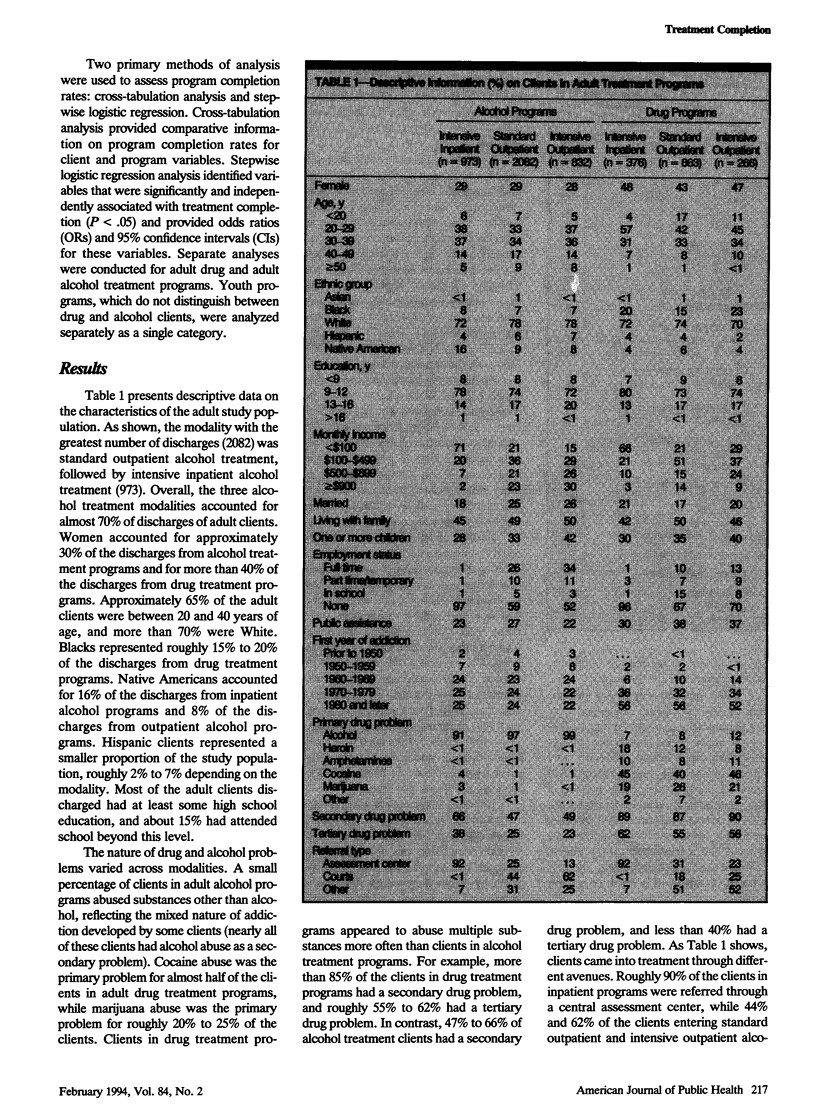
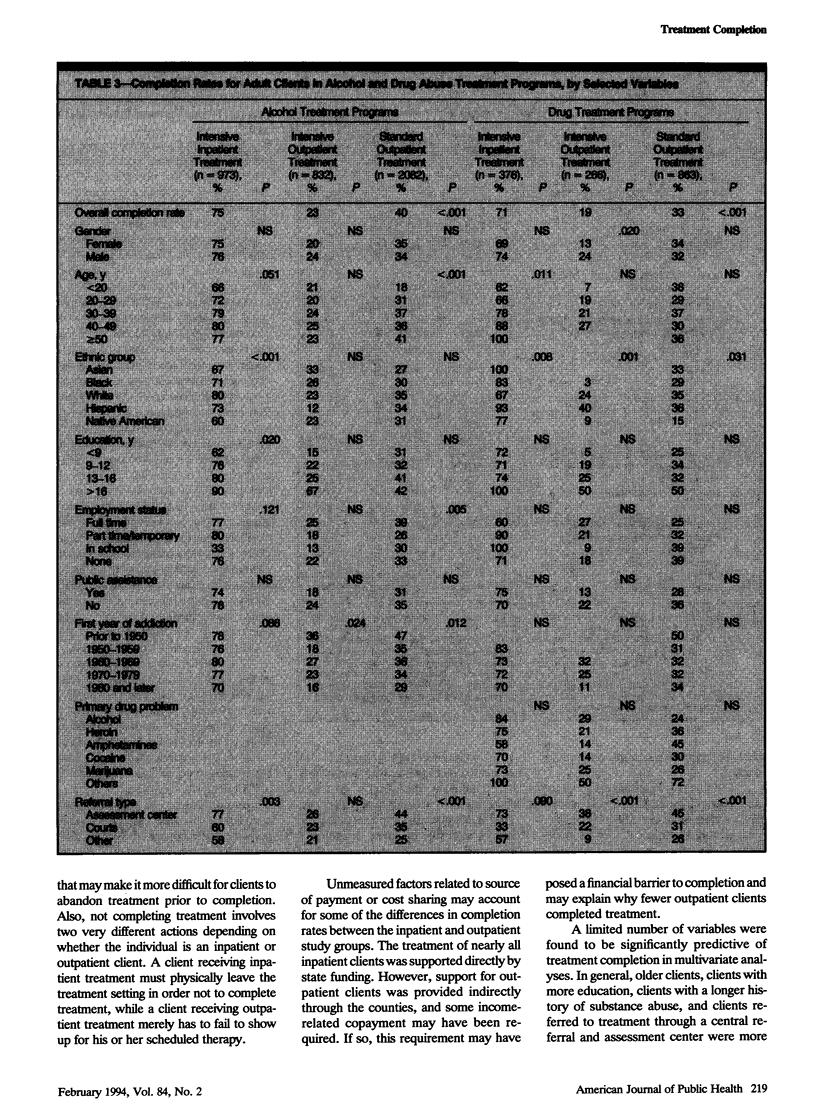
OBJECTIVES. The primary goal of this study was to analyze completion rates of clients in drug and alcohol abuse treatment programs in Washington State and to assess the factors associated with treatment completion. A secondary goal was to examine the utility of a state information system as a source of evaluative data. METHODS. Analyses were conducted of 5827 client records contained in the Washington State Substance Abuse Monitoring System, representing a census of public clients discharged during the last quarter of 1990 from all state-funded alcohol and drug treatment programs in four treatment modalities. Logistic regression was performed to determine the independent predictors of treatment completion. RESULTS. Completion rates were highest for intensive inpatient alcohol treatment (75%) and lowest for intensive outpatient drug programs (18%). Factors associated with treatment completion included screening at a referral assessment center, education, age, ethnicity, and existence of a secondary drug problem. CONCLUSIONS. The fit between clients and treatment programs may be an important factor explaining why some clients complete treatment and others drop out. State client information systems are an important source of data for analyzing treatment completion and other outcomes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addenbrooke W. M., Rathod N. H. Relationship between waiting time and retention in treatment amongst substance abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1990 Nov;26(3):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(90)90167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan C. Seeking help for drinking problems from a community-based voluntary agency. Patterns of compliance amongst men and women. Br J Addict. 1987 Oct;82(10):1143–1147. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1987.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekeland F., Lundwall L. Dropping out of treatment: a critical review. Psychol Bull. 1975 Sep;82(5):738–783. doi: 10.1037/h0077132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. T., Twemlow S. W. Staff absence as a factor in the patient dropout rate in alcoholism treatment programs. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1978 Jun;29(6):361–367. doi: 10.1176/ps.29.6.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer L. G., Zawadski M. L., Lincoln R. Characteristics of alcoholics and codependents who did and did not complete treatment. Int J Addict. 1990 Jun;25(6):653–663. doi: 10.3109/10826089009061326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizer D. A., Maslansky R., Galanter M. Treatment retention of patients referred by public assistance to an alcoholism clinic. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1990;16(3-4):259–264. doi: 10.3109/00952999009001587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. S., Joe G. W., Thompson P. Minority group status and treatment retention. Int J Addict. 1985 Feb;20(2):319–335. doi: 10.3109/10826088509044914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. J. Reducing the treatment drop out rate in drug abuse programs. J Subst Abuse Treat. 1985;2(4):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0740-5472(85)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigelman W. Day-care treatment for multiple drug abusing adolescents: social factors linked with completing treatment. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1987 Oct-Dec;19(4):335–344. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1987.10472421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink E. B., Rudden S., Longabaugh R., McCrady B., Stout R. Adherence in a behavioral alcohol treatment program. Int J Addict. 1984 Nov;19(7):709–719. doi: 10.3109/10826088409057218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Linn M. W., Pratt T. C. A comparison of dropouts and disciplinary discharges from a therapeutic community. Int J Addict. 1980 Jul;15(5):749–756. doi: 10.3109/10826088009040052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber N. A., Danahy S. Use of the MMPI in predicting completion and evaluating changes in a long-term alcoholism treatment program. J Stud Alcohol. 1975 Sep;36(9):1230–1237. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1975.36.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. W. Predicting patients' withdrawal against medical advice from an alcoholism treatment center. Psychol Rep. 1985 Dec;57(3 Pt 1):991–994. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1985.57.3.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnoff A. Differences between alcoholics who complete or withdraw from treatment. J Stud Alcohol. 1976 Nov;37(11):1666–1671. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1976.37.1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnoff A. Failure of MMPI scales to predict treatment completion. J Stud Alcohol. 1977 Jul;38(7):1440–1442. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh G., Ogborne A. C., Cleland P. Factors associated with patient dropout from an outpatient alcoholism treatment service. J Stud Alcohol. 1984 Jul;45(4):359–362. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1984.45.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn M. W. Attrition of older alcoholics from treatment. Addict Dis. 1978;3(3):437–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means L. B., Small M., Capone D. M., Capone T. J., Condren R., Peterson M., Hayward B. Client demographics and outcome in outpatient cocaine treatment. Int J Addict. 1989 Aug;24(8):765–783. doi: 10.3109/10826088909047312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise R., Reed B. G., Conell C. Women in drug abuse treatment programs: factors that influence retention at very early and later stages in two treatment modalities. A summary. Int J Addict. 1981 Oct;16(7):1295–1300. doi: 10.3109/10826088109039187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. W., Beech H. R., Hore B. D. Some factors associated with compliance in the treatment of alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol. 1984;19(4):303–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roffe M. W. Predictive correlates of treatment program completion in a sample of male alcoholics. Int J Addict. 1981 Jul;16(5):849–857. doi: 10.3109/10826088109038894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L. J., Jr Internal-external control and withdrawal AMA from an alcohol rehabilitation program. J Clin Psychol. 1978 Apr;34(2):571–573. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(197804)34:2<571::aid-jclp2270340269>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder D. J., Bowen W. T., Twemlow S. W. Factors related to patient attrition from alcoholism treatment programs. Int J Addict. 1982 Apr;17(3):463–472. doi: 10.3109/10826088209064051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddall J. W., Conway G. L. Interactional variables associated with retention and success in residential drug treatment. Int J Addict. 1988;23(12):1241–1254. doi: 10.3109/10826088809058855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Campbell B. K. Personality, drug use, and early attrition from substance abuse treatment. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1988;14(4):475–485. doi: 10.3109/00952998809001565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer R. A. Retention in drug-free counseling. Int J Addict. 1983 Dec;18(8):1109–1114. doi: 10.3109/10826088309027373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verinis J. S. Ward atmosphere as a factor in irregular discharge from an alcohol rehabilitation unit. Int J Addict. 1983 Aug;18(6):895–899. doi: 10.3109/10826088309033057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson A. E., Prado W. M., Williams W. O., Schnadt F. W. Psychological test characteristics and length of stay in alcoholism treatment. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1971 Mar;32(1):60–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. N., Whelan W. M. Anxiety as a factor in continuance and dropout in treatment. Int J Addict. 1983 May;18(4):577–582. doi: 10.3109/10826088309033040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


