Abstract
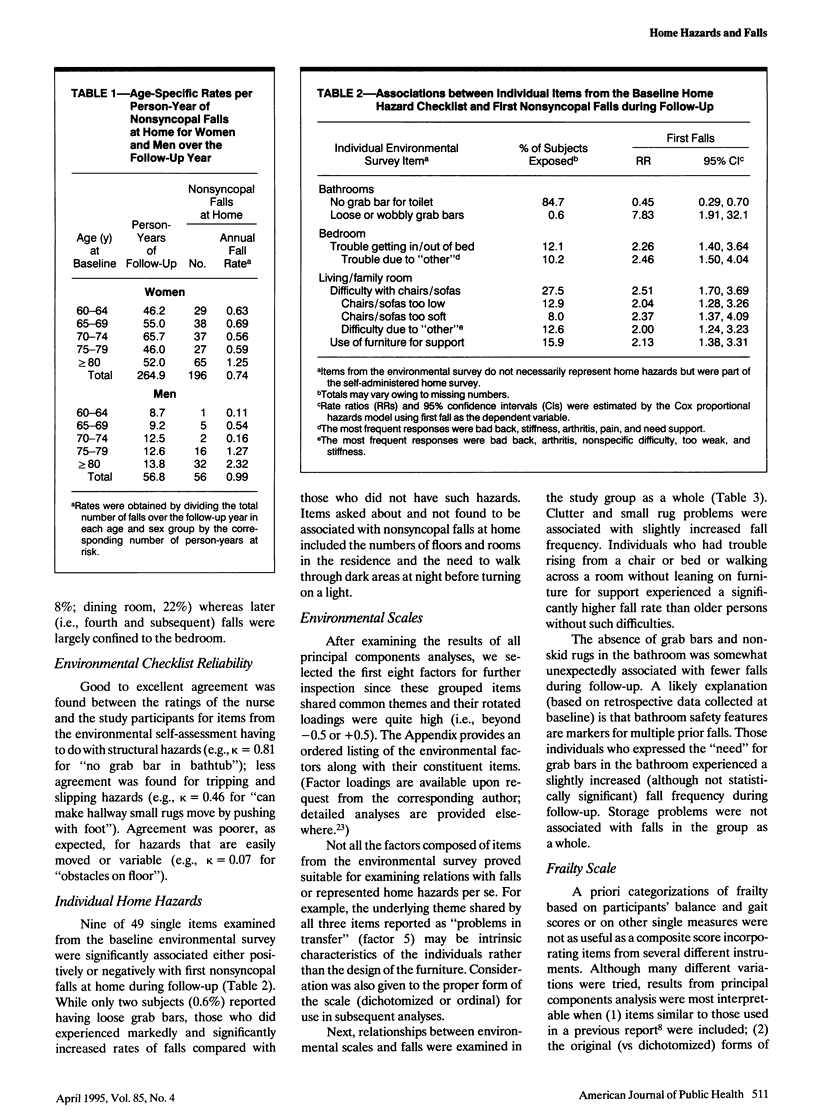
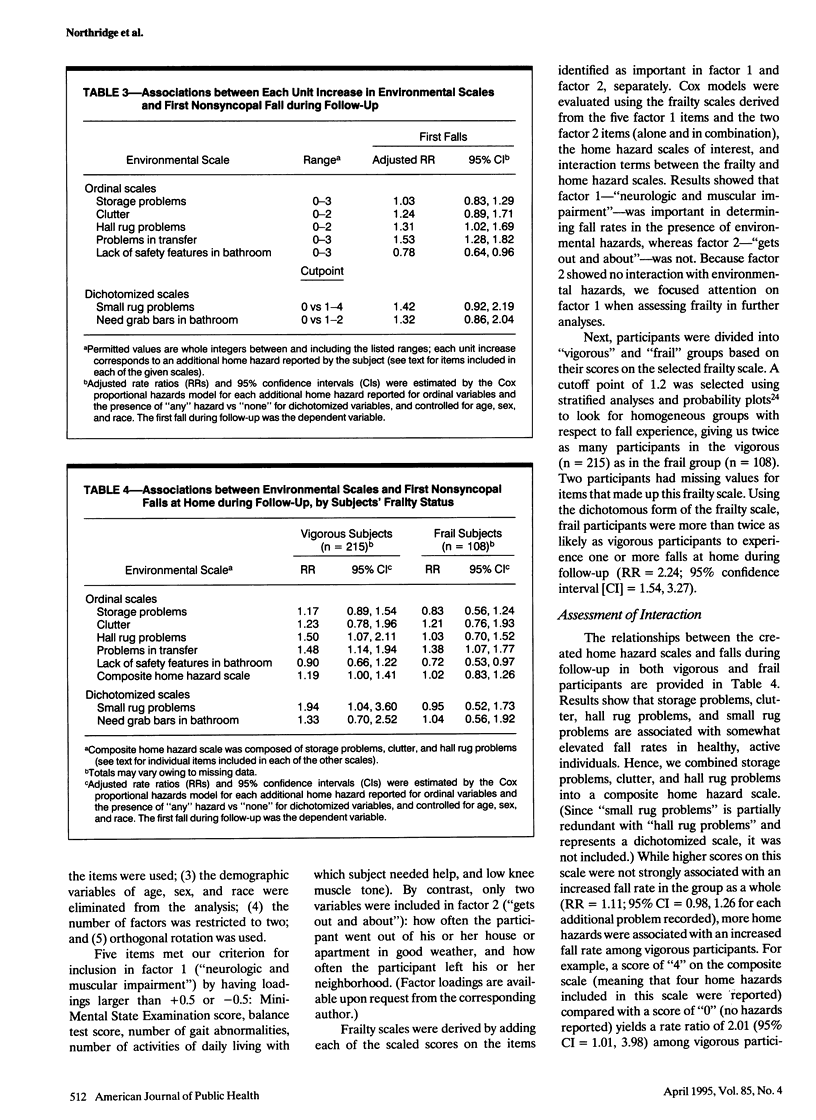
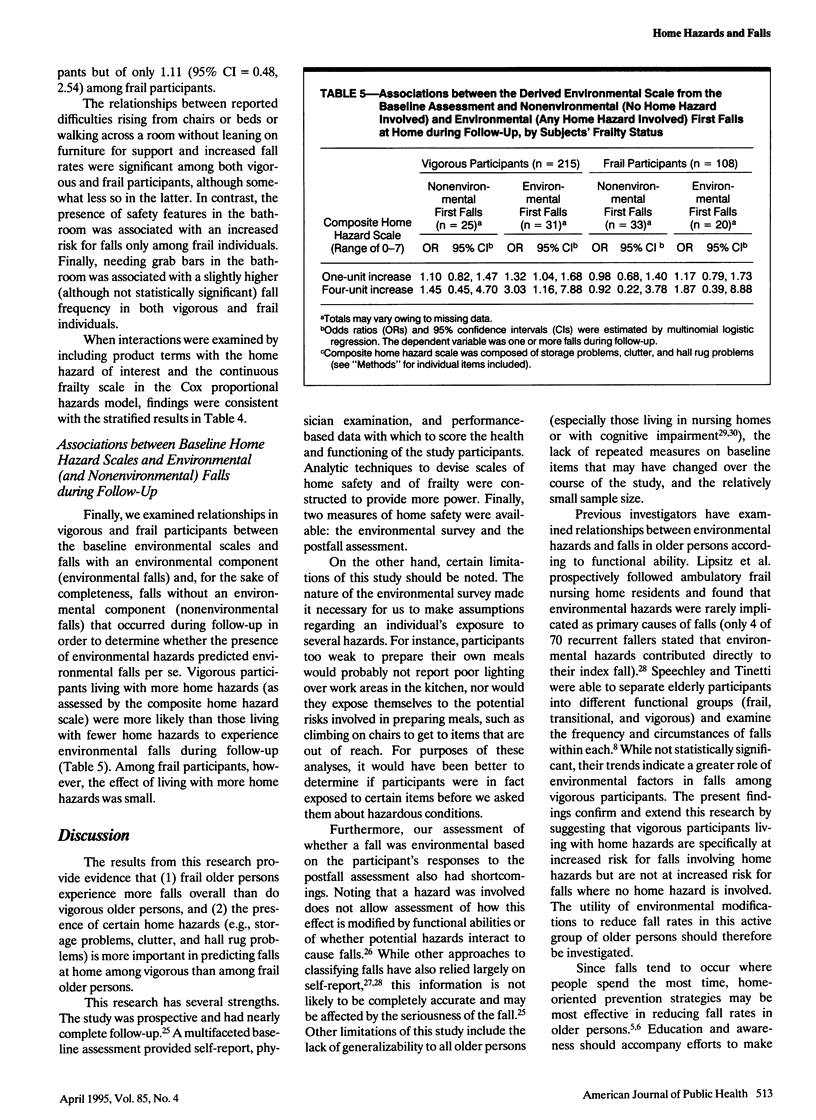
OBJECTIVES. This study was undertaken to determine whether vigorous and frail older people who identify environmental hazards in their homes have an increased risk for falls. METHODS. A 1-year prospective study was conducted among 266 female and 59 male community-dwelling volunteers aged 60 to 93 years who had fallen at least once during the previous year. Composite measures of home safety and of frailty were derived using principal components analysis. Participants were divided into vigorous and frail groups, and associations between baseline home safety measures and falls at home over the follow-up year were compared between the two groups. RESULTS. Frail individuals were more than twice as likely as vigorous individuals to fall during follow-up (rate ratio [RR] = 2.24; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.54, 3.27). In the study group as a whole, falls were not strongly associated with the presence of home hazards. However, when compared with vigorous older persons living with fewer home hazards, vigorous older persons living with more home hazards were more likely to fall. The increased risk for falls among vigorous elderly was limited to falls where home hazards were present. By contrast, living with more home hazards was not associated with increased likelihood of falls among frail older persons. CONCLUSIONS. While frail older persons experience higher overall fall rates, vigorous older persons should not be overlooked in fall prevention projects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey I. L., Lovie J. E. New design principles for visual acuity letter charts. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1976 Nov;53(11):740–745. doi: 10.1097/00006324-197611000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E. M., Kleban M. H., Moss M. S., Kleban F. Predictors of falls among institutionalized women with Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1984 Dec;32(12):877–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1984.tb00886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner D. M., Larson E. B. Falls and fractures in patients with Alzheimer-type dementia. JAMA. 1987 Mar 20;257(11):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings S. R., Nevitt M. C., Kidd S. Forgetting falls. The limited accuracy of recall of falls in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1988 Jul;36(7):613–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1988.tb06155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwikel J., Fried A. V., Galinsky D. Falls and psychosocial factors among community-dwelling elderly persons: a review and integration of findings from Israel. Public Health Rev. 1989;17(1):39–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson K. R., Fabacher D. A., Rubenstein L. Z. Home safety and fall prevention. Clin Geriatr Med. 1991 Nov;7(4):707–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lach H. W., Reed A. T., Arfken C. L., Miller J. P., Paige G. D., Birge S. J., Peck W. A. Falls in the elderly: reliability of a classification system. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991 Feb;39(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1991.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitz L. A., Jonsson P. V., Kelley M. M., Koestner J. S. Causes and correlates of recurrent falls in ambulatory frail elderly. J Gerontol. 1991 Jul;46(4):M114–M122. doi: 10.1093/geronj/46.4.m114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. C., Amin M. A. Falls in the elderly. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1990 May;8(2):309–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevitt M. C., Cummings S. R., Hudes E. S. Risk factors for injurious falls: a prospective study. J Gerontol. 1991 Sep;46(5):M164–M170. doi: 10.1093/geronj/46.5.m164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevitt M. C., Cummings S. R., Kidd S., Black D. Risk factors for recurrent nonsyncopal falls. A prospective study. JAMA. 1989 May 12;261(18):2663–2668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein L. Z., Robbins A. S., Schulman B. L., Rosado J., Osterweil D., Josephson K. R. Falls and instability in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1988 Mar;36(3):266–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1988.tb01811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin R. W., Lambert Huber D. A., DeVito C. A., Rodriguez J. G., Ros A., Bacchelli S., Stevens J. A., Waxweiler R. J. The incidence of fall injury events among the elderly in a defined population. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jun;131(6):1028–1037. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speechley M., Tinetti M. Falls and injuries in frail and vigorous community elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991 Jan;39(1):46–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1991.tb05905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tideiksaar R. Falls among the elderly: a community prevention program. Am J Public Health. 1992 Jun;82(6):892–893. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.6.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tideiksaar R., Kay A. D. What causes falls? A logical diagnostic procedure. Geriatrics. 1986 Dec;41(12):32–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tideiksaar R. Preventing falls: home hazard checklists to help older patients protect themselves. Geriatrics. 1986 May;41(5):26–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinetti M. E. Performance-oriented assessment of mobility problems in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986 Feb;34(2):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1986.tb05480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg D., Northridge M. Defining exposure in case-control studies: a new approach. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 May 15;133(10):1058–1071. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


