Abstract
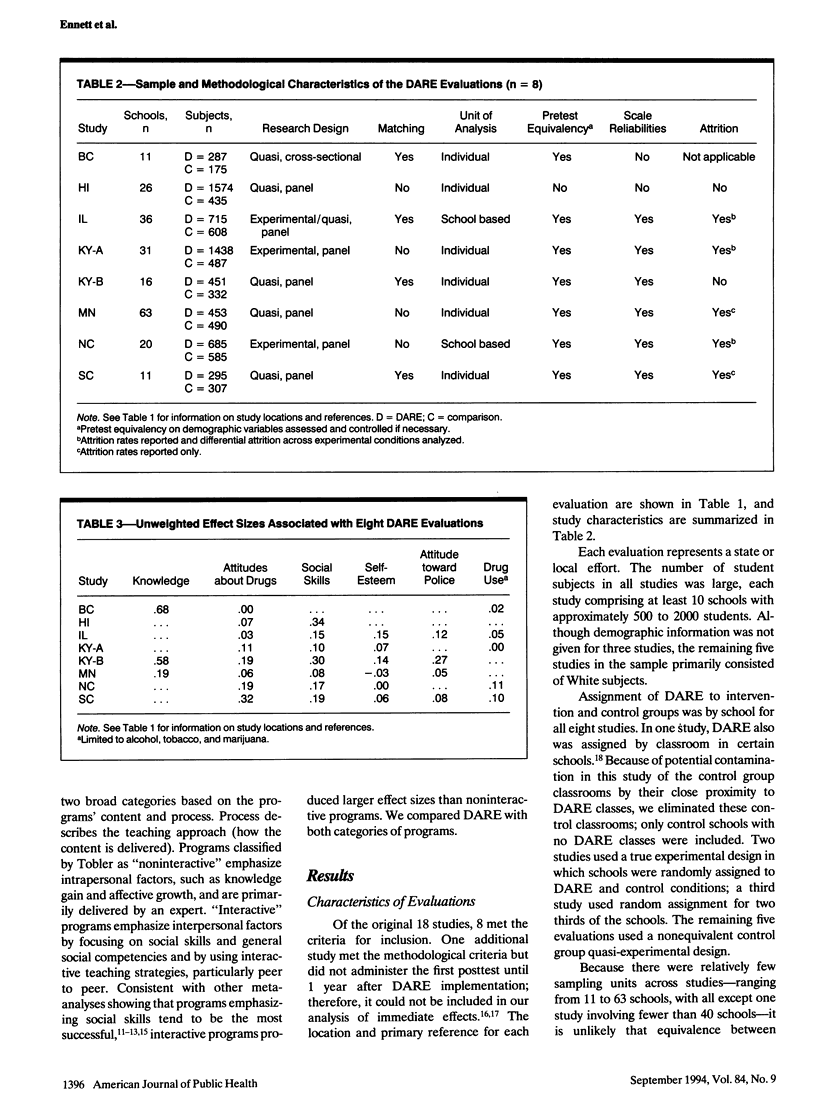
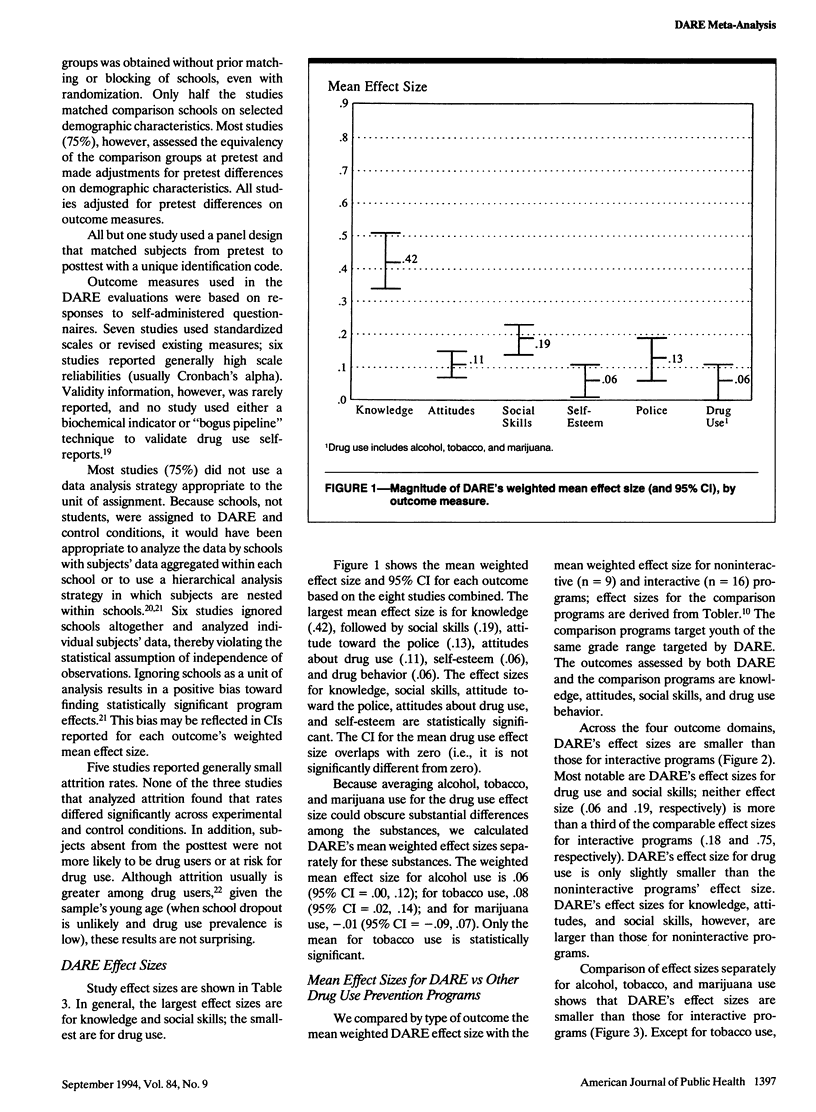
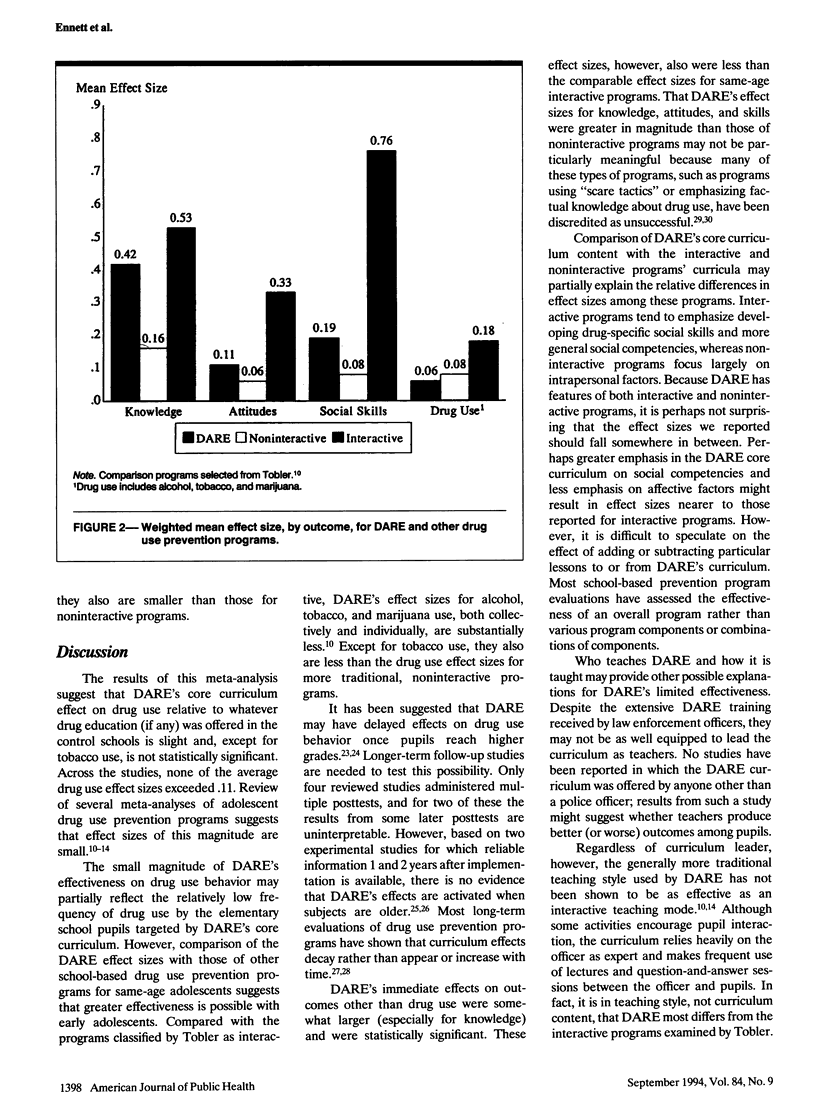
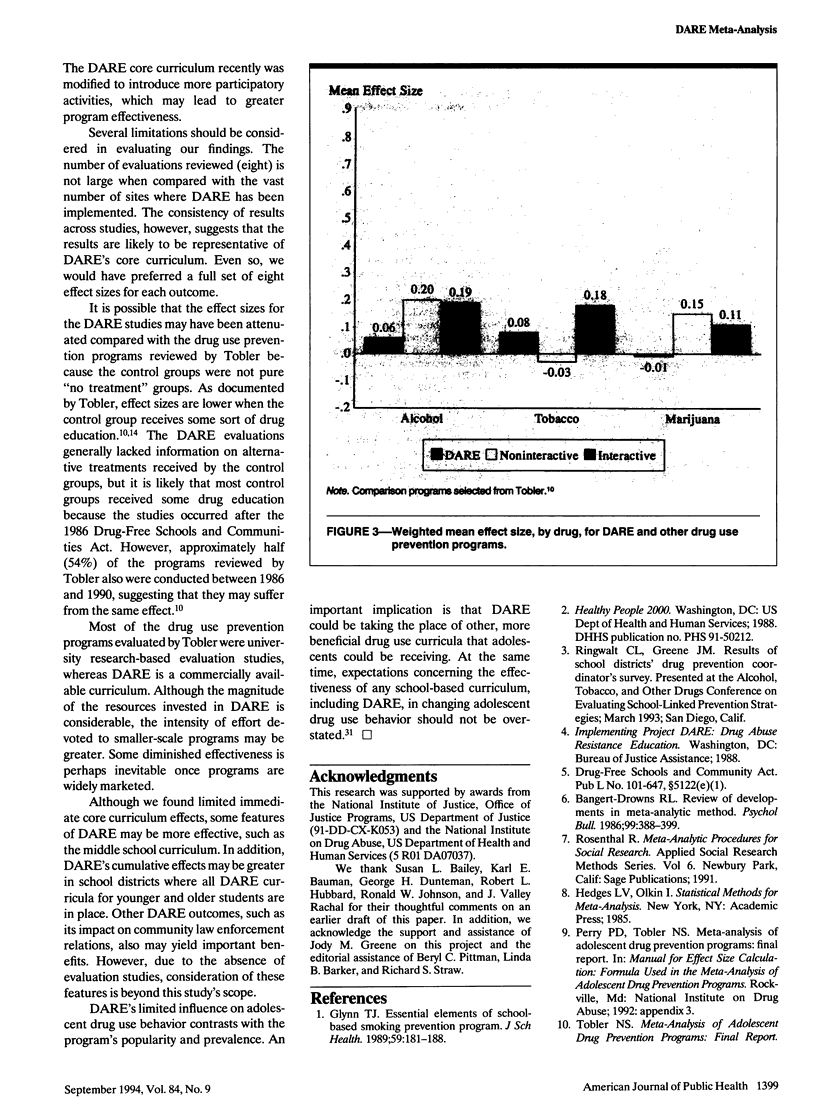
OBJECTIVES. Project DARE (Drug Abuse Resistance Education) is the most widely used school-based drug use prevention program in the United States, but the findings of rigorous evaluations of its effectiveness have not been considered collectively. METHODS. We used meta-analytic techniques to review eight methodologically rigorous DARE evaluations. Weighted effect size means for several short-term outcomes also were compared with means reported for other drug use prevention programs. RESULTS. The DARE effect size for drug use behavior ranged from .00 to .11 across the eight studies; the weighted mean for drug use across studies was .06. For all outcomes considered, the DARE effect size means were substantially smaller than those of programs emphasizing social and general competencies and using interactive teaching strategies. CONCLUSIONS. DARE's short-term effectiveness for reducing or preventing drug use behavior is small and is less than for interactive prevention programs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison K. R., Silverman G., Dignam C. Effects on students of teacher training in use of a drug education curriculum. J Drug Educ. 1990;20(1):31–46. doi: 10.2190/HDRV-3RYR-56FY-YM1X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangert-Drowns R. L. The effects of school-based substance abuse education--meta-analysis. J Drug Educ. 1988;18(3):243–264. doi: 10.2190/8U40-WP3D-FFWC-YF1U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman K. E., Dent C. W. Influence of an objective measure on self-reports of behavior. J Appl Psychol. 1982 Oct;67(5):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H. K., Agopian M. W., Yeh S. Impact evaluation of Drug Abuse Resistance Education (DARE). J Drug Educ. 1992;22(4):283–291. doi: 10.2190/53NH-R0GM-7QC6-4NQ3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruvold W. H. A meta-analysis of adolescent smoking prevention programs. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):872–880. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJong W. A short-term evaluation of project DARE (Drug Abuse Resistance Education): preliminary indications of effectiveness. J Drug Educ. 1987;17(4):279–294. doi: 10.2190/N2JC-9DXB-BLFD-41EA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dielman T. E., Shope J. T., Butchart A. T., Campanelli P. C. Prevention of adolescent alcohol misuse: an elementary school program. J Pediatr Psychol. 1986 Jun;11(2):259–282. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/11.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dielman T. E., Shope J. T., Campanelli P. C., Butchart A. T. Elementary school-based prevention of adolescent alcohol misuse. Pediatrician. 1987;14(1-2):70–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dielman T. E., Shope J. T., Leech S. L., Butchart A. T. Differential effectiveness of an elementary school-based alcohol misuse prevention program. J Sch Health. 1989 Aug;59(6):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.1989.tb04718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryfoos J. G. Preventing substance use: rethinking strategies. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):793–795. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellickson P. L., Bell R. M., McGuigan K. Preventing adolescent drug use: long-term results of a junior high program. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):856–861. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennett S. T., Rosenbaum D. P., Flewelling R. L., Bieler G. S., Ringwalt C. L., Bailey S. L. Long-term evaluation of drug abuse resistance education. Addict Behav. 1994 Mar-Apr;19(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennett S. T., Rosenbaum D. P., Flewelling R. L., Bieler G. S., Ringwalt C. L., Bailey S. L. Long-term evaluation of drug abuse resistance education. Addict Behav. 1994 Mar-Apr;19(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flay B. R., Koepke D., Thomson S. J., Santi S., Best J. A., Brown K. S. Six-year follow-up of the first Waterloo school smoking prevention trial. Am J Public Health. 1989 Oct;79(10):1371–1376. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.10.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flay B. R., Ryan K. B., Best J. A., Brown K. S., Kersell M. W., d'Avernas J. R., Zanna M. P. Are social-psychological smoking prevention programs effective? The Waterloo study. J Behav Med. 1985 Mar;8(1):37–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00845511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist L. D., Schinke S. P., Trimble J. E., Cvetkovich G. T. Skills enhancement to prevent substance abuse among American Indian adolescents. Int J Addict. 1987 Sep;22(9):869–879. doi: 10.3109/10826088709027465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn T. J. Essential elements of school-based smoking prevention programs. J Sch Health. 1989 May;59(5):181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.1989.tb04698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W. B. School-based substance abuse prevention: a review of the state of the art in curriculum, 1980-1990. Health Educ Res. 1992 Sep;7(3):403–430. doi: 10.1093/her/7.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray D. M., Hannan P. J. Planning for the appropriate analysis in school-based drug-use prevention studies. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1990 Aug;58(4):458–468. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.58.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray D. M., Pirie P., Leupker R. V., Pallonen U. Five- and six-year follow-up results from four seventh-grade smoking prevention strategies. J Behav Med. 1989 Apr;12(2):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00846551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinke S. P., Gilchrist L. D., Snow W. H., Schilling R. F., 2nd Skills-building methods to prevent smoking by adolescents. J Adolesc Health Care. 1985 Nov;6(6):439–444. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0070(85)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinke S. P., Gilchrist L. D., Snow W. H. Skills intervention to prevent cigarette smoking among adolescents. Am J Public Health. 1985 Jun;75(6):665–667. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.6.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


