Abstract
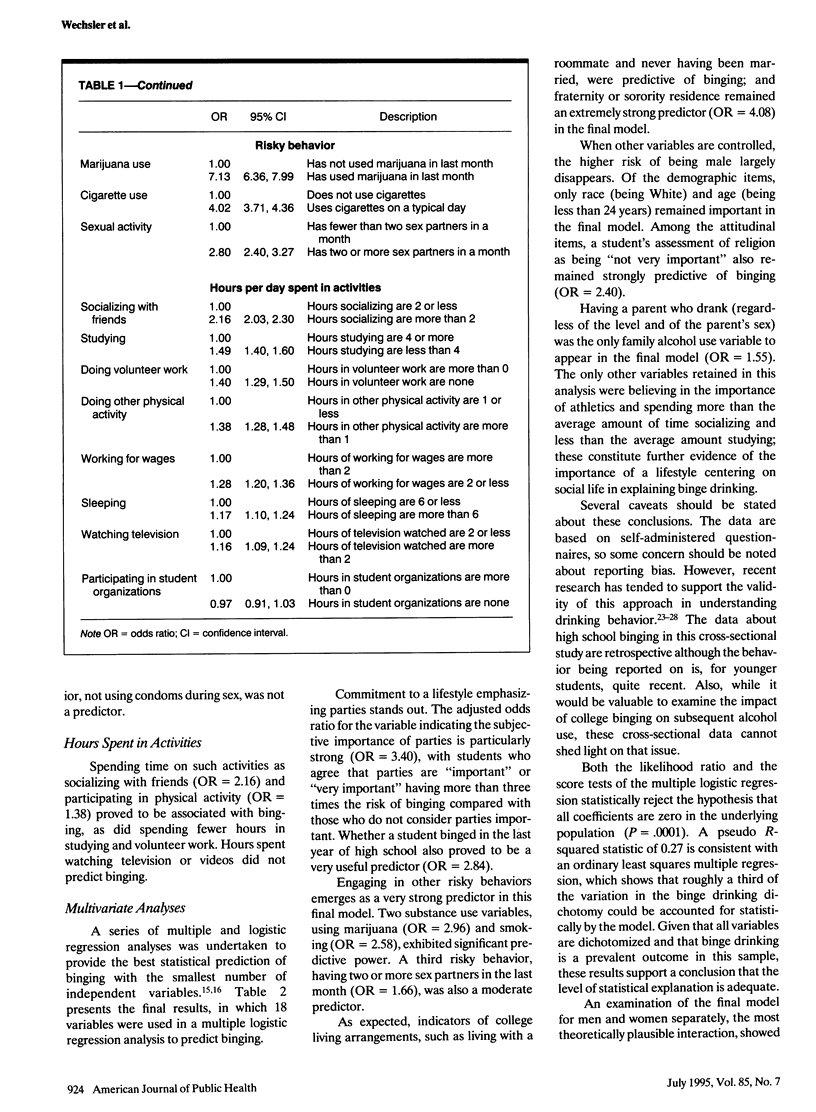
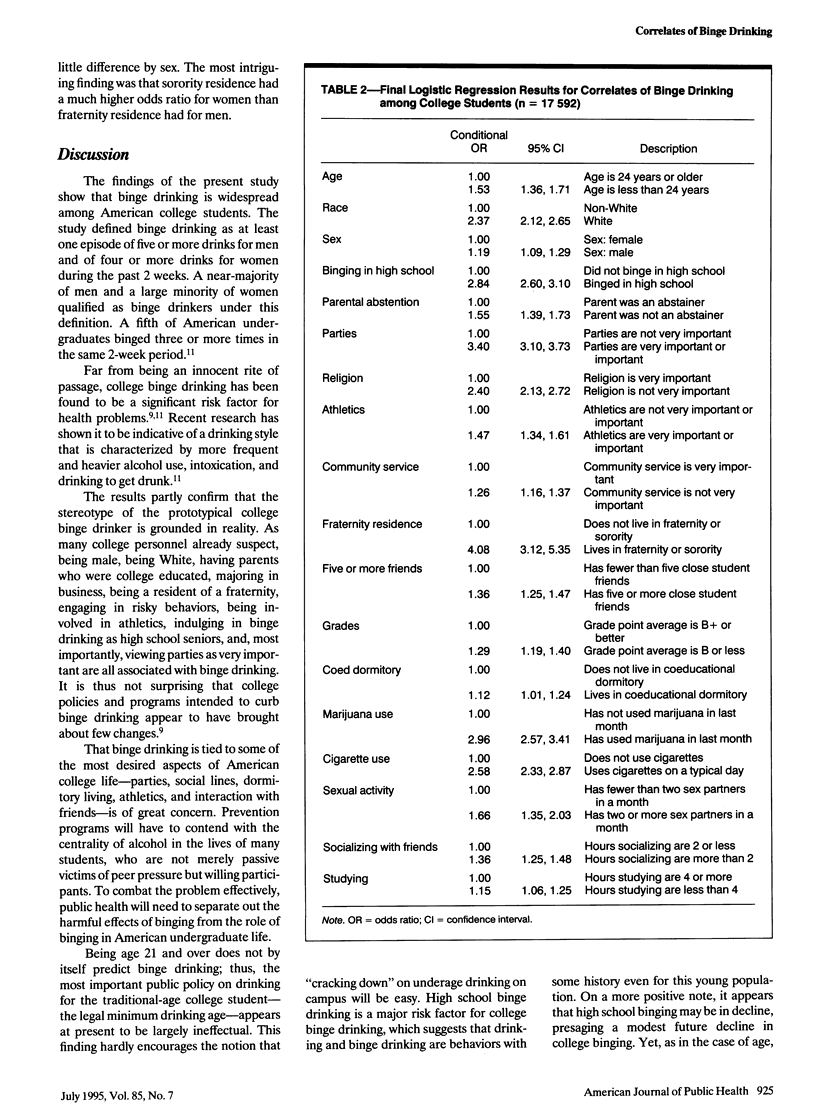
OBJECTIVES. This study examines the individual correlates of college student binge drinking. METHODS. Questionnaires were completed by a representative national sample (n = 17,592) of students on 140 campuses in 1993. Binge drinking was defined as five or more drinks per episode for men and as four or more drinks per episode for women. RESULTS. Overall, 44% of the students (50% of the men and 39% of the women) binged. While demographic factors such as sex and race were significantly related to binge drinking, prior binging in high school was crucial, suggesting that for many students, binge drinking begins before college. The strongest predictors of college binge drinking were residence in a fraternity or sorority, adoption of a party-centered life-style, and engagement in other risky behaviors. CONCLUSIONS. Interventions must be targeted at high school binge drinking as well as at several characteristics of college life--most notably fraternity residence. Legal drinking age fails to predict binge drinking, raising questions about the effectiveness of the legal minimum drinking age of 21 in college alcohol policies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andréasson S., Allebeck P., Brandt L. Predictors of alcoholism in young Swedish men. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):845–850. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andréasson S., Allebeck P., Brandt L., Romelsjö A. Antecedents and covariates of high alcohol consumption in young men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Aug;16(4):708–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb00666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachman J. G., Wallace J. M., Jr, O'Malley P. M., Johnston L. D., Kurth C. L., Neighbors H. W. Racial/Ethnic differences in smoking, drinking, and illicit drug use among American high school seniors, 1976-89. Am J Public Health. 1991 Mar;81(3):372–377. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. L. Adolescents' multisubstance use patterns: the role of heavy alcohol and cigarette use. Am J Public Health. 1992 Sep;82(9):1220–1224. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.9.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. M., Sobell M. B., Sobell L. C., Maisto S. A. Validity of alcoholic's self-reports: duration data. Int J Addict. 1981 Apr;16(3):401–406. doi: 10.3109/10826088109038841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingson R. W., Strunin L., Berlin B. M., Heeren T. Beliefs about AIDS, use of alcohol and drugs, and unprotected sex among Massachusetts adolescents. Am J Public Health. 1990 Mar;80(3):295–299. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVeist T. A. Beyond dummy variables and sample selection: what health services researchers ought to know about race as a variable. Health Serv Res. 1994 Apr;29(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. M., Foege W. H. Actual causes of death in the United States. JAMA. 1993 Nov 10;270(18):2207–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midanik L. T. Validity of self-reported alcohol use: a literature review and assessment. Br J Addict. 1988 Sep;83(9):1019–1030. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1988.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peele S. The conflict between public health goals and the temperance mentality. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):805–810. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. J., Rimm E. B., Walsh D. C. Commentary: alcohol, the heart, and public policy. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):801–804. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutocky J. W., Shultz J. M., Kizer K. W. Alcohol-related mortality in California, 1980 to 1989. Am J Public Health. 1993 Jun;83(6):817–823. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler H., Davenport A., Dowdall G., Moeykens B., Castillo S. Health and behavioral consequences of binge drinking in college. A national survey of students at 140 campuses. JAMA. 1994 Dec 7;272(21):1672–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler H., Dowdall G. W., Davenport A., Rimm E. B. A gender-specific measure of binge drinking among college students. Am J Public Health. 1995 Jul;85(7):982–985. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.7.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler H., Isaac N. 'Binge' drinkers at Massachusetts colleges. Prevalence, drinking style, time trends, and associated problems. JAMA. 1992 Jun 3;267(21):2929–2931. doi: 10.1001/jama.267.21.2929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



