Abstract
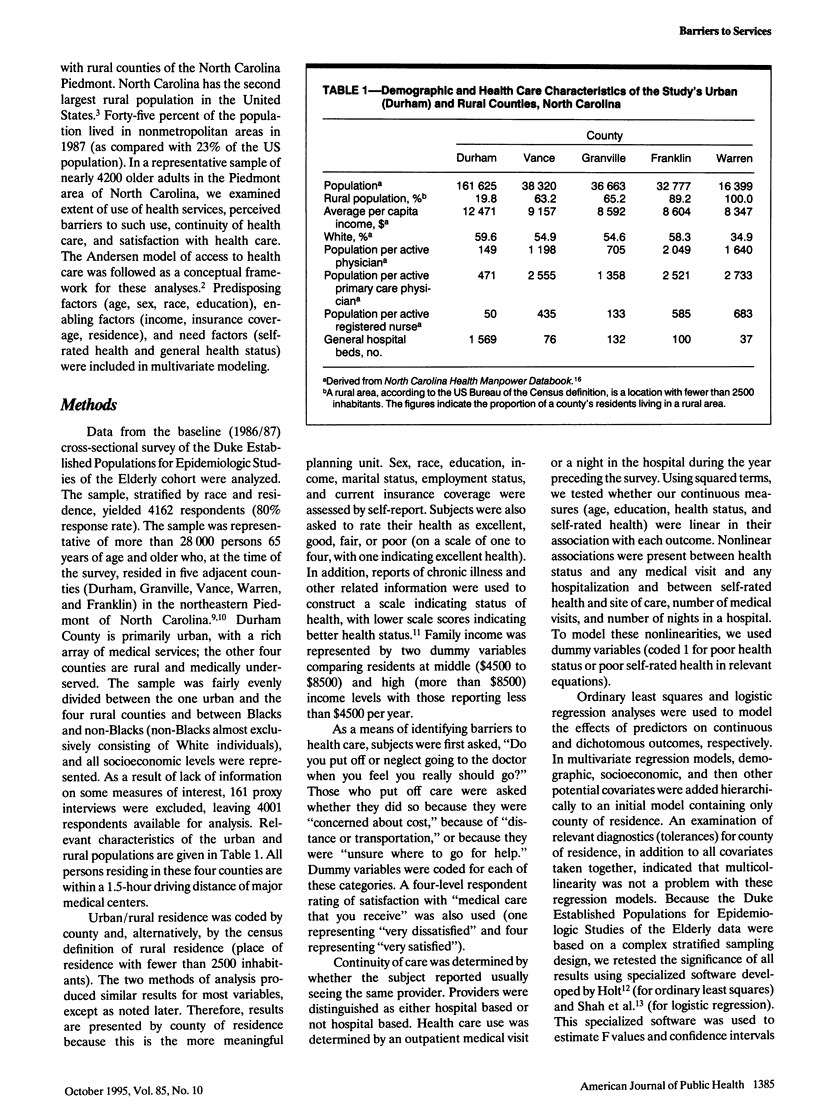
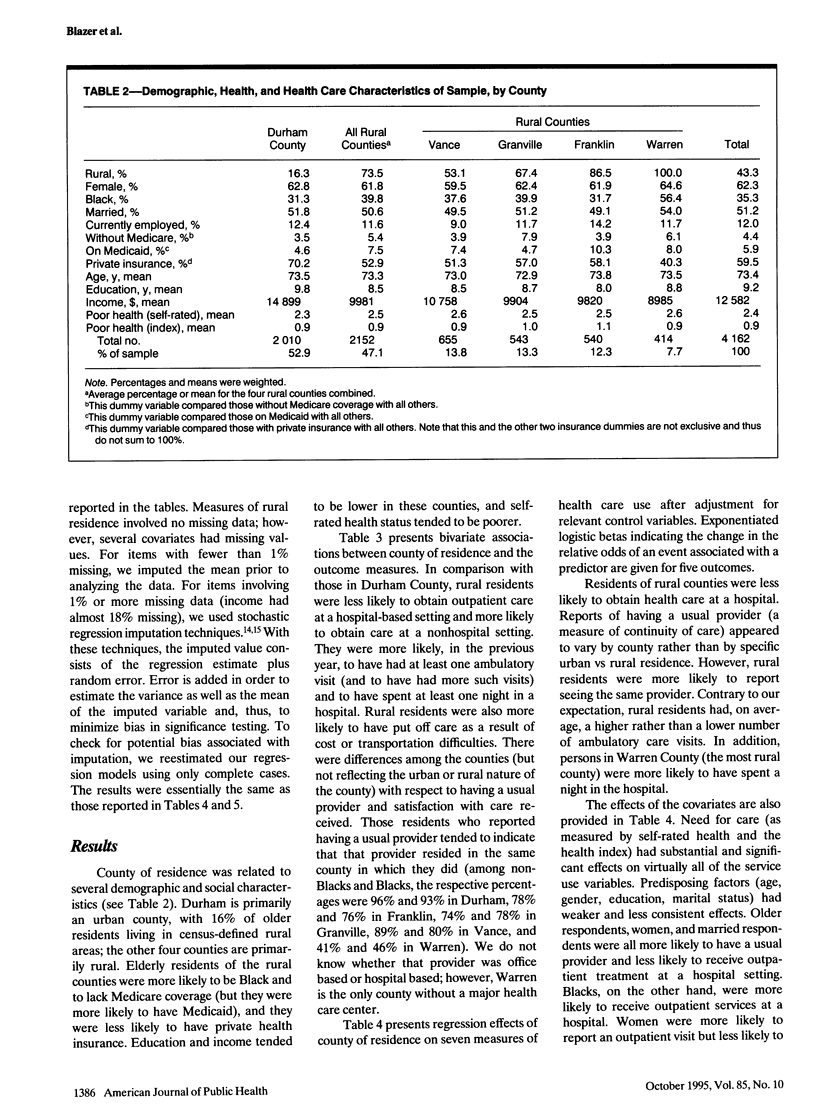
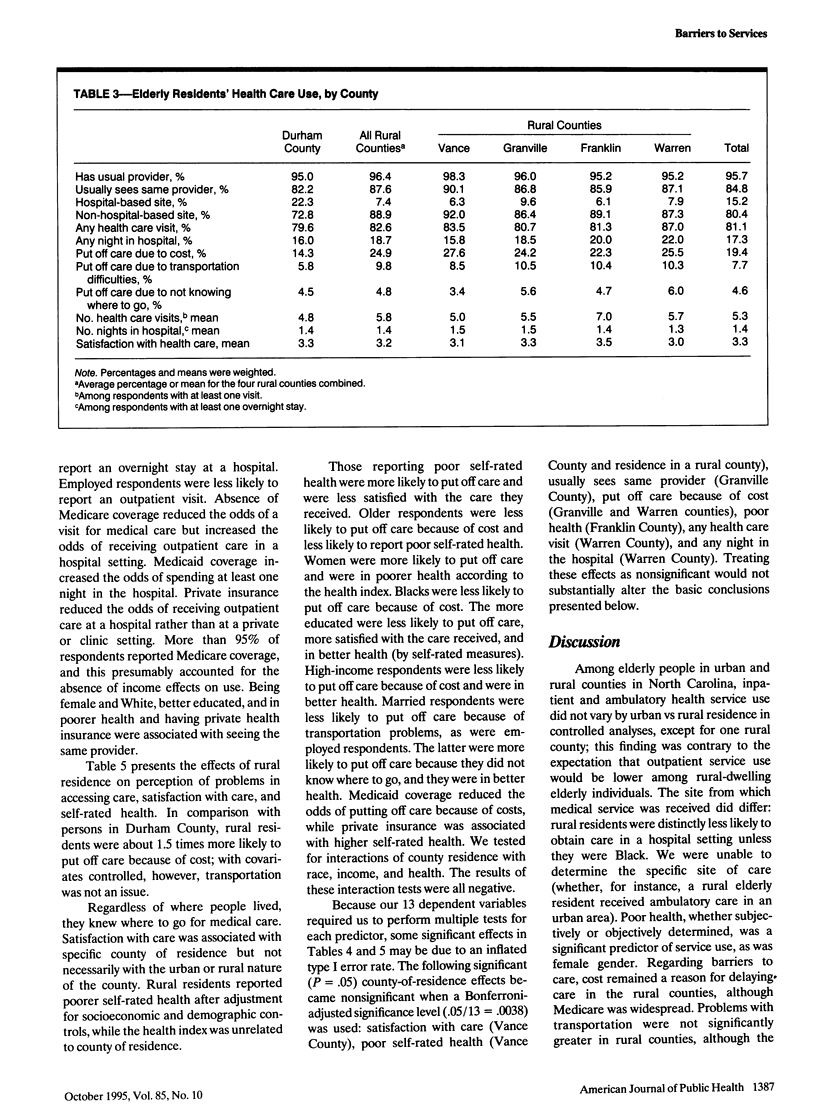
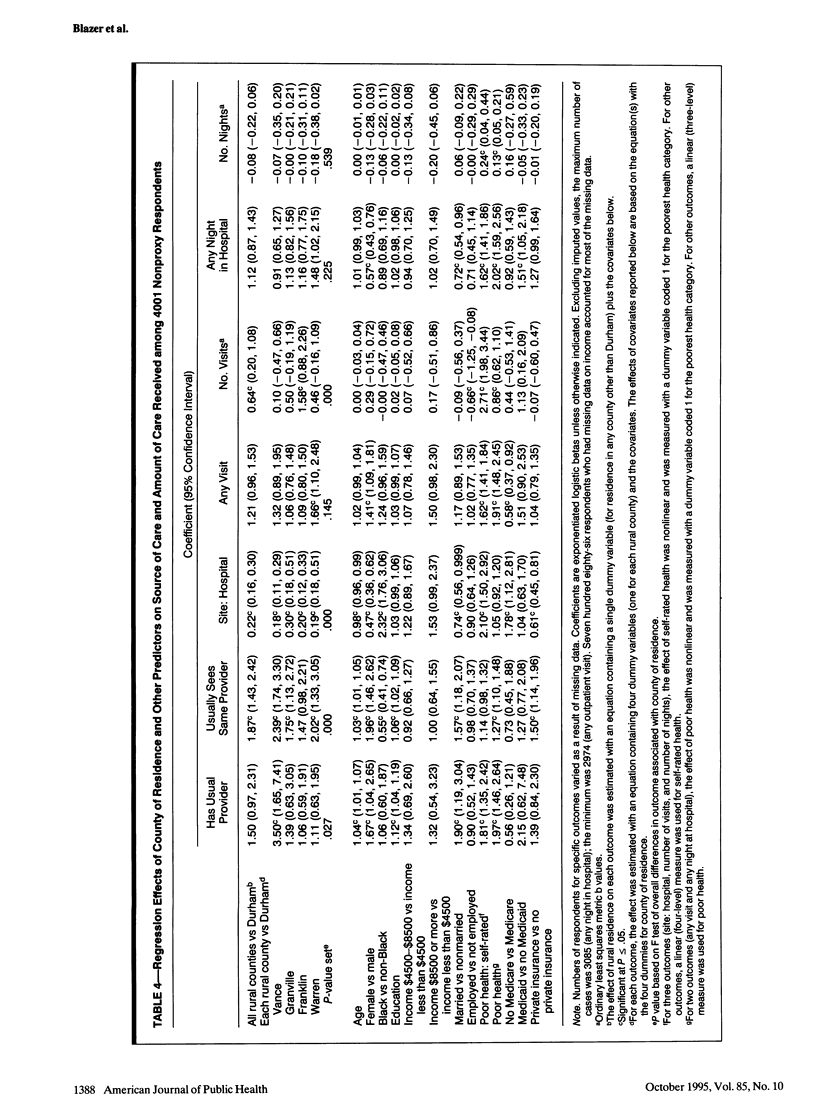
OBJECTIVES. This study compared health service use and satisfaction with health care among older adults living in urban vs rural counties in North Carolina. METHODS. A stratified random sample of 4162 residents of one urban and four rural counties of North Carolina was surveyed to determine urban/rural variation in inpatient and outpatient health service use, continuity of care and satisfaction with care, and barriers (transportation, cost) to care. RESULTS. Inpatient and outpatient service use did not vary by residence in controlled analyses. Continuity of care was more frequent in rural counties. Transportation was not perceived as a barrier to health care more frequently in rural than in urban counties, but cost was a greater barrier to care among rural elderly people. CONCLUSIONS. In this sample, older persons living in rural counties within reasonable driving distance of urban counties with major medical centers used health services as frequently and were as satisfied with their health care as persons in urban counties. Cost of care, however, was a significant and persistent barrier among rural elderly people, despite Medicare coverage.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R., Newman J. F. Societal and individual determinants of medical care utilization in the United States. Milbank Mem Fund Q Health Soc. 1973 Winter;51(1):95–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazer D., Burchett B., Service C., George L. K. The association of age and depression among the elderly: an epidemiologic exploration. J Gerontol. 1991 Nov;46(6):M210–M215. doi: 10.1093/geronj/46.6.m210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. A., Rosenthal T. C. Access to health care in rural western New York State. N Y State J Med. 1992 Nov;92(11):465–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D. L., Stein J., Porta M., Porter C. Q., Ricketts T. C. Poverty, health services, and health status in rural America. Milbank Q. 1988;66(1):105–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


