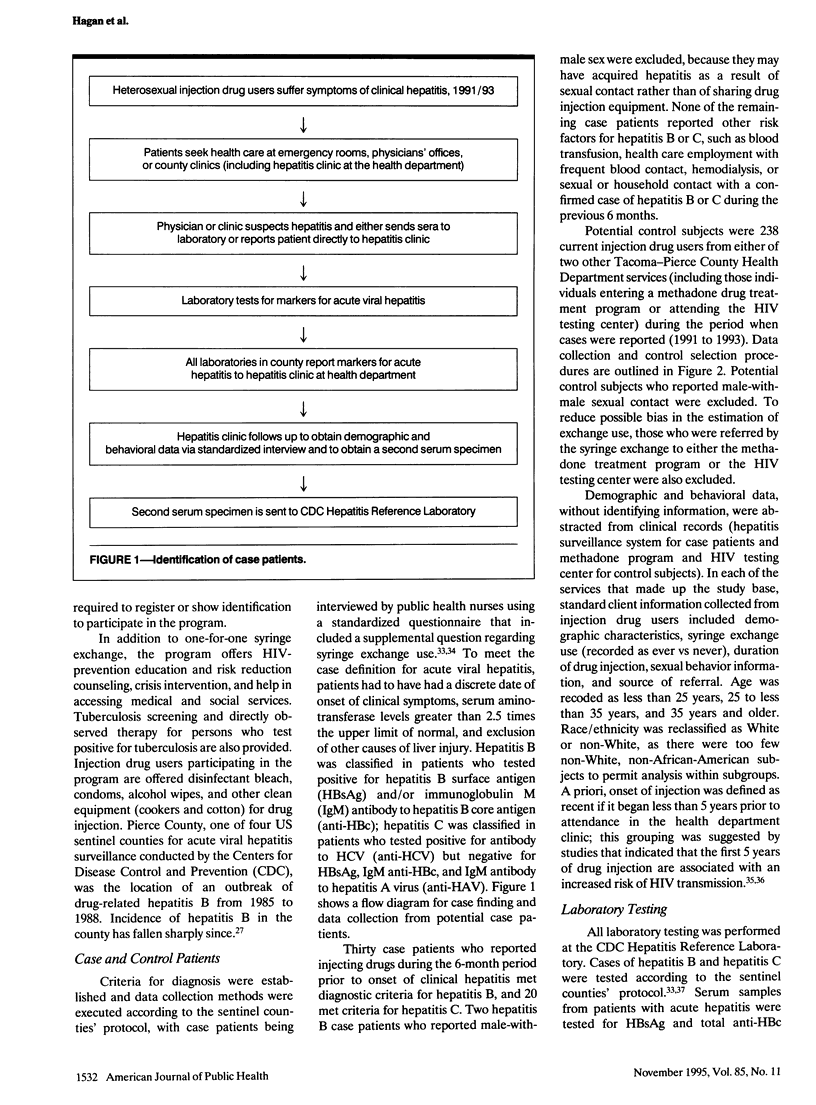
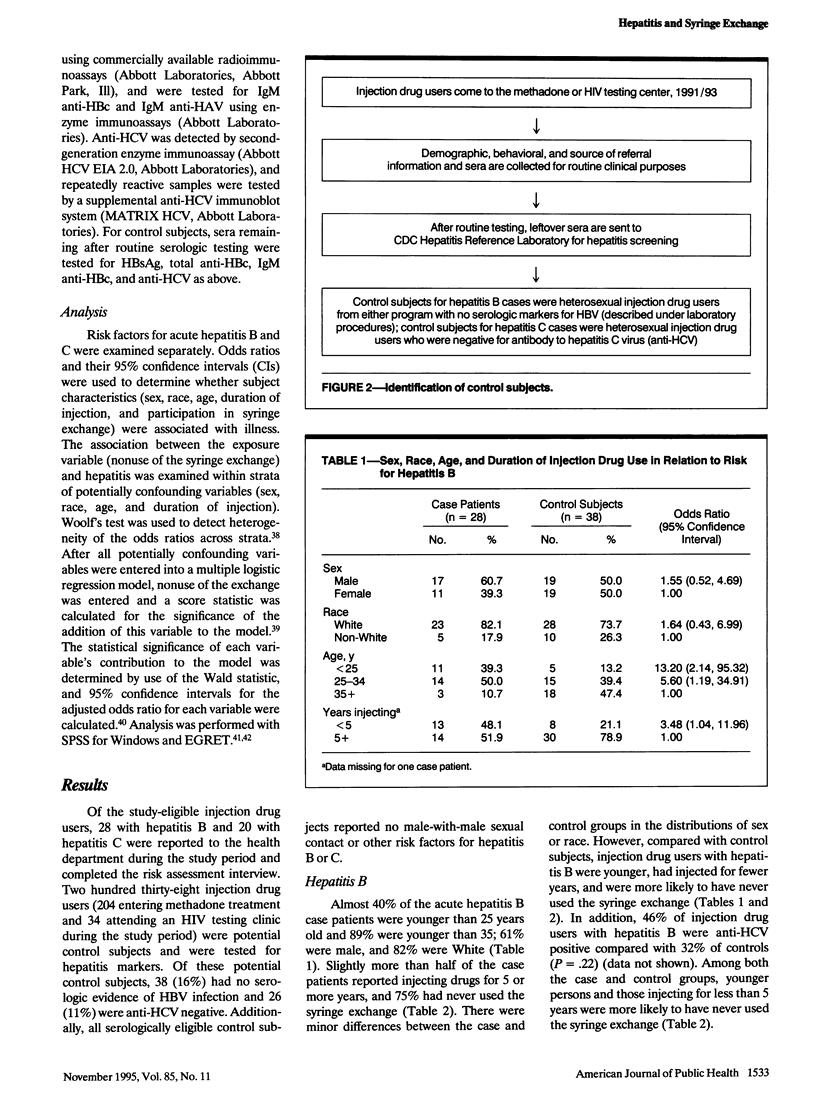
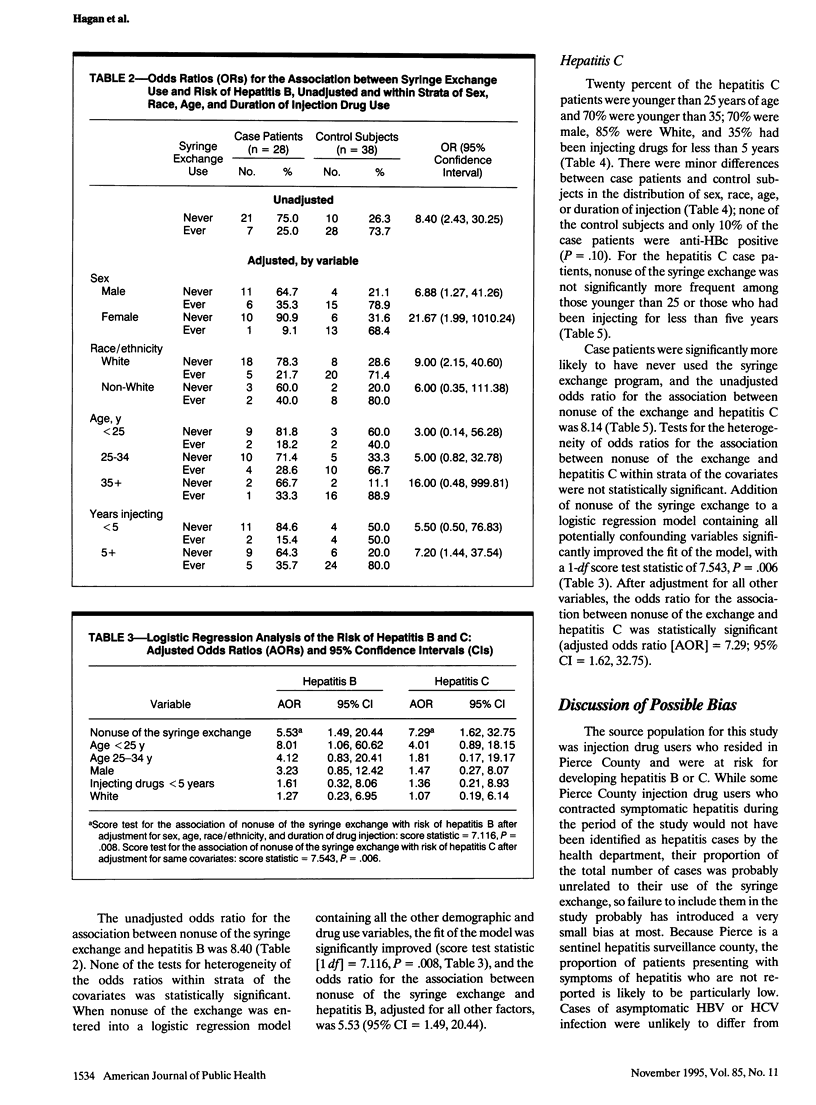
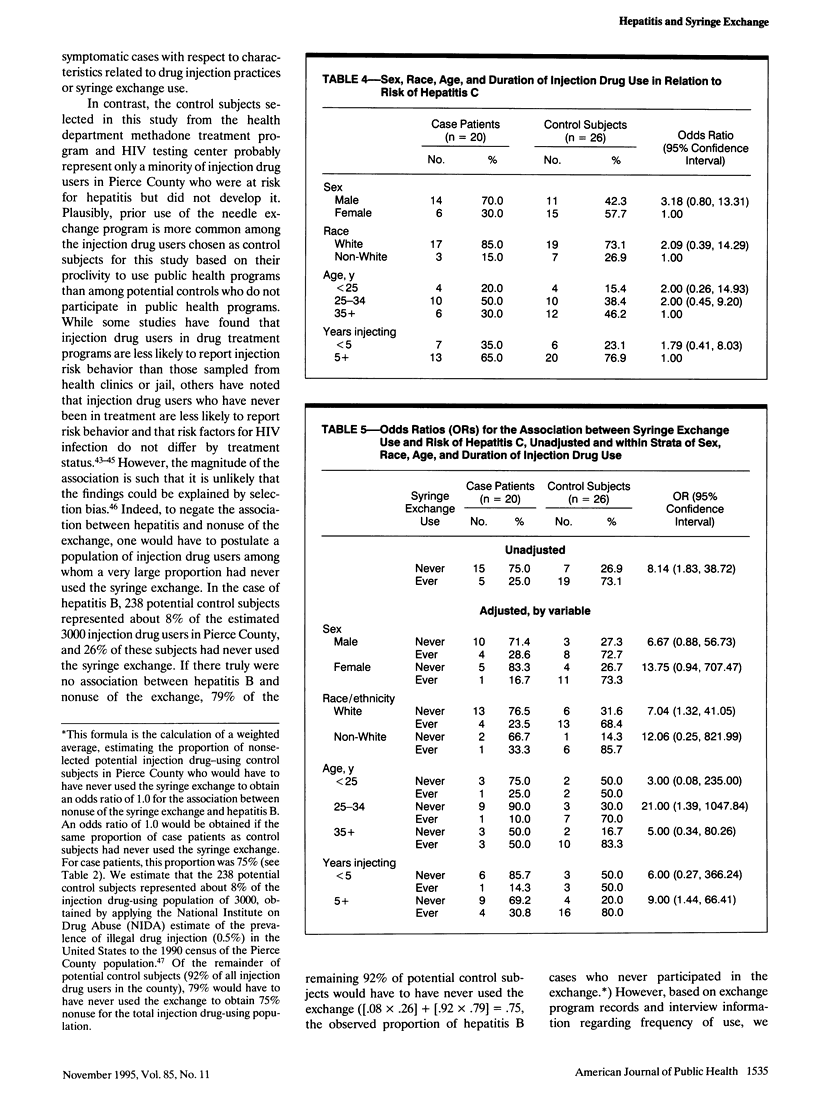
Abstract
OBJECTIVES. This case-control study examined the association between syringe exchange use and hepatitis B and C in injection drug users. METHODS. Case patients included 28 injection drug users with acute hepatitis B and 20 with acute hepatitis C reported to the health department in a sentinel hepatitis surveillance county; control subjects were injection drug users with no markers of exposure to hepatitis B or C (n = 38 and 26, respectively) attending health department services during the same period. Data were abstracted from clinic records. RESULTS. Seventy-five percent of case patients with hepatitis B and 26% of control subjects had never used the exchange; similar proportions were found for the hepatitis C case and control groups. After adjustment for demographic characteristics and duration of injecting drugs, nonuse of the exchange was associated with a sixfold greater risk of hepatitis B (odds ratio [OR] = 5.5; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.5, 20.4) and a sevenfold greater risk of hepatitis C (OR = 7.3; 95% CI = 1.6, 32.8). CONCLUSIONS. The results suggest that use of the exchange led to a significant reduction in hepatitis B and hepatitis C in the county and may have also prevented a substantial proportion of human immunodeficiency virus infections in injection drug users.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcabes P., Vlahov D., Anthony J. C. Correlates of human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users: are treatment-program samples misleading? Br J Addict. 1992 Jan;87(1):47–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1992.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Hadler S. C., Judson F. N., Mares A., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Miller J. K., Moyer L. A., Fields H. A., Bradley D. W. Risk factors for acute non-A, non-B hepatitis in the United States and association with hepatitis C virus infection. JAMA. 1990 Nov 7;264(17):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Hadler S. C., Margolis H. S., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Judson F. N., Mares A., Miller J. K., Moyer L. A. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis B in the United States. Need for alternative vaccination strategies. JAMA. 1990 Mar 2;263(9):1218–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Margolis H. S., Krawczynski K., Judson F. N., Mares A., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Miller J. K., Gerber M. A., Sampliner R. E. The natural history of community-acquired hepatitis C in the United States. The Sentinel Counties Chronic non-A, non-B Hepatitis Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 31;327(27):1899–1905. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212313272702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J. The detection, transmission, and outcome of hepatitis C virus infection. Infect Agents Dis. 1993 Jun;2(3):155–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. The New York Needle Trial: the politics of public health in the age of AIDS. Am J Public Health. 1991 Nov;81(11):1506–1517. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.11.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Bertaggia A., Cadrobbi P., Crivellaro C., Pornaro E., Realdi G. Epidemiological aspects of acute viral hepatitis in drug abusers. Infection. 1982 Sep-Oct;10(5):277–279. doi: 10.1007/BF01640873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buning E. C. Effects of Amsterdam needle and syringe exchange. Int J Addict. 1991 Dec;26(12):1303–1311. doi: 10.3109/10826089109062162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamot E., de Saussure P., Hirschel B., Déglon J. J., Perrin L. H. Incidence of hepatitis C, hepatitis B and HIV infections among drug users in a methadone-maintenance programme. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):430–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCock K. M., Jones B., Govindarajan S., Redeker A. G. Prevalence of hepatitis delta (delta) virus infection. A seroepidemiologic study. West J Med. 1988 Mar;148(3):307–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. R., Des Jarlais D. C., Neaigus A., Abdul-Quader A., Sotheran J. L., Sufian M., Tross S., Goldsmith D. AIDS and the new drug injector. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):333–334. doi: 10.1038/339333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. B. THE ENVIRONMENT AND DISEASE: ASSOCIATION OR CAUSATION? Proc R Soc Med. 1965 May;58:295–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan H., Des Jarlais D. C., Purchase D., Friedman S. R., Reid T., Bell T. A. An interview study of participants in the Tacoma, Washington, syringe exchange. Addiction. 1993 Dec;88(12):1691–1697. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1993.tb02044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan H., Reid T., Des Jarlais D. C., Purchase D., Friedman S. R., Bell T. A. The incidence of HBV infection and syringe exchange programs. JAMA. 1991 Sep 25;266(12):1646–1647. doi: 10.1001/jama.1991.03470120048019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Carvell A. L., Woodward N., Johnson A. M., Williams P., Parry J. V. Evaluation of needle exchange in central London: behaviour change and anti-HIV status over one year. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):261–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Woodward N., Johnson A. M., Tighe J., Parry J. V., Adler M. W. Prevalence of HIV, hepatitis B and associated risk behaviours in clients of a needle-exchange in central London. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):543–547. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee H., Faugier J., Hayes C., Boulton T., Morris J. Factors associated with risk behaviour among injecting drug users. AIDS Care. 1990;2(2):133–145. doi: 10.1080/09540129008257724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungberg B., Christensson B., Tunving K., Andersson B., Landvall B., Lundberg M., Zäll-Friberg A. C. HIV prevention among injecting drug users: three years of experience from a syringe exchange program in Sweden. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(9):890–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Alter M. J., Hadler S. C. Hepatitis B: evolving epidemiology and implications for control. Semin Liver Dis. 1991 May;11(2):84–92. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J., Koblin B., Lewis B. F., Sullivan J. Demographic characteristics, risk behaviors, and HIV seroprevalence among intravenous drug users by site of contact: results from a community-wide HIV surveillance project. Am J Public Health. 1990 Sep;80(9):1062–1067. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.9.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Goilav C., Kegels E. Hepatitis B: transmission by sexual contact and needle sharing. Vaccine. 1990 Mar;8 (Suppl):S37–S43. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto A., Seeff L. B., Buskell-Bales Z., Ishak K. G., Hoofnagle J. H., Zimmerman H. J., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Hepatitis B markers in United States drug addicts with special emphasis on the delta hepatitis virus. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1111–1115. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. E., Osborn J. E. AIDS policy. Two divisive issues. JAMA. 1993 Jul 28;270(4):494–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum L., Darrow W., Witte J., Cohen J., French J., Gill P. S., Potterat J., Sikes K., Reich R., Hadler S. Sexual practices in the transmission of hepatitis B virus and prevalence of hepatitis delta virus infection in female prostitutes in the United States. JAMA. 1992 May 13;267(18):2477–2481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimson G. V. Syringe-exchange programmes for injecting drug users. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):253–260. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ameijden E. J., Van den Hoek J. A., Mientjes G. H., Coutinho R. A. A longitudinal study on the incidence and transmission patterns of HIV, HBV and HCV infection among drug users in Amsterdam. Eur J Epidemiol. 1993 May;9(3):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00146260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters J. K., Estilo M. J., Clark G. L., Lorvick J. Syringe and needle exchange as HIV/AIDS prevention for injection drug users. JAMA. 1994 Jan 12;271(2):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolk J., Wodak A., Morlet A., Guinan J. J., Gold J. HIV-related risk-taking behaviour, knowledge and serostatus of intravenous drug users in Sydney. Med J Aust. 1990 May 7;152(9):453–458. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1990.tb125302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis J. B., Jain S., Kuramoto I. K., Richards C., Sazama K., Samuels S., Holland P. V., Flynn N. Seroepidemiology of viral infections among intravenous drug users in northern California. West J Med. 1992 Jan;156(1):30–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ameijden E. J., van den Hoek J. A., van Haastrecht H. J., Coutinho R. A. The harm reduction approach and risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seroconversion in injecting drug users, Amsterdam. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Jul 15;136(2):236–243. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beek I., Buckley R., Stewart M., MacDonald M., Kaldor J. Risk factors for hepatitis C virus infection among injecting drug users in Sydney. Genitourin Med. 1994 Oct;70(5):321–324. doi: 10.1136/sti.70.5.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastrecht H. J., van den Hoek J. A., Bardoux C., Leentvaar-Kuypers A., Coutinho R. A. The course of the HIV epidemic among intravenous drug users in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Am J Public Health. 1991 Jan;81(1):59–62. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., van Haastrecht H. J., Goudsmit J., de Wolf F., Coutinho R. A. Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of hepatitis C virus infection among drug users in Amsterdam. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):823–826. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


