Abstract
Two Stx-converting phages, designated Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II, were isolated from an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain, Morioka V526, and their entire nucleotide sequences were determined. The genomes of both phages were similar except for the stx gene-flanking regions. Comparing these phages to other known Stx-converting phages, we concluded that Stx1φ is a novel Stx1-converting phage closely related to Stx2-converting phages so far reported.
Infection with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) causes severe illnesses including hemorrhagic colitis, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, and encephalosis (13). Such critical illnesses are due to Shiga toxin (Stx) produced by EHEC. EHEC produces two types of Stx, namely Stx1, which is identical to Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 (17), and Stx2, which has immunological properties that are different from those of Stx1 but biological properties that are similar to those of Stx1 (22). Both of these Stxs are encoded by stx genes in the genome of the lysogenic bacteriophage (Stx phage) of EHEC (12, 16).
The fact that the expression of stx genes is linked to Stx phage induction (1, 11) is clinically quite important because DNA-damaging drugs such as quinolones, which induce an SOS response in bacteria, are supposed to enhance Stx production as well as Stx phage release from EHEC (4, 23). In fact, several studies on the effects of antibiotics on EHEC infection have been published (2, 19, 20). Thus, a need to analyze the nature or structure of Stx-converting phages has led to several studies on genome analysis of some Stx-converting phages (7, 9, 10, 14, 21). We also isolated three Stx-converting phages from EHEC strains collected in Japan, i.e., Stx1φ, Stx2φ-I, and Stx2φ-II (18), and we determined their complete DNA sequences. In this paper, we report the genomic analysis of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II, both derived from a single EHEC strain, Morioka V526.
Phage isolation and DNA sequence determination.
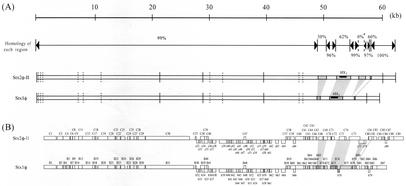
Isolation of Stx-converting phages from the EHEC Morioka V526 strain, preparation of the restriction map, and subcloning were performed as described previously (18). DNA sequencing was done by using the Dye Terminator kit (Applied Biosystems, Norwalk, Conn.) and 377PRISM autosequencer (Applied Biosystems) with synthetic oligonucleotides as primers. It was found that the genome size of Stx1φ was 59,866 bp, while that of Stx2φ-II was 62,706 bp. As shown in Fig. 1, although these two phages carry different stx genes, their genomic structures were quite homologous. The 2.8-kb size difference was attributed mainly to the BamHI-XhoI fragment-containing stx gene (Fig. 1). Also, insertion sequence IS1203 v (6) was found in this region in Stx2φ-II (Fig. 1).
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II. (A) Comparison of DNAs of Stx2φ-II and Stx1φ. The linear sequences of XhoI fragments are shown. The open bars represent homologous portions, while the different portions of Stx1φ are represented by shaded bars and the corresponding regions in Stx2φ-II are represented by dotted bars. The DNA sizes are shown on the top of the figure in kilobases (kb). Homology percentages are given above and below the second line of the figure. The asterisk indicates 0% homology, which is due to IS1203 v. Vertical lines on the two lower bars indicate XhoI sites (solid lines) and BamHI sites (broken lines). (B) Comparison of ORFs of Stx2φ-II and Stx1φ. The predicted ORFs are illustrated; the boxes above and below the horizontal lines are ORFs with rightward and leftward transcription directions, respectively. Open boxes are ORFs identical to the corresponding ORFs in any Stx2-converting phage(s) described in Table 1. Shaded boxes are ORFs characteristic of Stx1-converting phages, and dotted boxes are ORFs nearly identical to those of any Stx2-converting phage(s).
Comparison to other reported Stx-converting phages.
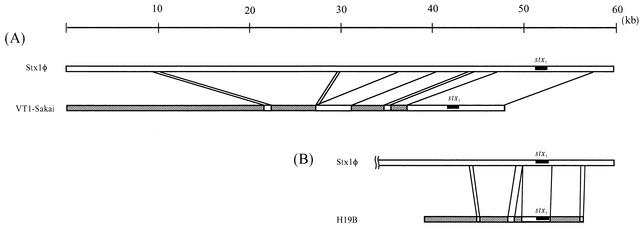
The genomic structures of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II were compared to those of other Stx-converting phages so far reported. It was found that they were quite similar to those of other known Stx2-converting phages, except for the stx-flanking regions (Fig. 1 and Table 1), but not to those of other Stx1-converting phages such as VT1-Sakai and H19B (Fig. 2).
TABLE 1.
ORFs of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II
| Stx1φ
|
% Identity between Stx1φ and Stx2φ-IIa (aa) | Stx2φ-II
|
Gene | Orientationb | Homologous ORFs ina:
|
Description | % Identity (aa) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 933W
|
VT2-Sakai
|
VT1-Sakai
|
||||||||||||||||
| ORF | Start | Stop | aae | ORF | Start | Stop | aa | % Identity (aa) | Label | % Identity (aa) | Label | % Identity (aa) | Label | |||||
| B0 | −452 | 1255 | 568 | 100 (568) | C0 | −452 | 1255 | 568 | > | |||||||||
| B1 | 1255 | 3399 | 714 | 100 (714) | C1 | 1255 | 3399 | 714 | > | 100 (714) | L0114 | 100 (714) | H0130 | |||||
| B3 | 3557 | 4564 | 335 | 100 (335) | C3 | 3557 | 4564 | 335 | > | 100 (335) | L0115 | 100 (335) | H0131 | |||||
| B4 | 4588 | 5121 | 177 | 100 (162) | C4 | 4588 | 5802 | 404 | > | 100 (162) | L0116 | 100 (162) | H0132 | |||||
| B5 | 5118 | 5801 | 227 | 100 (227) | C4 | 4588 | 5802 | 404 | > | 100 (227) | L0116 | 100 (227) | H0132 | |||||
| B7 | 5857 | 6246 | 129 | 100 (129) | C6 | 5858 | 6247 | 129 | > | 100 (129) | L0117 | 100 (129) | H0133 | |||||
| B9 | 6269 | 6757 | 162 | 100 (162) | C8 | 6270 | 6758 | 162 | > | 100 (162) | L0118 | 100 (162) | H0134 | |||||
| B10 | 6633 | 7304 | 223 | 100 (223) | C9 | 6634 | 7305 | 223 | > | 100 (223) | L0119 | 100 (223) | H0135 | |||||
| B12 | 7304 | 7954 | 216 | 100 (216) | C11 | 7305 | 7955 | 216 | > | 100 (216) | L0120 | 100 (216) | H0136 | |||||
| B14 | 7951 | 9888 | 645 | 100 (645) | C13 | 7952 | 9889 | 645 | > | 100 (645) | L0121 | 99 (645) | H0137 | Collagen alpha 1 (I) chain | 40 (422) | |||
| B18 | 9770 | 10159 | 129 | 100 (129) | C17 | 9771 | 10160 | 129 | > | 100 (129) | L0122 | 100 (129) | H0138 | 92 (129) | H0003 | |||
| B19 | 10206 | 10487 | 93 | 100 (93) | C18 | 10207 | 10488 | 93 | > | 100 (93) | L0123 | 100 (93) | H0139 | |||||
| B20 | 10704 | 12407 | 567 | 100 (567) | C19 | 10705 | 12408 | 567 | > | 100 (567) | L0124 | 100 (567) | H0140 | |||||
| B21 | 12404 | 13672 | 422 | 100 (422) | C20 | 12405 | 13673 | 422 | > | 100 (422) | L0125 | 100 (422) | H0141 | |||||
| B22 | 13738 | 13965 | 75 | 100 (75) | C21 | 13739 | 13966 | 75 | > | 100 (75) | L0126 | 100 (75) | H0142 | |||||
| B23 | 13971 | 14588 | 205 | 100 (205) | C22 | 13972 | 14589 | 205 | lom | > | 100 (205) | L0127 | 100 (205) | H0143 | ||||
| B24 | 14679 | 15413 | 244 | 100 (244) | C23 | 14680 | 15414 | 244 | > | 100 (244) | L0128 | 100 (244) | H0144 | Phage lambda Lom | 35 (174) | |||
| B25 | 15843 | 16244 | 133 | 100 (133) | C24 | 15844 | 16245 | 133 | > | 100 (133) | L0129 | 100 (133) | H0145 | |||||
| B26 | 16338 | 16994 | 218 | 100 (218) | C25 | 16339 | 16995 | 218 | > | 100 (218) | L0130 | 100 (218) | H0146 | |||||
| B28 | 16997 | 17443 | 148 | 100 (148) | C27 | 16998 | 17444 | 148 | > | 100 (148) | L0131 | 100 (148) | H0147 | |||||
| B29 | 17453 | 17704 | 83 | 100 (83) | C28 | 17454 | 17705 | 83 | > | 100 (83) | L0132 | 100 (83) | H0148 | |||||
| B30 | 17715 | 18980 | 421 | 100 (421) | C29 | 17716 | 18981 | 421 | > | 100 (421) | L0133 | 100 (421) | H0149 | |||||
| B31 | 19011 | 27431 | 2,806 | 99 (2,565) | C30 | 19012 | 26742 | 2,576 | > | 99 (2,806) | L0134 | 100 (2,806) | H0150 | |||||
| B38 | 27714 | 27902 | 62 | 100 (62) | C37 | 27714 | 27902 | 62 | > | 100 (62) | L0135 | 100 (62) | H0151 | |||||
| b32 | 28326 | 27982 | 114 | 100 (114) | c32 | 28326 | 27982 | 114 | < | 100 (114) | L0136 | 100 (114) | H0152 | |||||
| B39 | 28646 | 29395 | 249 | 100 (249) | C38 | 28646 | 29395 | 249 | > | 98 (72) | 100 (249) | |||||||
| b33 | 28658 | 28446 | 70 | 100 (70) | c33 | 28658 | 28446 | 70 | gef | < | 100 (70) | L0137 | 100 (70) | H0153 | E. coli K-12 Gef | 73 (69) | ||
| b34 | 29362 | 28892 | 156 | 100 (156) | c34 | 29362 | 28892 | 156 | < | 100 (156) | L0139 | 92 (130) | ||||||
| B40 | 29380 | 29748 | 122 | 100 (122) | C39 | 29380 | 29748 | 122 | > | 100 (122) | 99 (122) | |||||||
| B41 | 29735 | 30019 | 94 | 100 (94) | C40 | 29735 | 30019 | 94 | ehly2 | > | 85 (84) | 100 (94) | Bacteriophage C3208 enterohemolysin 2 | 89 (74) | ||||
| b35 | 29946 | 29287 | 219 | 100 (219) | c35 | 29946 | 29287 | 219 | < | 98 (219) | L0140 | 99 (219) | H0156 | Enterohemolysin-associated protein | 88 (77) | |||
| b36 | 30456 | 30172 | 94 | 100 (94) | c36 | 30456 | 30172 | 94 | < | 98 (94) | H0158 | |||||||
| b37 | 30674 | 30453 | 73 | 100 (73) | c37 | 30674 | 30453 | 73 | < | 91 (73) | L0141 | 98 (73) | H0159 | |||||
| b38 | 31351 | 30722 | 209 | 100 (209) | c38 | 31351 | 30722 | 209 | antB | < | 99 (209) | L0142 | 100 (209) | H0160 | E. coli AntB | 84 (209) | ||
| b39 | 33251 | 31917 | 444 | 100 (444) | c39 | 33251 | 31917 | 444 | int | < | 100 (444) | L0061 | 100 (444) | H0071 | 65 (423) | H0070 | E. coli K-12 putative transposase | 55 (385) |
| b40 | 33579 | 33280 | 99 | 100 (99) | c40 | 33579 | 33280 | 99 | ydaQ | < | 100 (99) | L0062 | 100 (99) | H0072 | 47 (74) | H0069 | E. coli YdaQ | 35 (62) |
| b41 | 33961 | 33650 | 103 | 100 (103) | c41 | 33961 | 33650 | 103 | < | 100 (103) | L0063 | 100 (103) | H0073 | |||||
| b42 | 34386 | 34021 | 121 | 100 (121) | c42 | 34386 | 34021 | 121 | < | 100 (121) | L0064 | 100 (121) | H0074 | |||||
| b43 | 34921 | 34298 | 207 | 100 (207) | c43 | 34921 | 34298 | 207 | < | 100 (207) | L0065 | 100 (207) | H0075 | 84 (44) | H0060 | |||
| b44 | 35212 | 34925 | 95 | 100 (95) | c44 | 35212 | 34925 | 95 | < | 100 (95) | L0066 | 100 (95) | H0076 | |||||
| b45 | 35432 | 35214 | 72 | 100 (72) | c45 | 35432 | 35214 | 72 | < | 100 (72) | L0067 | 100 (72) | H0077 | |||||
| b46 | 35721 | 35434 | 95 | 100 (95) | c46 | 35721 | 35434 | 95 | < | 100 (95) | L0068 | 100 (95) | H0078 | |||||
| b47 | 36118 | 35651 | 155 | 100 (155) | c47 | 36118 | 35651 | 155 | < | 100 (115) | 100 (115) | |||||||
| B48 | 36217 | 36567 | 116 | 100 (116) | C47 | 36217 | 36567 | 116 | ehly2 | > | 100 (116) | 100 (116) | Bacteriophage C3208 enterohemolysin 2 | 95 (102) | ||||
| b48 | 36764 | 35991 | 257 | 100 (257) | c48 | 36764 | 35991 | 257 | < | 100 (257) | L0069 | 100 (257) | H0079 | 79 (146) | H0066 | Enterohemolysin-associated protein | 97 (177) | |
| b50 | 36982 | 36761 | 73 | 100 (73) | c50 | 36982 | 36761 | 73 | < | 79 (73) | L0141 | 100 (73) | H0080 | 94 (73) | H0065 | |||
| b51 | 37362 | 37081 | 93 | 100 (93) | c51 | 37362 | 37081 | 93 | < | 100 (93) | L0070 | 100 (93) | H0081 | 100 (93) | H0064 | Phage lambda orf61 | 93 (46) | |
| b52 | 37564 | 37373 | 63 | 100 (63) | c52 | 37564 | 37373 | 63 | < | 98 (63) | L0071 | 100 (63) | H0082 | 98 (63) | H0063 | Phage lambda orf63 | 90 (61) | |
| b53 | 37725 | 37537 | 62 | 100 (62) | c53 | 37725 | 37537 | 62 | < | 93 (62) | L0072 | 100 (62) | H0083 | 93 (62) | H0062 | Phage lambda orf60 | 96 (60) | |
| b54 | 38396 | 37716 | 226 | 100 (226) | c54 | 38396 | 37716 | 226 | exo | < | 99 (226) | L0073 | 100 (226) | H0084 | 97 (225) | H0061 | Phage lambda exonuclease | 98 (226) |
| b55 | 39178 | 38393 | 261 | 100 (261) | c55 | 39178 | 38393 | 261 | bet | < | 100 (261) | L0074 | 100 (261) | H0085 | 99 (261) | H0060 | Phage lambda Bet | 99 (261) |
| b57 | 39600 | 39184 | 138 | 100 (138) | c57 | 39600 | 39184 | 138 | gam | < | 97 (98) | L0075 | 100 (98) | H0086 | 95 (98) | H0059 | Phage lambda Gam | 97 (138) |
| b58 | 39824 | 39555 | 89 | 100 (89) | c58 | 39824 | 39555 | 89 | kil | < | 97 (89) | L0076 | 100 (89) | H0087 | 96 (89) | H0058 | Phage lambda Kil | 98 (89) |
| b59 | 39831 | 39667 | 54 | 100 (54) | c59 | 39831 | 39667 | 54 | cIII | < | 98 (54) | L0077 | 100 (54) | H0088 | 100 (54) | H0057 | Phage lambda CIII | 100 (54) |
| b60 | 40272 | 39904 | 122 | 100 (122) | c60 | 40272 | 39904 | 122 | ea10 | < | 98 (122) | L0078 | 100 (122) | H0089 | 98 (122) | H0056 | Phage lambda Ea10 | 99 (122) |
| b61 | 40706 | 40455 | 83 | 100 (83) | c61 | 40706 | 40455 | 83 | < | 100 (83) | H0090 | |||||||
| b62 | 41109 | 40765 | 114 | 100 (144) | c62 | 41109 | 40765 | 114 | N | < | 41 (127) | L0080 | 100 (90) | H0091 | 47 (90) | H0054 | Phage HK97 N | 42 (127) |
| b63 | 42287 | 41766 | 173 | 100 (173) | c63 | 42287 | 41766 | 173 | < | 100 (173) | H0093 | |||||||
| b64 | 43484 | 42789 | 231 | 100 (231) | c64 | 43484 | 42789 | 231 | cI | < | L0085 | 99 (217) | H0094 | H0052 | Phage lambda CI | 71 (212) | ||
| B58 | 43560 | 43775 | 71 | 100 (71) | C57 | 43560 | 43775 | 71 | cro | > | L0086 | 100 (71) | H0095 | H0051 | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium bacteriophage ST64T Cro | 69 (71) | ||
| B59 | 43917 | 44213 | 98 | 100 (98) | C58 | 43917 | 44213 | 98 | cII | > | 98 (98) | L0087 | 100 (98) | H0096 | 90 (98) | H0050 | Phage HK022 CII | 96 (98) |
| B60 | 44385 | 45284 | 299 | 92 (194) | C59 | 44385 | 45029 | 214 | O | > | L0088 | 100 (299) | H0098 | H0049 | Phage HK022 O | 98 (299) | ||
| B61 | 45259 | 46710 | 483 | 100 (483) | C60 | 45258 | 46709 | 483 | P | > | L0089 | 100 (478) | H0099 | H0048 | Phage HK022 P | 99 (413) | ||
| b66 | 45272 | 44913 | 119 | 100 (117) | c66 | 45271 | 44855 | 138 | < | 100 (119) | ||||||||
| B62 | 46710 | 46979 | 89 | 100 (89) | C61 | 46709 | 46978 | 89 | > | 100 (89) | H0100 | |||||||
| B63 | 47050 | 47328 | 92 | 100 (92) | C62 | 47049 | 47327 | 92 | > | 100 (92) | L0091 | 100 (92) | H0101 | 98 (92) | H0045 | |||
| B64 | 47461 | 47676 | 71 | 100 (71) | C63 | 47460 | 47675 | 71 | > | 97 (71) | orf 6c | 100 (71) | H0102 | 98 (71) | H0044 | |||
| B65 | 47681 | 47923 | 80 | 100 (80) | C64 | 47680 | 47922 | 80 | > | 100 (48) | L0092 | 100 (78) | H0103 | 100 (78) | H0043 | |||
| B66 | 47781 | 48326 | 181 | 100 (181) | C65 | 47780 | 48325 | 181 | ninB | > | 99 (181) | L0093 | 100 (148) | H0104 | 99 (148) | H0042 | Bacteriophage 21 NinB | 43 (148) |
| B67 | 48323 | 48850 | 175 | 98 (175) | C66 | 48322 | 48849 | 175 | dam | > | 98 (175) | L0094 | 98 (175) | H0105 | 100 (175) | H0041 | DNA adenine methyltransferase | 32 (158) |
| B68 | 48847 | 49023 | 58 | 100 (58) | C67 | 48846 | 49028 | 60 | ninE | > | 85 (27) | orf 11c | 100 (58) | H0106 | 100 (58) | H0040 | Bacteriophage P22 NinE | 98 (58) |
| C68 | 49303 | 50037 | 244 | ant | > | Phage P22 Ant | 82 (104) | |||||||||||
| C69 | 50106 | 50834 | 242 | roi | > | 88 (242)d | L0096 | 100 (242)d | H0108 | Phage HK022 Roi | 82 (241) | |||||||
| B69 | 48984 | 49427 | 147 | > | 100 (135) | H0039 | ||||||||||||
| B70 | 49589 | 50194 | 201 | 96 (201) | C70 | 50834 | 51439 | 201 | ninG | > | 96 (201) | L0097 | 96 (201) | H0109 | 100 (201) | H0037 | Phage lambda Nin G | 90 (203) |
| B71 | 50221 | 50385 | 54 | 100 (54) | C71 | 51466 | 51630 | 54 | ninH | > | 100 (54) | L0098 | 100 (54) | H0110 | 100 (54) | H0036 | Phage lambda Nin H | 78 (50) |
| B72 | 50339 | 50812 | 157 | 97 (157) | C72 | 51584 | 52057 | 157 | Q | > | 97 (157) | L0099 | 97 (157) | H0111 | 100 (157) | H0035 | Q | |
| B73 | 51319 | 52266 | 315 | stxA1 | > | 100 (315) | H0034 | StxA1 subunit | 100 (315) | |||||||||
| B74 | 52276 | 52545 | 89 | stxB1 | > | 100 (89) | H0033 | StxB1 subunit | 100 (89) | |||||||||
| C73 | 52841 | 53800 | 319 | stxA2 | > | 100 (319)d | L0103 | 100 (319)d | H0112 | StxA2 subunit | 100 (319) | |||||||
| C74 | 53812 | 54081 | 89 | stxB2 | > | 100 (89)d | L0104 | 100 (89)d | H0113 | StxB2 subunit | 100 (89) | |||||||
| b70 | 52929 | 52606 | 107 | < | 100 (107) | S. dysenteriae hypothetical protein | 59 (61) | |||||||||||
| B75 | 53056 | 55002 | 648 | 89 (570) | C75 | 54568 | 56472 | 634 | yjhS | > | 91 (648) | L0105 | 98 (415) | H0115 | 100 (648) | H0032 | S. dysenteriae YjhS | 67 (656) |
| S. somnei bacteriophage 7888 hypothetical protein | 91 (648) | |||||||||||||||||
| c73 | 57169 | 56279 | 296 | < | 100 (296)d | H0116 | 100 (296)d | H0021 | IS1203 v ORFb | 100 (296) | ||||||||
| c74 | 57492 | 57166 | 108 | < | 100 (108)d | H0117 | 99 (108)d | H0020 | IS1203 v ORFa | 100 (108) | ||||||||
| B78 | 55140 | 55319 | 59 | 100 (59) | C80 | 57954 | 58133 | 59 | > | 100 (59) | orf 25c | 100 (59) | H0119 | 100 (59) | H0031 | |||
| B79 | 55186 | 55605 | 139 | 82 (136) | C81 | 58000 | 58446 | 148 | > | 79 (148) | L0106 | 81 (136) | 100 (81) | H0030 | S. sonnei bacteriophage 7888 hypothetical protein | 79 (148) | ||
| S. dysenteriae hypothetical protein | 91 (81) | |||||||||||||||||
| B80 | 55608 | 55898 | 96 | 100 (71) | C82 | 58523 | 58738 | 71 | S | > | 100 (71) | L0107 | 100 (71) | H0121 | 100 (71) | H0029 | S. sonnei bacteriophage 7888 S | 100 (71) |
| S. dysenteriae S | 95 (71) | |||||||||||||||||
| B81 | 55903 | 56436 | 177 | 100 (177) | C83 | 58743 | 59276 | 177 | R | > | 100 (177) | L0108 | 100 (177) | H0122 | 100 (177) | H0028 | S. sonnei bacteriophage 7888 R | 96 (177) |
| B82 | 56707 | 57276 | 189 | 100 (189) | C84 | 59547 | 60116 | 189 | ant | > | 100 (189) | L0109 | 100 (189) | H0123 | 100 (189) | H0027 | S. sonnei bacteriophage Ant | 94 (189) |
| B83 | 57430 | 57894 | 154 | 100 (154) | C85 | 60270 | 60734 | 154 | Rz | > | 100 (154) | L0110 | 100 (154) | H0124 | 96 (153) | H0026 | S. sonnei bacteriophage 7888 Rz | 84 (133) |
| B84 | 57650 | 57835 | 61 | 100 (61) | C86 | 60490 | 60675 | 61 | > | 100 (61) | L0110 | 100 (61) | H0125 | 98 (61) | Phage lambda Rz1 | 72 (61) | ||
| b79 | 58219 | 57926 | 97 | 100 (97) | c80 | 61059 | 60766 | 97 | bor | < | 100 (97) | L0111 | 100 (97) | H0126 | Phage lambda Bor | 96 (97) | ||
| B85 | 58327 | 58572 | 81 | 100 (81) | C87 | 61167 | 61412 | 81 | > | 100 (81) | 100 (81) | |||||||
| B86 | 58628 | 59434 | 268 | 100 (268) | C88 | 61468 | 62274 | 268 | > | 100 (268) | L0112 | 100 (268) | H0127 | |||||
| B87 | 59415 | 1255 | 568 | 100 (568) | C89 | 62255 | 1255 | 568 | > | 100 (568) | L0113 | 100 (389) | H0128 | |||||
| 100 (138) | H0129 | |||||||||||||||||
Homologous ORF(s) of Stx2φ-II, 933W (14), VT2-Sakai (7) and VT1-Sakai (21) compared with each ORF of Stx1φ are shown as % identity in amino acid residues indicated. Identities higher than 95% are shown in bold, and ORFs which are identical to the corresponding ORF in Stx1φ are underlined.
>, rightward transcription; <, leftward transcription in Fig. 1.
This ORF was reported in reference 3.
Comparison with Stx2φ-II.
aa, amino acids.
FIG. 2.
Comparison of Stx1φ with other related Stx1-converting phages. The open bars represent portions homologous to Stx1φ, while the different portions of each Stx1-converting phage are cross-hatched. (A) Comparison between Stx1φ and VT1-Sakai phages; (B) comparison between Stx1φ and H19B phages. The DNA sequence of VT1-Sakai phage was modified from that reported by Yokoyama et al. (21) for convenience. Note that most regions of Stx1φ were not homologous to Stx1-converting phages, except for the stx1-flanking region.
ORF analysis.
Open reading frames (ORFs) that showed significant homologies to the genes registered in DDBJ or that consisted of more than 80 amino acid residues were picked up. This definition enabled us to identify 167 putative ORFs in Stx1φ and 170 putative ORFs in Stx2φ-II (for detailed ORF information, please refer to DDBJ). The ORFs that show homology to any genes in other Stx-converting phages or bacterium-associated genes were picked up and are listed in Table 1. ORFs of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II were also almost completely identical, reflecting the high DNA sequence homology between these two phages. The exception was the stx-flanking regions including four ORFs, B69, B73, B74, and b70 in Stx1, which are identical to or almost the same as the corresponding ORFs of VT1-Sakai (Table 1). This region might be characteristic of Stx1-converting pages, since H19B (10) also has a homology in the corresponding region at the DNA level (data not shown). ORFs B4, B5, and B30 of Stx1φ are not identical to the corresponding ORFs of Stx2φ-II due to frameshift mutations (data not shown). From these data, we conclude that Stx1φ is closely related to other Stx2-converting phages even at the ORF level.
It is noteworthy that there are several ORFs homologous to those of Shigella sonnei phage 7888 (15) and S. dysenteriae (8) in the stx-flanking regions of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II (Table 1). Recently, an Stx-converting phage was isolated from Stx1-producing S. sonnei (L. Beutin, E. Strauch, and I. Fischer, Letter, Lancet 353:1498, 1999). Treatment with mitomycin C increases Stx production and induces Stx phage from some EHEC (5) and S. sonnei (Beutin et al., letter) bacteria. It has been a focus of discussion whether Stx-converting phages in EHEC are derived from Shigella species. Our data rather support that Stx-converting phages might be derived from, or at least related to, Shigella species.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The entire nucleotide sequences of Stx1φ and Stx2φ-II were submitted to DDBJ under accession numbers AP005153 and AP005154, respectively.
Acknowledgments
We thank G. Balakrish Nair for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was supported by the Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research.
This work formed a part of the Ph.D. thesis of T. Sato.
REFERENCES
- 1.Fuchs, S., I. Muhldorfer, A. Donohue-Rolfe, M. Kerenyi, L. Emody, R. Alexiev, P. Nenkov, and J. Hacher. 1999. Influence of RecA on in vivo virulence and Shiga toxin 2 production in Escherichia coli pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 27:13-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Grif, K., M. P. Dierich, H. Karch, and F. Allerberger. 1998. Strain-specific differences in the amount of Shiga toxin released from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 following exposure to subinhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17:761-766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Karch, H., H. Schmidt, C. Janetzki-Mittmann, J. Scheef, and M. Kroeger. 1999. Shiga toxins even when different are encoded at identical positions in the genomes of related temperate bacteriophages. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262:600-607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kimmit, P. T., C. R. Harwood, and M. R. Barer. 2000. Toxin gene expression by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: the role of antibiotics and the bacterial SOS response. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 6:458-465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kohler, B., H. Karch, and H. Schmidt. 2000. Antibacterials that are used as growth promoters in animal husbandry can affect the release of Shiga-toxin-2-converting bacteriophages and Shiga toxin 2 from Escherichia coli strains. Microbiology 146:1085-1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kusumoto, M., Y. Nishiya, Y. Kawamura, and K. Shinagawa. 1999. Identification of an insertion sequence, IS1203 variant, in a Shiga toxin 2 gene of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 87:93-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Makino, K., K. Yokoyama, Y. Kubota, C. H. Yutsudo, S. Kitamura, K. Kurokawa, K. Ishii, M. Hattori, I. Tatsuno, H. Abe, T. Iida, K. Yamamoto, M. Onishi, T. Hayashi, T. Yasunaga, T. Honda, C. Sasakawa, and H. Shinagawa. 1999. Complete nucleotide sequence of the prophage VT2-Sakai carrying the verotoxin 2 genes of the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 derived from the Sakai outbreak. Genes Genet. Syst. 74:227-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McDonough, M. A., and J. R. Butterton. 1999. Spontaneous tandem amplification and deletion of the Shiga toxin operon in Shigella dysenteriae 1. Mol. Microbiol. 34:1058-1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Miyamoto, H., W. Nakai, N. Yajima, A. Fujibayashi, T. Higuchi, K. Sato, and A. Matsushiro. 1999. Sequence analysis of Stx2-converting phage VT2-Sa shows a great divergence in early regulation and replication regions. DNA Res. 6:235-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Neely, M. N., and D. I. Friedman. 1998. Arrangement and functional identification of genes in the regulatory region of lambdoid phage H-19B, a carrier of a Shiga-like toxin. Gene 223:105-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Neely, M. N., and D. I. Friedman. 1998. Functional and genetic analysis of regulatory regions of coliphage H-19B: location of Shiga-like toxin and lysis genes suggest a role for phage functions in toxin release. Mol. Microbiol. 28:1255-1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.O'Brien, A. D., J. W. Newland, S. F. Miller, R. K. Holmes, H. W. Smith, and S. B. Formal. 1984. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages form Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science 226:694-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Paton, J. C., and A. W. Paton. 1998. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 11:450-479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Plunkett, G. I., D. J. Rose, T. J. Durfee, and F. R. Blattner. 1999. Sequence of Shiga toxin 2 phage 933W from Escherichia coli O157:H7: Shiga toxin as a phage late-gene product. J. Bacteriol. 181:1767-1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Strauch, E., R. Lurz, and L. Beutin. 2001. Characterization of a Shiga toxin-encoding temperate bacteriophage of Shigella sonnei. Infect. Immun. 69:7588-7595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Strockbine, N. A., L. R. M. Marques, J. W. Newland, H. W. Smith, R. K. Holmes, and A. D. O'Brien. 1986. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect. Immun. 53:135-140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Takao, T., T. Tanabe, Y.-M. Hong, Y. Shimonishi, H. Kurazono, T. Yutsudo, C. Sasakawa, M. Yoshikawa, and Y. Takeda. 1988. Identity of molecular structure of Shiga-like toxin I (VT1) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 with that of Shiga toxin. Microb. Pathog. 5:357-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Watarai, M., T. Sato, M. Kobayashi, T. Shimizu, S. Yamasaki, T. Tobe, C. Sasakawa, and Y. Takeda. 1998. Identification and characterization of a newly isolated Shiga toxin 2-converting phage from Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 66:4100-4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wong, C. C., S. Jelacic, R. L. Harbeeb, and S. L. Watkins. 2000. The risk of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 342:1930-1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yoh, M., E. K. Frimpong, and T. Honda. 1997. Effect of antimicrobial agents, especially fosfomycin, on the production and release of vero toxin by enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 19:57-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yokoyama, K., K. Makino, Y. Kubota, M. Watanabe, S. Kimura, C. H. Yutsudo, K. Kurokawa, K. Ishii, M. Hattori, I. Tatsuno, H. Abe, M. Yoh, T. Iida, M. Ohnishi, T. Hayashi, T. Yasunaga, T. Honda, C. Sasakawa, and H. Shinagawa. 2000. Complete nucleotide sequence of the prophage VT1-Sakai carrying the Shiga toxin 1 genes of the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain derived from the Sakai outbreak. Gene 258:127-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yutsudo, T., N. Nakabayashi, T. Hirayama, and Y. Takeda. 1987. Purification and some properties of a vero toxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7 that is immunologically unrelated to Shiga toxin. Microb. Pathog. 3:21-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang, X., A. D. McDaniel, L. E. Wolf, G. T. Keusch, M. K. Waldor, and D. K. A. Acheson. 2000. Quinolone antibiotics induce Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophages, toxin production, and death in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 181:664-670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]