Abstract
Background
We report our experience of the simultaneous occurrence of adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH). Liver cell adenoma together with FNH was found in five out of 30 cases of "multiple benign hepatocytic nodules" collected in our files of the Department of Pathology of the University Hospital of Bordeaux, during the last 12 years. All five cases were women on oral contraceptives. In all cases, the reason for surgery was the discovery, by imaging techniques, of an adenoma (4 cases) or of an unidentified benign tumor, possibly an adenoma.
Results
Four cases of FNH were discovered by imaging techniques, prior to surgery. Additional small nodules were diagnosed either during surgery or during the slicing of the specimen in 3 cases. Adenoma and the FNH cases identified by imaging techniques were confirmed as such by light microscopy. Some small nodules could not be categorized with certainty because they contained biliary structures without ductular reaction. In one case, the non-nodular liver was abnormal around the area in which there were multiple nodules: there was approximation of portal tracts with portal and hepatic venous thromboses, and portal tract remnants with arteries surrounded with a rim of fibrosis. In two cases, some large hepatic veins had thickened walls.
Conclusions
The association of FNH and adenoma could be coincidental or secondary to shared causal mechanisms: a) systemic and local angiogenic abnormalities induced by oral contraceptives; b) tumor-induced growth factors; c) thrombosis and local arterio-venous shunting. A better recognition of the association of adenoma and FNH, particularly in the context of multiple nodules, could be useful in clinical practice.
Background
Adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) are both benign nodular hepatocellular lesions occurring in child bearing women, in a liver that is otherwise histologically normal or nearly normal. Both lesions looked like histologically quite different in their typical forms; however, some non-typical nodules, especially those of small size, could be extremely challenging to hepatologists.
A central stellate fibrous region containing malformed large arteries but usually no portal veins characterizes typical FNH. The lesion is multinodular, composed of nearly normal hepatocytes, arranged in 1–2 cell-thick plates, associated with a prominent bile ductular reaction, and intermingled with inflammatory cells (at the interface between hepatocytic nodules and fibrous bands). FNH is considered as a hyperplastic process resulting from an increased arterial flow. At the opposite, adenoma is a true benign neoplasia, composed of slightly enlarged but nearly normal hepatocytes, arranged in 1–2 cell-thick plates, with numerous thin arteries dispersed within the tumor, whereas there are no portal tracts and particularly no biliary ducts. Adenoma exhibited usually peliotic and necrotic hemorrhagic changes, steatotic areas and sometimes dysplasia. Their transformation into HCC is well documented but remains rare.
The simultaneous occurrence of adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) has been infrequently documented [1-6]. FNH associated with adenomas or adenomatosis has been reported [7-9], suggesting a link between these conditions.
We report the experience of a single French academic center, which supports the possibility that the association is more than by chance. Liver cell adenoma together with FNH was found in five out of 30 cases of "multiple benign hepatocytic nodules" collected in our files of the Department of Pathology of the University Hospital of Bordeaux, during the last 12 years.
Results and Discussion
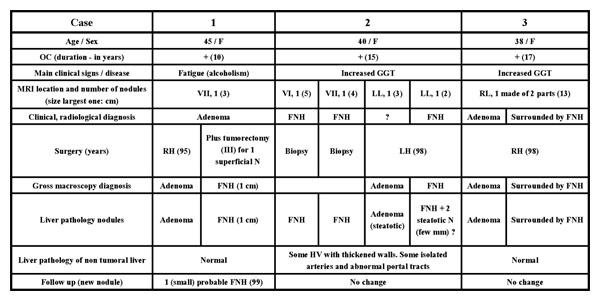
Relevant clinical, radiological and surgical data are presented in Figures 1, 2 and 3. All 5 cases of liver cell adenoma together with FNH were women on oral contraceptives. In all cases, the reason for surgery was the discovery, by imaging techniques, of an adenoma (cases 1, 3, 4, 5) or of an unidentified benign tumor possibly an adenoma (case 2). In four cases (2, 3, 4, 5) FNH were discovered by imaging techniques prior to surgery. The case in which the diagnosis of FNH was missed by pre-operative imaging was case 1 that had a small 1 cm superficial FNH.
Figure 1.
Adenoma plus focal nodular hyperplasia (cases 1, 2 and 3). Liver segments are indicated by roman numbers. FNH – focal nodular hyperplasia; GGT – gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; Hem: hemorrhagic; HV – hepatic vein; LH – left hepatectomy; LL – left lobe; MRI – magnetic resonance imaging; N – nodule; OC – oral contraceptives; PV – portal vein; RH – right hepatectomy; RL – right lobe; T – tumorectomy. (Abbreviations are valid for Figures 2 and 3.)
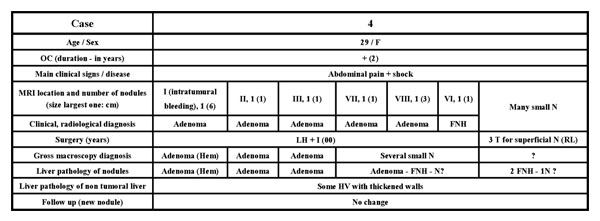
Figure 2.
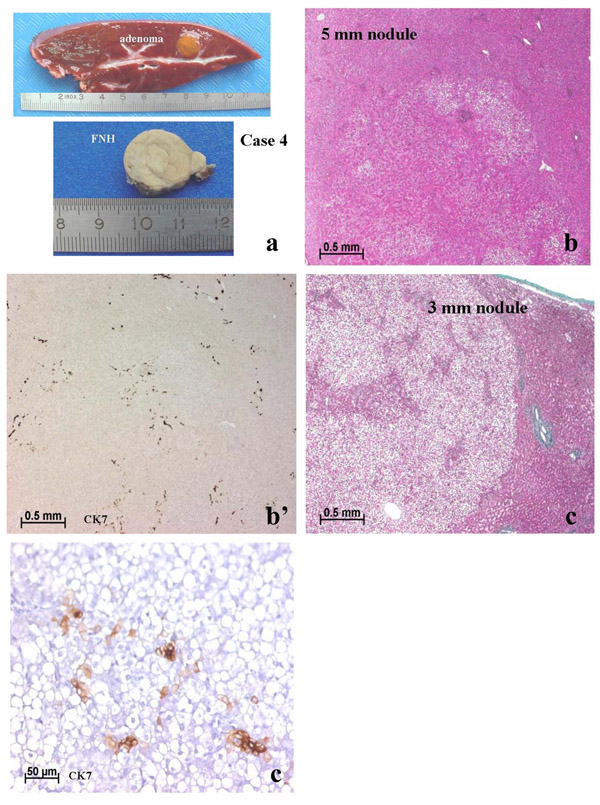
Adenoma plus focal nodular hyperplasia (case 4).
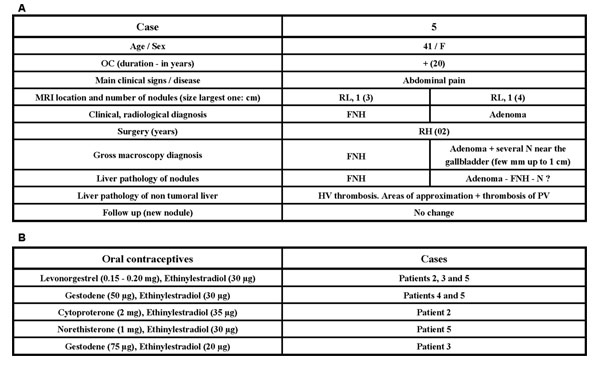
Figure 3.
A - Adenoma plus focal nodular hyperplasia (case 5) B - Details of contraceptives, for all five cases.
Additional small nodules were discovered (cases 2, 4 and 5; Figs. 4,5,6,7) either during surgery or during post-resection dissection of the specimen. Case 4 was known to have multiple nodules, one of which, at least, was identified as FNH (Fig. 6) by pre-operative imaging. Additional small superficial nodules (in case 4) were interpreted as adenomas by the surgeon and resected, and were solid FNH by light microscopy.
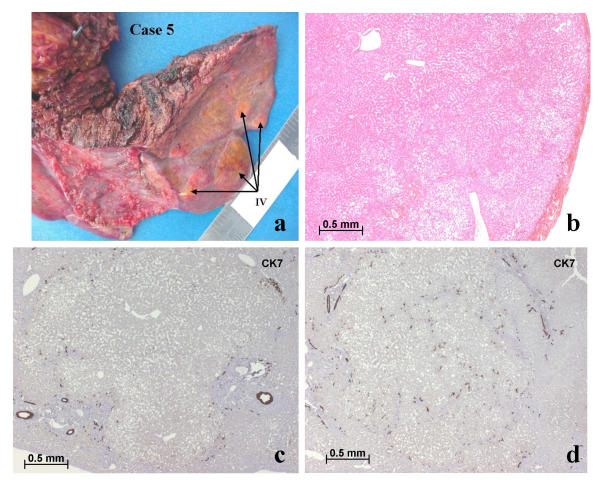
Figure 4.
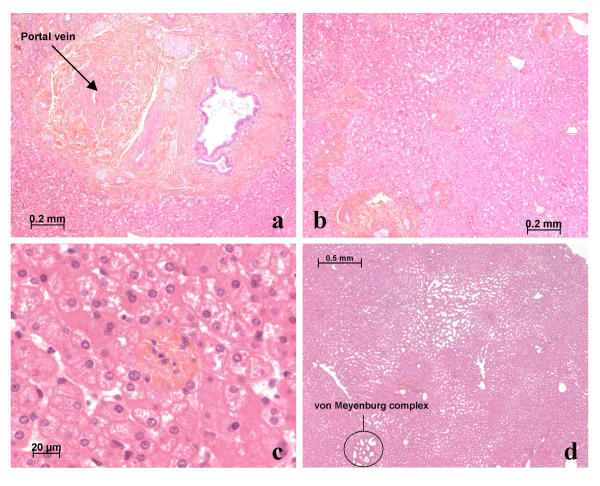
Case 5, segment IV. (a) shows several small nodules on the surface of segment IV (arrows). Among the nodules (surface and cut sections) there were several small adenomas (b, c). One nodule contained numerous CK7 positive biliary cells (d); it could not be classified with certainty, but it could be an early FNH lesion.
Figure 5.
Case 5, segment IV. Around the nodules, there were many abnormalities such as obstruction of portal vein branches (a), areas of portal tract approximation (b), portal tract remnants (c), and sinusoidal dilatation (d). Some von Meyenburg complexes were also observed (d).
Figure 6.
Case 4. In addition to the presence of adenomas and FNH seen macroscopically (a), there were many tiny nodules (b, c). In (b) there were many CK7 positive biliary cells (b') in the vicinity of arteries. This nodule could be an early FNH lesion. In another nodule (c) CK7 positive cells were faintly stained, isolated and did not form biliary structures. This nodule (c') is more likely an adenoma than a pre-FNH lesion.
Figure 7.
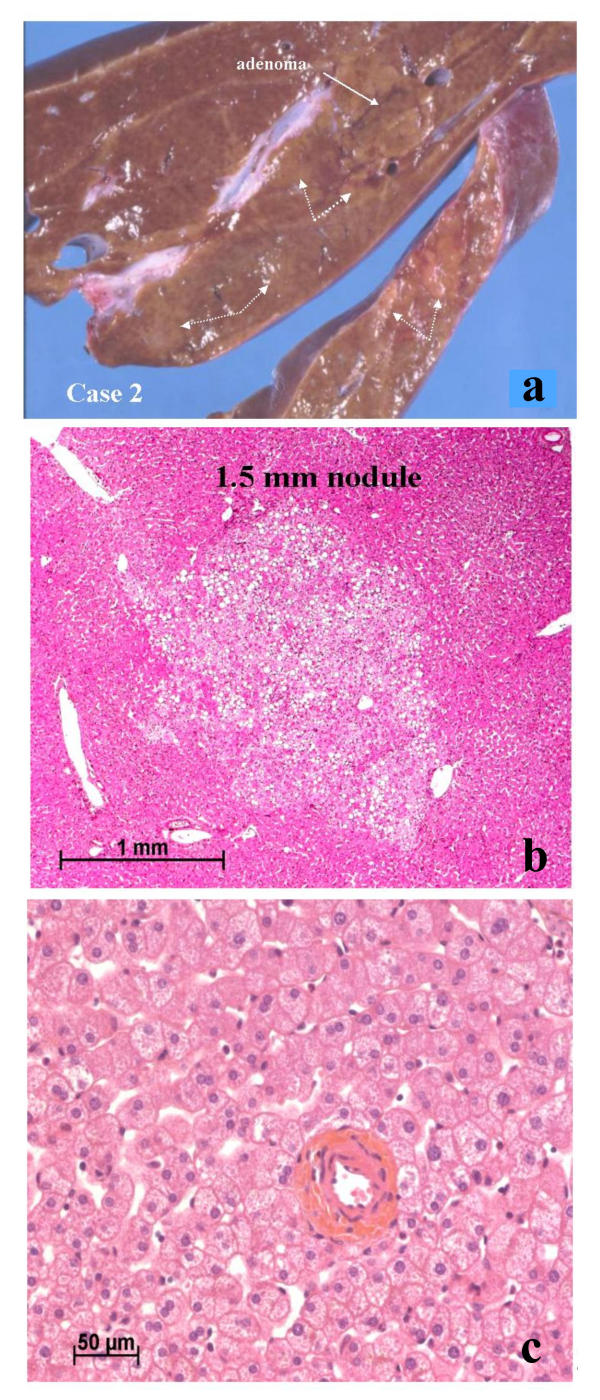
Case 2. In addition to the presence of several FNH and one adenoma (white solid arrow) (a), there were many small areas that were difficult to differentiate from the surrounding non-nodular tissue (white dotted arrows) (a). These areas corresponded to steatotic zones that could not be defined with certainty (b). In the non-nodular tissue there was an isolated hepatic artery (c).
Adenoma and FNH recognized by imaging techniques were easily identified as such by light microscopy. Conversely, some small nodules could not be identified with certainty because of the presence of biliary structures without ductular reaction (Figs. 4,5,6,7). To achieve a categorical assignment for the purposes of this study, we classified these small nodules with intralesional arteries and few/rare biliary cells, better identified by cytokeratin 7 (CK7) immunostaining, as adenoma [10]; and nodules with some/frequent biliary cells associated with intralesional arteries as FNH.
In one case (case 5) there were additional abnormalities in the non-nodular liver in the area around the multiple nodules that were found (Figs. 4, 5). These abnormalities consisted of portal tract approximation, portal venous and hepatic venous thromboses (totally or partially), portal tract remnants with arteries surrounded with a rim of fibrosis, and some von Meyenburg complexes were also observed. In two cases (cases 2 and 4) some large hepatic veins had thick walls.
In our referral center (3 million inhabitants), we receive mainly difficult cases either because the nature of the nodule(s) is unknown or because surgery might be technically difficult. Our patients thus consist of a highly selected population. Nevertheless, our finding of liver cell adenoma together with FNH in 5 out of 30 cases of "multiple benign hepatocytic nodules", collected in the files of the Department of Pathology of the University Hospital of Bordeaux during the last 12 years, suggests the possibility of a significant association.
If we omit case 1 which could be a co-incidental association of a known adenoma and a separate small FNH discovered incidentally during surgery, the four other cases show features that suggest a close relationship between adenoma and FNH:
- Case 3 is a rare example of the intermingling of the two lesions, with the FNH surrounding the adenoma [3]. The two lesions were diagnosed by pre-operative imaging.
- Case 4 demonstrates the presence of FNH in a patient with multiple adenomas (so-called adenomatosis) [8]. Here, pre-operative imaging identified at least one FNH, too.
- Case 2 illustrates the converse situation with at least, one adenoma in a patient with multiple FNH.
- Case 5 is similar to case 2 except that only one large FNH was picked up by imaging techniques.
It is thought that in FNH, increased arterial flow leads to secondary hepatocellular hyperplasia. Therefore, FNH is considered the consequence of a hyperplastic rather than a neoplastic process [11]. The association of FNH and adenoma could be coincidental or secondary to shared causal mechanisms [12-14]:
a) systemic and local abnormalities of angiogenesis induced by oral contraceptives (in our series all of the patients were women on oral contraceptives).
b) neoplastic growth factors inducing a nearby hyperplastic reaction; the surrounding of the adenoma by FNH (case 3) represents the best example.
c) thrombosis and local arterio-venous shunting [12]; in three cases, there were obvious abnormalities of veins in the non-nodular liver.
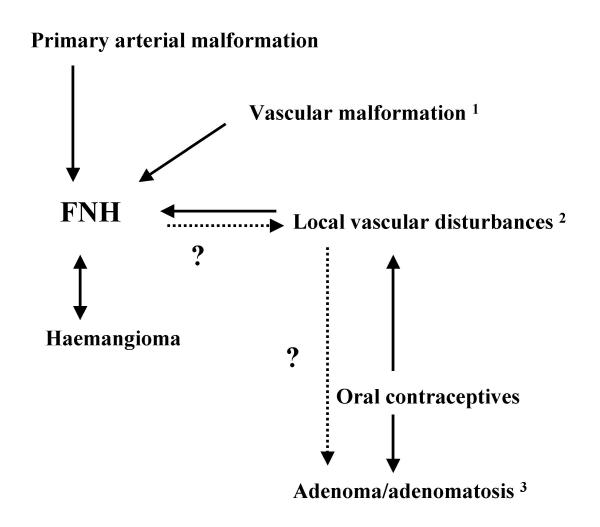
On the one hand, FNH might occur as a consequence of adenoma/adenomatosis; on the other hand, vascular abnormalities (congenital or acquired, and which are the key factor for the formation of FNH [11,13,14]), could favor the development of adenomas/adenomatosis (Fig. 8). The risk link to estrogen was thought to decrease with the use of the third generation of OC (lesser estrogens). However, the reduction of the dose of estrogens had limited effect on reducing the risk of venous thrombosis. Moreover, third generation of progestins in combination preparation increases the extent of adverse hemostatic changes and the associated risk of thrombosis [15].
Figure 8.
Hypothetical relationships between adenoma/adenomatosis and FNH. 1Vascular malformations: hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; congenital absence of portal vein; intra hepatic venous shunt. 2Local vascular disturbances: Budd Chiari; cirrhosis; tumors (epithelioid haemangio-endothelioma; fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma). 3The risk linked to estrogens.
One important finding shown in this study is that the number of nodules seen on the resected specimen is occasionally much greater than the number of nodules detected by imaging techniques. Some of these nodules cannot be identified with certainty [16]. This is certainly a major limitation of histopathology (and imaging). Clonality assessment [17] and gene analysis [18] could help to solve the identification of those small nodules. The size of the nodule (and thus the stage of the development of either adenoma or FNH) are probably the main reasons for the diagnostic difficulty which could be used as an argument to postpone the resection of small yet unidentified "benign" nodules (as long as their growth remains slow).
A better knowledge of the association of adenoma and FNH particularly in the context of multiple nodules, either adenomas or FNH, should prevent clinicians to conclude a final diagnosis in patients with multiple liver lesions of either type, simply on the basis of characterizing any single lesion. This will be helpful for a better follow-up of patients thought to have only multiple FNH or only multiple adenomas.
Conclusions
Liver adenoma and FNH in the context of multiple nodules may be significantly associated. The number of nodules seen in a resected specimen is occasionally much greater than nodules detected by imaging techniques. Small nodules present diagnostic difficulties. A better recognition of the association of adenoma and FNH, particularly in the context of multiple nodules, should be useful in clinical practice.
Methods
In the last 12 years, we collected in our files of the Department of Pathology of the University Hospital of Bordeaux, 30 cases of "multiple benign hepatocytic nodules". In our Institution, resected liver tumors are sliced thinly in the Department of Pathology. Each lesion detected prior to, or during resection or slicing is sampled. In addition, non-lesional liver near to and distant from the nodules are also sampled. Haematoxylin and eosin, Massons's trichrome, reticulin, and Perls' stains are performed routinely. For this study, slides were reviewed (by P.B-S and C.B.), and additional sections and immunostaining (CK7, alpha smooth muscle actin and CD 34) were performed whenever necessary. Standard criteria were used for the identification of adenoma and FNH [19]. Liver cell adenoma together with FNH was found in five cases out of 30 cases of "multiple benign hepatocytic nodules". Clinical, radiological and surgical data of these cases were reviewed.
Authors' Contributions
C Laurent contributed with clinical data. H Trillaud contributed with radiological data. C Balabaud reviewed slides and wrote the paper. S Lepreux contributed to the pathological examination. P Bioulac-Sage did the pathological examination and reviewed the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Jean Saric, Jean Frédéric Blanc, Noureddine Kerioui, Pierre Henri Bernard, Brigitte Le Bail and Antonio Sá Cunha for their participation in the patient's diagnosis and care.
Contributor Information
Christophe Laurent, Email: christophe.laurent@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Hervé Trillaud, Email: herve.trillaud@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Sébastien Lepreux, Email: sebastien.lepreux@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Charles Balabaud, Email: charles.balabaud@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Paulette Bioulac-Sage, Email: paulette.bioulac-sage@gref.u-bordeaux2.fr.
References
- Reichlin B, Stalder GA, Ruedi T, Bianchi L. Co-occurring liver cell adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia due to contraceptives. Case report. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1980;110:873–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance R, Zafrani ES, Hannoun S, Saada M, Fagniez PL, Metreau JM. Association of hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver in a woman on oral contraceptives. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1982;6:949–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntz M, Francois H, Ben Bouali A, Joubaud F, Taviaux R. Hepatocellular adenoma within focal nodular hyperplasia. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1983;7:826–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman LS, Gang DL, Hedberg SE, Isselbacher KJ. Simultaneous occurrence of hepatic adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: report of a case and review of the literature. Hepatology. 1984;4:536–540. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange JD, Guechot J, Legendre C, Giboudeau J, Darnis F, Poupon R. Liver adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia in a man with high endogenous sex steroids. Gastroenterology. 1987;93:1409–1413. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks WH, Thompson N, Appleman H. Failure of hepatic adenomas (HCA) to regress after discontinuance of oral contraceptives. An association with focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) and uterine leiomyoma. Ann Surg. 1988;208:190–195. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198808000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa T, Federle MP, Grazioli L, Nalesnik M. Hepatocellular adenoma: multiphasic CT and histopathologic findings in 25 patients. Radiology. 2000;214:861–868. doi: 10.1148/radiology.214.3.r00mr28861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grazioli L, Federle MP, Ichikawa T, Balzano E, Nalesnik M, Madariaga J. Liver adenomatosis: clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings in 15 patients. Radiology. 2000;216:395–402. doi: 10.1148/radiology.216.2.r00jl38395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen BN, Flejou JF, Terris B, Belghiti J, Degott C. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: a comprehensive pathologic study of 305 lesions and recognition of new histologic forms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:1441–1454. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199912000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libbrecht L, De Vos R, Cassiman D, Desmet V, Aerts R, Roskams T. Hepatic progenitor cells in hepatocellular adenomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25:1388–1396. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200111000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanless IR, Mawdsley C, Adams R. On the pathogenesis of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver. Hepatology. 1985;5:1194–1200. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanless IR, Terris B, Bioulac-Sage P. Focal Hyperplasia (FH) of liver associated with localized hepatic vein thrombosis: a lesion with some features of "focal nodular hyperplasia". Am J Surg Pathol. 2000. p. 191A.
- Wanless IR. Vascular disorders. In: MacSween RNM BA, Portmann BC, Ishak PJ, Scheur PJ, Anthony PP, editor. Pathology of the liver. 4. London, Churchill Livingstone; 2002. pp. 539–573. [Google Scholar]
- Wanless IR. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, multiple focal nodular hyperplasias, and cavernous hemangiomas of the liver. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124:1105–1107. doi: 10.5858/2000-124-1105-EHMFNH. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke JP, Rosing J, Bloemenkamp KW, Middeldorp S, Helmerhorst FM, Bouma BN, Rosendaal FR. Oral contraceptives and the risk of venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1527–1535. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105173442007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Wanless IR. Diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia: not so easy. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25:1322–1325. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200110000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis V, Laurent A, Flejou JF, Vidaud M, Bedossa P. Evidence for the polyclonal nature of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver by the study of X-chromosome inactivation. Hepatology. 1997;26:891–895. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluteau O, Jeannot E, Bioulac-Sage P, Marques JM, Blanc JF, Bui H, Beaudoin JC, Franco D, Balabaud C, Laurent-Puig P, Zucman-Rossi J. Bi-allelic inactivation of TCF1 in hepatic adenomas. Nat Genet. 2002;32:312–315. doi: 10.1038/ng1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- International Working Party Terminology of nodular hepatocellular lesions. Hepatology. 1995;22:983–993. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(95)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]