Abstract
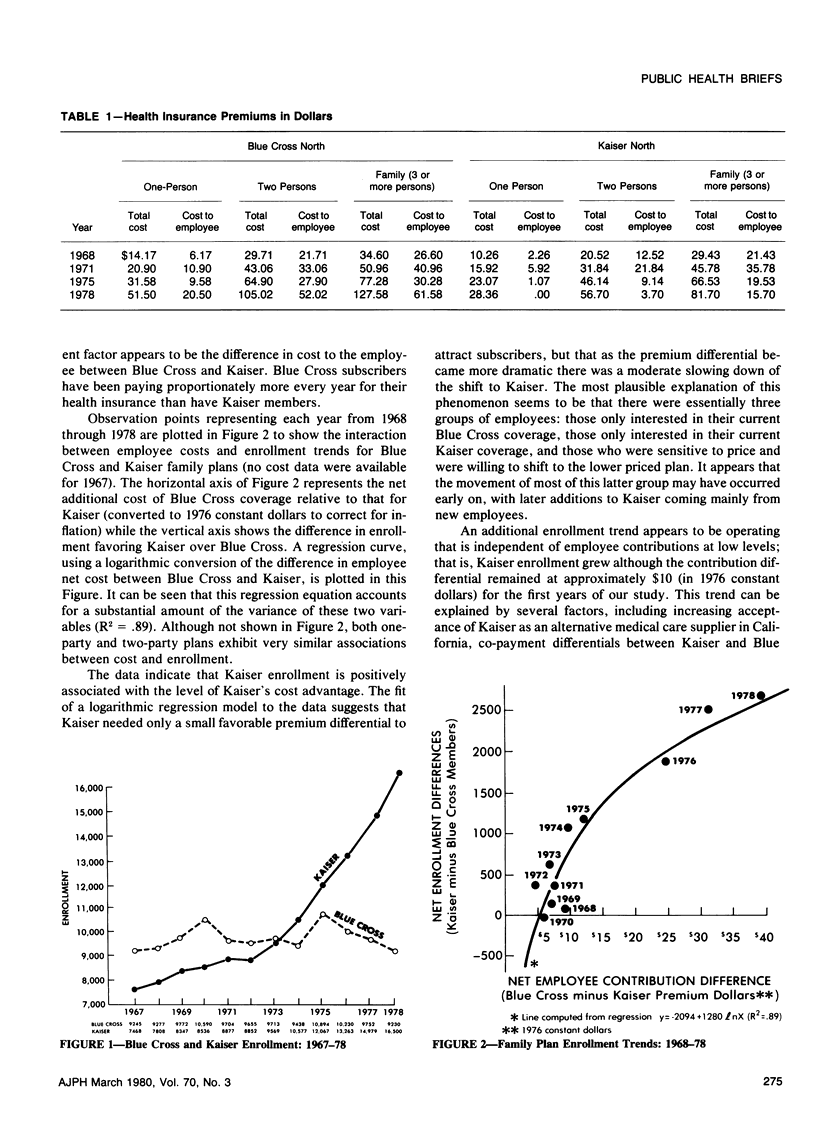
Enrollment trends for a large employee group were analyzed to determine the extent to which consumers chose Blue Cross or Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) health insurance under various premium differentials. Data were collected from employment records of six University of California campuses for the period 1967 to 1978. Enrollment in the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan (an HMO) more than doubled during this period while enrollment in Blue Cross remained relatively stable. This increased preference for Kaiser coverage was associated with a concurrent relative rise in costs to employees of Blue Cross coverage. These data suggest that consumers are sensitive to insurance costs, and that given the opportunity HMOs can compete effectively with traditional health insurance.
Full text
PDF