Abstract
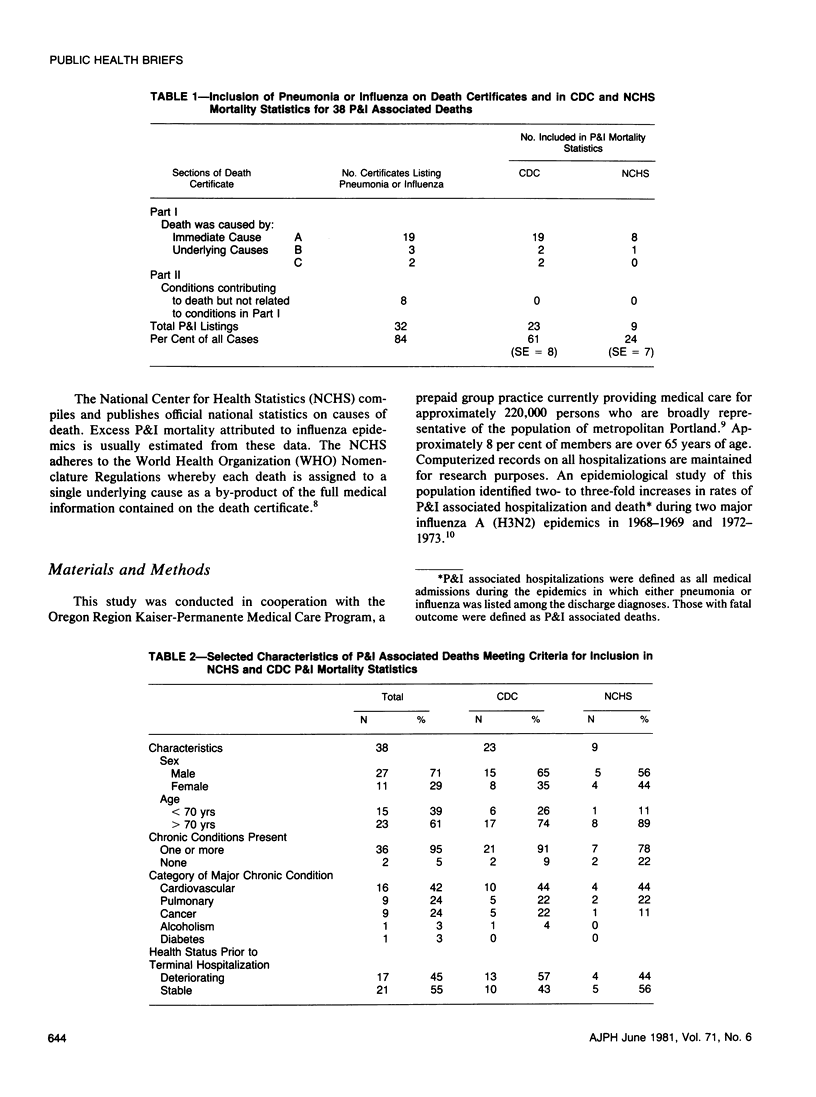
Underestimation of pneumonia and influenza (P&I) mortality during influenza epidemics was explored in 38 P&U associated deaths among a population of adults during two influenza A (H3N2) epidemics. Pneumonia or influenza was mentioned on 32 (84 per cent) of the death certificates. However, based on rules for assigning cause of death, only nine (24 per cent, SE = 7) and 23 (61 per cent, SE = 8) of the cases would have been included in P&I mortality statistics compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics and the Center for Disease Control, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaad F., Cockburn W. C., Sundaresan T. K. Use of excess mortality from respiratory diseases in the study of influenza. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(3):219–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. H., Mullooly J. P. Impact of epidemic type A influenza in a defined adult population. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Dec;112(6):798–811. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. H., Mullooly J. P. Influenza vaccination of elderly persons. Reduction in pneumonia and influenza hospitalizations and deaths. JAMA. 1980 Dec 5;244(22):2547–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., SHERMAN I. L., SERFLING R. E. Observations on excess mortality associated with epidemic influenza. JAMA. 1961 Jun 3;176:776–782. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040220024005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg M. B., Bregman D. J., O'Brien R. J., Millar J. D. Influenza-related mortality. JAMA. 1978 Jan 9;239(2):115–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. Mortality from pneumonia and risk conditions during influenza epidemics. High influenza morbidity during nonepidemic years. JAMA. 1977 Jun 27;237(26):2823–2828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


